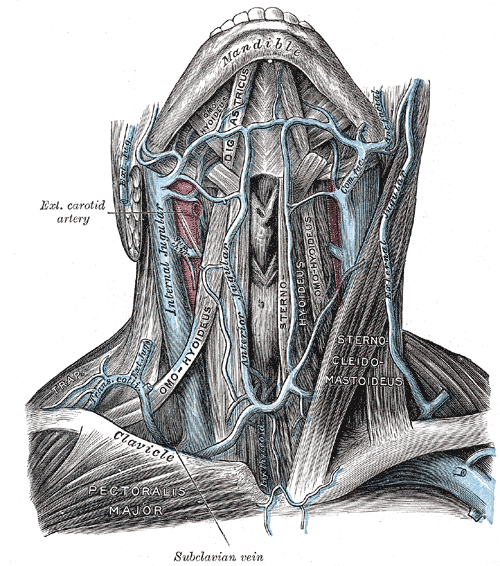
Jugular veins are the veins that take blood from the head to the heart via Superior Venacava (SVC).
| Internal Jugular Vein (IJV) | External Jugular Vein (EJV) | |
| Formation (Drains from) | Inferior petrosal sinus + Sigmoid sinus (At or just distal to Jugular foramen) | Posterior div. of retromandibular vein + Posterior auricular vein (Within parotid gland at the angle of mandible) |
| Course | Carotid sheath (lateral-most) | Subcutaneous anterolateral neck (superficial then posterior to sternocleidomastoid) |
| Tributaries | Mnemonic: Medical Schools Let Fun People In | Mnemonic: PAST |
| 1. Middle thyroid vein 2. Superior thyroid vein 3. Lingual vein 4. common Facial vein (facial vein + ant. branch of retromandibular vein) 5. Pharyngeal plexus 6. Inferior petrosal sinus | 1. Posterior external jugular vein 2. Anterior jugular vein 3. Suprascapular vein 4. Transverse cervical vein | |
| Termination (Drains to) | Brachiocephalic vein (posterior to sternal end of clavicle deep to sternocleidomastoid) | Subclavian vein |
| Drainage area | Major venous return from Brain, Upper face and Neck | Scalp, Face and part of Scapular region |
| Clinical significance | Jugular venous pulse and pressure | Jugular vein distension |