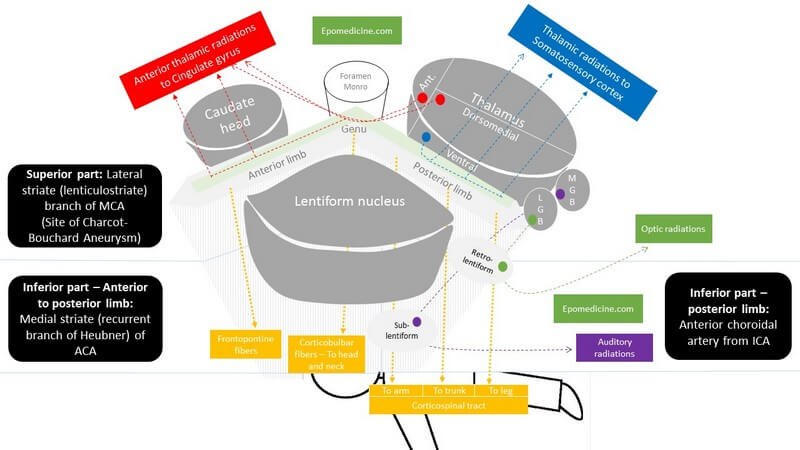
Internal Capsule is a “boomerang” shaped (on horizontal section) and “funnel” shaped, i.e. tapering from superior to inferior (on sagittal section) white matter structure sandwiched between:
- Medially: Head of Caudate nucleus and Thalamus
- Laterally: Lenticular nucleus (Globus pallidus and Putamen)
Parts of Internal Capsule
1. Anterior limb:
- Carries fibers to and from the prefrontal cortex and cingulate gyrus.
- Fronto-pontine fibers descend through it.
2. Posterior limb: Carries fibers to and from the parietal lobe
- Thorugh it, corticospinal tract descend from cerebral cortex to the anterior horn of spinal cord.
- The somatotropy from anterior to posterior is Arm, Trunk and Leg.
3. Intervening genu (knee):
- Through it, corticonuclear fibers descend from cerebral cortex to the motor nuclei of cranial nerves, i.e. to the muscles of head and neck.
4. Retrolenticular part (behind lenticular nucleus):
- Carries visual fibers to and from the visual cortex of the occipital lobe.
5. Sublenticular part (below lenticular nucleus):
- Carries auditory system fibers to and from the auditory cortex of the temporal lobe.
Thalamo-cortical fibers:
- Run from anterior to posterior of internal capsule.
- Anterior limb: Carries fibers from anterior and dorsomedial thalamus to prefrontal cortex and cingulate gyrus.
- Posterior limb: Carries fibers from ventral (sensory) thalamus to somatosensory cortex.
Blood Supply of Internal Capsule
Superior part: Lateral striate (lenticulostriate) branch of MCA (Site of Charcot-Bouchard Aneurysm)
- Lenticulostriate branches also supply the basal ganglia.
Inferior part:
- Anterior to posterior limb: Medial striate (recurrent branch of Heubner) of ACA
- Posterior limb: Anterior choroidal artery from ICA
Lesions of Internal Capsule
- Upper Motor Neuron Lesions (UMNL) with contralateral hemiparesis (lesion is above the crossing of corticospinal tract which occurs in medulla) and contralateral lower facial palsy.
- Arms and legs are equally affected.
- Sensory loss is contralateral as the fibers cross below the internal capsule.
Charcot Bouchard Microaneurysm of Lenticulostriate branches of Middle Cerebral Artery:
- “Lacunar” syndromes of:
- Pure motor hemiparesis (Hemiparesis): Corticospinal tract invovlement in posterior limb of internal capsule
- Mixed sensorimotor stroke (Hemiparesis + Hemisensory loss): Additional involvement of spinothalamic tract in posterior limb of internal capsule
Thrombosis of Reccurent branch (Heubner’s) of Anterior Cerebral Artery:
- Affects the genu
- Paralysis of contralateral lower face, tongue and upper limb (UMNL).
- If the lesion is on left: also motor dysphasia.
Obstruction of Anterior choroidal artery:
- Affects the posterior limb of internal capsule.
- Depends upon the severity of infarction: Produces syndrome involving one of the many features listed below.
- May be symptomless due to collateral circulation.
- Contralateral hemiparesis – UMNL (Corticospinal tract)
- Contralateral homonymous hemianopia – Involvement of retrolenticular part which carries visual fibers
- Contralateral hemianesthesia – Involvement of thalamic radiation
Pure sensory stroke:
- It is a rare form of lacunar stroke.
- Can occur with exclusive involvement of thalamic radiations in internal capsule or ventral thalamus.