Glucose-6-Phosphate central to the 4 major metabolic pathways of glucose, i.e. glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenesis, glycogenolysis and HMP shunt (Pentose phosphate pathway). Glucose is immediately phosphorylated inside the cells to Glucose-6-Phsophate to trap them inside cell and prevent diffusion out of the cell.
Glucose-6-Phosphate is the key intermediate to understand the glucose metabolism. Whenever asked a question about glucose metabolism, go back and forth from the Glucose-6-Phosphate to answer the question. This way it’s easier and requires less of mugging up a lot of unnecessary details.
Glucose-6-Phosphate Production
From Glucose
Mediated by enzyme: Glucokinase and Hexokinase
The difference between these 2 enzymes are:
| Glucokinase | Hexokinase | |
| Site of action | Liver | All tissues including liver |
| Activity | Active only when large quantity of glucose present in liver. | Remains active even at low glucose state. |
| Km value | High | Low |
| Allosteric enzyme | Not allosteric enzyme | Allosteric enzyme |
| Induction by insulin | Yes | No |
| Feedback inhibition | No direct feedback inhibition | Feedback is inhibited by Glucose-6-Phosphate |
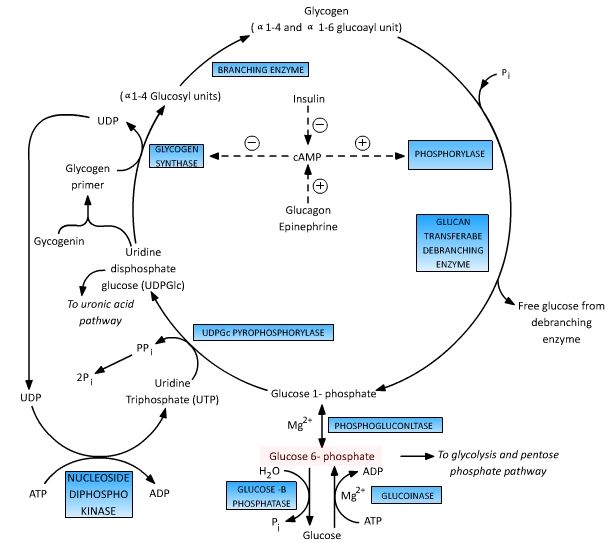
From Glycogen
- Glycogen phosphorylase and Debranching enzyme: breaks glycogen into Glucose-1-Phosphate.
- Phosphoglucomutase: converts Glucose-1-Phosphate into Glucose-6-Phosphate.
Fate of Glucose-6-Phosphate
Glycolysis
- Sequentially, leads to formation of Pyruvate and Lactate.
HMP shunt
The objective of HMP shunt is to:
1. Generate NADPH – a reducing agent necessary mainly for 2 reactions:
- Fatty acid synthesis
- Glutathione reduction in RBCs (NADPH reduces glutathione to GSH. When this reduced glutathione GSH is oxidized to Glutathione by Glutathione peroxidase, the hydrogen is used to reduce hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 to water H2O).
2. Nucleotide synthesis from Ribose-5-Phosphate:
Glucose-6-Phosphate is irreversibly generates NADPH and Ribulose-5-Phosphate mediated by G6PD. Ribulose-5- phosphate by epimerization and isomerization generates Xylulose-5-phosphate and Ribose-5-Phosphate respectively:
- Ribose-5-Phsophate can go into synthesis of Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides.
- Xylulose and Ribose-5-Phosphate both can be involved in transketolation (requires TPP) followed by Transaldolation and transketolation (requires TPP) again to generate the 2 glycolytic intermediates given below.
3. Generation of Intermediates for glycolysis:
- Fructose-6-Phosphate
- Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
Storage as Glycogen (Glycogenesis)
Glucose-6-Phosphate and Glucose-1-Phsophate undergoes inter-convertible reaction mediated by Phosphoglucomutase. Earlier in glycogenolysis, Glucose-1-Phosphate was converted to Glucose-6-Phosphate.
During glycogenesis, Glucose-6-Phosphate is converted to glucose-1-phosphate. With the help of glycogen synthase and branching enzyme, Glucose-6-Phosphate is converted to glycogen.
Dephosphorylation into Glucose
Phosphorylation of Glucose into Glucose-6-Phosphate by Glucokinase/Hexokinase is irreversible. Dephosphorylation of Glucose-6-Phosphate into Glucose require Glucose-6-Phosphatase.
This enzyme is present in liver but absent in muscles and brain.