SIADH causes
Mnemonic: SIADH
- Surgery
- Intracranial – Infection, Head injury, CVA
- Alveolar – Carcinoma, Pus
- Drugs – Opiates, Antiepileptics, Cytotoxics, Anti-psychotics
- Hormonal – Hypothyroid, Low corticosteroid level
SIADH diagnostic criteria
Mnemonic: SOD-IUM/S
- Serum Osmollity Decreased (<275 mOsm/kg)
- Increased Urine Molality/osmolality (>100 mOsm/kg)
- Increased Urine Sodium/Na+ (>40 Meq/L)
- Others:
- Euvolemic (Normal skin turgor, Blood pressure within normal range)
- Absence of other causes of hyponatremia (adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, cardiac failure, pituitary insufficiency, renal disease with salt wastage, hepatic disease, diuretics)
- Correction of hyponatremia with fluid restriction
Renal function tests and random blood sugar test should be done to check hyperglycemia and uremia as these are the potential causes of pseudohyponatremia.
Cerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome (CSWS) Causes
Mnemonic: CSWS
- Cranial trauma and neoplasm
- SAH (Subarachnoid hemorrhage)
- Worms, i.e. infection (meningitis, encephalitis)
- Surgery
CSWS pathophysiology (hypotheses)
- Impaired adrenergic tone to the nephrons:
- Decrease in renin secretion by JG cells leading to decreased level of aldosterone and decreased sodium reabsorption in PCT
- Dilation of afferent arteriole leading to increased gomerular filtration of plasma and sodium
- Paracrine effect of increased natriuretic peptides:
- Relaxation of afferent arteriole leading to increased GFR and decreased sodium
- Direct inhibition of angiotensin mediated sodium reabsorption in PCT
- Antagonizes action of vasopressin at Collecting duct
SIADH vs Cerebral Salt Wasting Syndrome (CSWS)
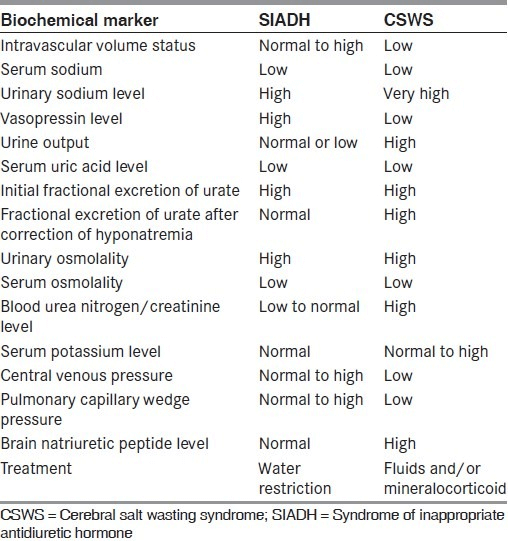
CSWS is usually associated with hypovolemia whereas patients with SIADH are euvolemic. In addition, patients with SIADH exhibit elevated ADH levels and rarely develop urine sodium levels > 100 mEq/L. Patients with CSWS usually have normal ADH levels and often develop urine sodium levels > 100 mEq/L.
It is important to distinguish SIADH from CSWS because the treatment for SIADH includes water restriction along with diuresis, demeclocycline (which inhibits ADH effects on renal tubules), and sodium replacement. On the other hand, this treatment would be inappropriate for a patient with CSWS, as water restriction and diuresis could exacerbate the hypovolemia associated with this disorder.
Fractional excretion of Uric acid (FEUa)
FEUa = [Urine uric acid X Serum creatinine]/[Serum uric acid X Urine creatinine] X 100
Normal values are less than 10%.
Patients with either cerebral salt wasting syndrome or SIADH can have hypouricemia and elevated FEUa.
However, after correction of hyponatremia, hypouricemia and elevated FEUa may normalize in SIADH but persist in CSWS (renal salt wasting).