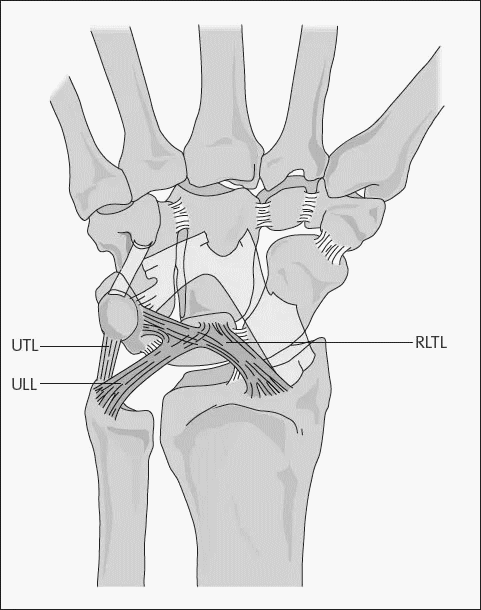
Deep to the plantar fascia, muscles of plantar foot exist in 4 different layers. Extensor digitorum brevis makes dorsal layer of foot and remaining 18 muscles and 4 tendons make the 4 layers of plantar aspect or sole of foot.
In general:
- Layer 1 and 3: 3 muscles each that contains intrinisc abductors, flexors and adductors
- Layer 2 and 4: 2 muscles and 2 tendons that contains lumbricals and interossei
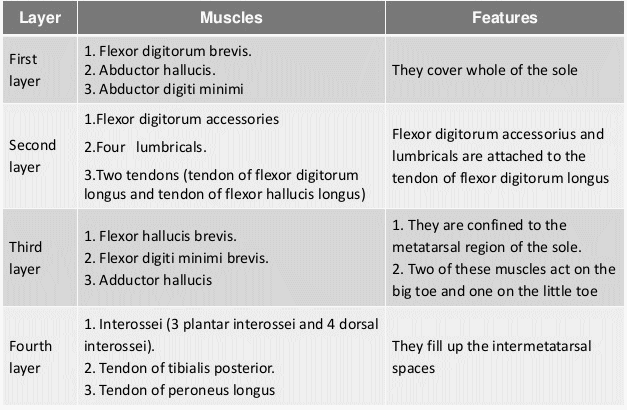
From superficial to deep, the layers are:
a. First layer
Mnemonic: Abs Flex Abs
- Abductor hallucis
- Flexor digitorum brevis (comparable to FDS of hand – both are superficial and insert into middle phalanx)
- Abductor digiti minimii
b. Second layer
Mnemonic: Quadratus Lumborum OR you can also remember it with Flexor digitorum longus (comparable to FDP of hand – deeper and attaches to distal phalanx and the 2 muscles that attaches to FDL)
- Quadratus plantae (Flexor digitorum accessorius)
- Lumbricals (4)
Both of these muscles have attachment to the Flexor Digitorum Longus (FDL).
It also has 2 tendons of extrinsic muscles: Flexor digitorum longus (FDL) and Flexor hallucis longus (FHL).
It also has medial and lateral plantar nervers which are the terminal branches of tibial nerve.
c. Third layer
Mnemonic: Flex Add Flex (Opposite of first layer)
- Flexor hallucis brevis
- Adductor hallucis (like in hand, it has 2 heads – transverse and oblique)
- Flexor digiti minimi
Both the flexor hallucis longus and brevis muscles have lateral origin, i.e. (distal fibula and cuboid/lateral cuneiform respectively) although they insert medially (towards great toe).
d. Fourth layer
Mnemonic: 4DAB and 3 PAD
- 4 Dorsal interossei: ABduct MTP joint
- 3 Plantar interossei: ADduct MTP joint
- 2 tendons of extrinsic muscles: Peroneus longus and Tibialis posterior
9 compartments of foot
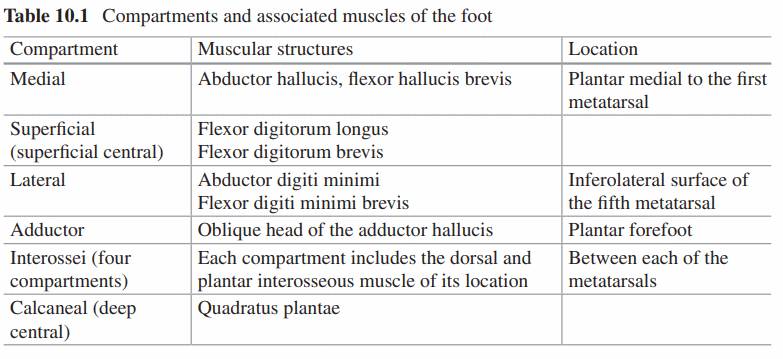
Please refer to an anatomy atlas and visualize for better understanding.