Hand comprises of 10 compartments:
- Thenar
- Adductor
- Hypothenar
- Palmar interosseous (3)
- Dorsal interosseous (4)
Thenar and Adductor Muscles
Thenar and Adductor muscles can be remembered using following technique:
Additionally, thenar, adductor and hypothenar muscles of hand can be remembered in their relative position in palm using the mnemonics given below.
1. A OF A OF A
2. All For One And One For All
From radial to ulnar –
1. Thenar: Abductor pollicis brevis (superficial), Opponens pollicis (deep), Flexor pollicis brevis (superficial and deep head)
2. Adductor: Adductor pollicis brevis (transverse and oblique head)
3. Hypothenar: Opponens digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi, Abductor digiti minimi (+ Palmaris brevis – not in the mnemonic)
Note: Abductor pollicis brevis is superficial to the opponens pollcis.
Hypothenar muscles
3 of these muscles have origin in transverse carpal ligament (TCL) or flexor retinaculum.
1. Palmaris brevis
2. Flexor digiti minimi
3. Opponens digiti minimi
Besides, these 3, superficial head of flexor pollicis brevis also originates from transverse carpal ligament.
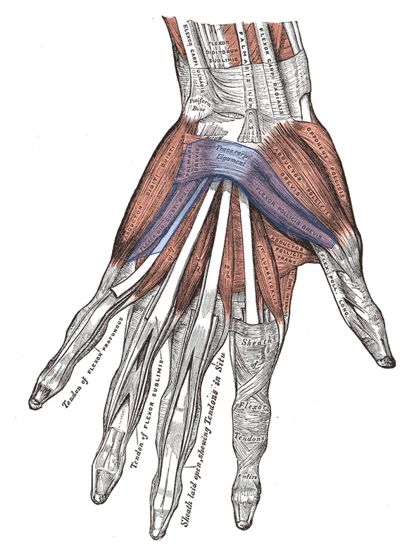
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Clinical relevance |
| Palmaris brevis | TCL | Medial palm skin | Protects ulnar nerve |
| Abductor digiti minimi (ADQ) | Pisiform (FCU tendon) | Base of proximal phalanx of little finger | Ulnar nerve and artery under it |
| Flexor digiti minimi (FDM) | TCL, Hamate | Base of proximal phalanx of little finger | Deep to ADQ and nerve |
| Opponens digiti minimi (ODQ) | TCL, Hamate | 5th metacarpal ulnar side | Deep to other muscles |
Arrangement of hypothenar muscles in layers from deep to superficial:
1. Opponens digiti minimi (deepest)
2. Flexor digiti minimi
3. Abductor digiti minimi
4. Palmaris brevis (most superficial)
This can be remembered using the same mnemonic: “OF A“. While the muscles go from radial to ulnar, they also come deep to superficial.
Interosseous muscles
These muscles originate from the metacarpals.
Palmar Interosseous (3)
Mnemonic: PAD (Palmar-ADduct)
3 Palmar interossei Adduct the fingers except thumb to the 3rd finger. These are UNIPENNATE muscles.
Origin: Metcarpal surface towards 3rd or middle fingers of index, ring and little finger
Insertion: Corresponding sides of the proximal phalanx and Extensor expansion (lateral bands)
Function: Adduct fingers, Flex MCP joint and Extend IP joints
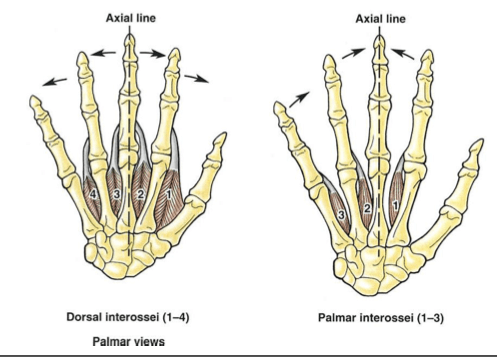
Dorsal Interosseous (4)
Mnemonic: DAB (Dorsal-ABduct-Bipennate)
4 Dorsal interossei Abduct the fingers. These are BIPENNATE muscles.
Origin: Opposing surface of metacarpals (each muscle in one intermetacarpal space)
Insertion: Proximal phalanx base and Extensor expansion (lateral bands)
Function: Abduct fingers, Flex MCP joint and Extend IP joints (like palmar interossei)
Lumbricals (4)
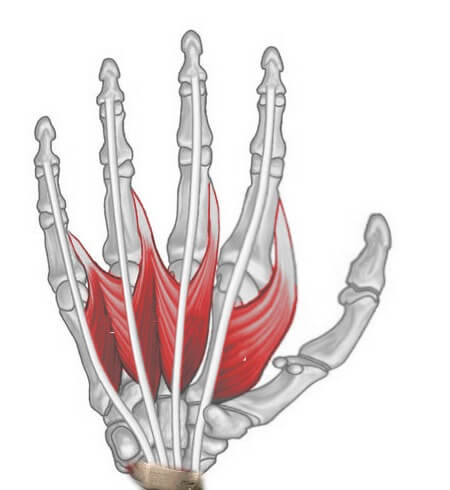
These are unique muscles which originate from flexor tendon and insert into extensor tendon and act as guy ropes to correct tension between two opposing forces to maintain balance.
Origin: Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
Insertion: Extensor hood on radial side (lateral bands)
Function: Flex MCP joint and extend PIP joint
Innervation
All the intrinsic muscles of hand are supplied by the deep branch of ulnar nerve except “half loaf half (1/2-LOAF-1/2)” muscles which are supplied by reccurent branch of median nerve. These are:
- 1/2 L (Half lumbricals): Lumbricals 1 and 2
- O: Opponens pollicis brevis
- A: Abductor pollicis brevis
- F 1/2 (Half flexor pollicis brevis): Superficial head of Flexor pollicis brevis
Thanks alot