Clinical Features
Mnemonic: FIBRO
1. Fatigue: 80-90%
- Feeling “overwhelming tiredness” or “completely washed out”
- Less prominent than in Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
2. Fibrofog: Dyscognition or Cognitive impairment e.g. trouble concentrating, forgetfulness, and disorganized or slow thinking
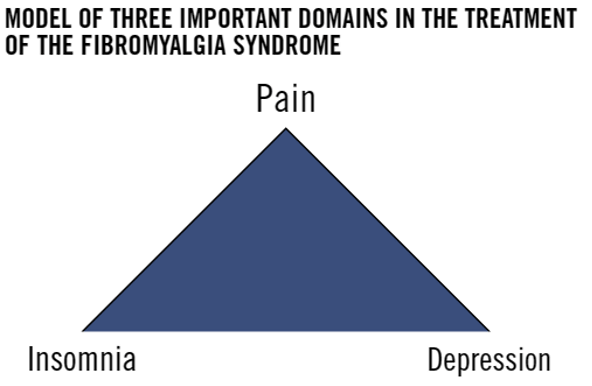
3. Insomnia: 90%
- Non-restorative sleep rather than insomnia
4. Blues: Depression and anxiety
5. Rigidity: Prolonged early morning stiffness not relieved by exercise and absence of synovitis
6. Ow!: Pain (the predominant symptom)
- “Pain all over the body” usually starting from 1 or 2 body parts and spreading to other later
- Pain worsened by physical activity, exertion or stress
- Usually unresponsive to NSAIDs
- 2011 ACR diagnostic criteria: Widespread pain for at least 3 months and does not have a disorder that would otherwise explain the pain. In addition, patients must have a Widespread Pain Index (WPI) > 7 and Symptom Severity Scale (SSS) score > 5 or WPI 3–6 and SSS score > 9.
- Tenderness (Hyperalgesia and Allodynia) and Tender points (basis of 1990 ACR criteria)
Mnemonic for 1990 ACR criteria: WOKE UP STIFF
1. Widespread pain for atleast 3 months and 11 out of 18 tender points –
a. Occiput (suboccipital muscle insertion)
b. Knee (medial fat pad)
c. Epicondyle (2 cm distal to lateral epicondyle)
d. Upper outer quadrant of buttocks
e. Parasternal (2nd costochondral junction)
f. Supraspinatus muscle (supraspinous fossa)
g. Trapezius muscle (upper border, midpoint)
h. Intertrasnsverse spaces at C5-C7
i. Femoral greater trochanter (posterior to prominence)
Four kg force on digital palpation (pressure at which nail bed blanches)
7. Other: gastrointestinal (nausea, vomiting, bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation), urogynecologic (urgency, frequency, incontinence, pelvic pain, and dysmenorrhea), and neurologic (dizziness, vertigo, paresthesia, and tinnitus)
Treatment Algorithm
Mnemonic: PAIN
1. Prescription medication for pain and associated symptoms:
a. Pain predominant: Tramadol (Available sedatives and antidepressants for minor insomnia and depression)
b. Pain and depression predominant: Duloxetine (Available sedative for minor insomnia)
c. Pain and insomnia predominant: Pregabalin (Available antidepressant for minor depression)
d. Pain, insomnia and depression predominant: Pregabalin + Duloxetine
2. Activity: Daily stretching, both low impact aerobic and resistance exercise alternating every other day
3. Information: Discuss fibromyalgia, give handouts and web-resource links
- CARE approach:
- Connect with the patient
- Assess for abuse or distress
- Running or aerobic exercise encouragement
- Educate the patient and Enhance self-efficacy
4. No narcotics
References and further reading:
- Current diagnosis and treatment – Rheumatology, 3rd Edition
- Boomershine CS. The FIBRO System: A Rapid Strategy for Assessment and Management of Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2010 Aug;2(4):187-200. doi: 10.1177/1759720X10374437. PMID: 22870447; PMCID: PMC3383515.
- Russell IJ. Fibromyalgia Syndrome: Approach to Management. CNS Spectrums. Cambridge University Press; 2008;13(S5):27–33.
- Microsoft PowerPoint – Diagnosis and management of fibromyalgia syn (scientiacme.org)
- Rheumotology