Superficial cervical fascia
Contents:
- Platysma muscle
- Cutaneous nerves, blood vessels and lymphatics
- Superficial lymph nodes
- Fat
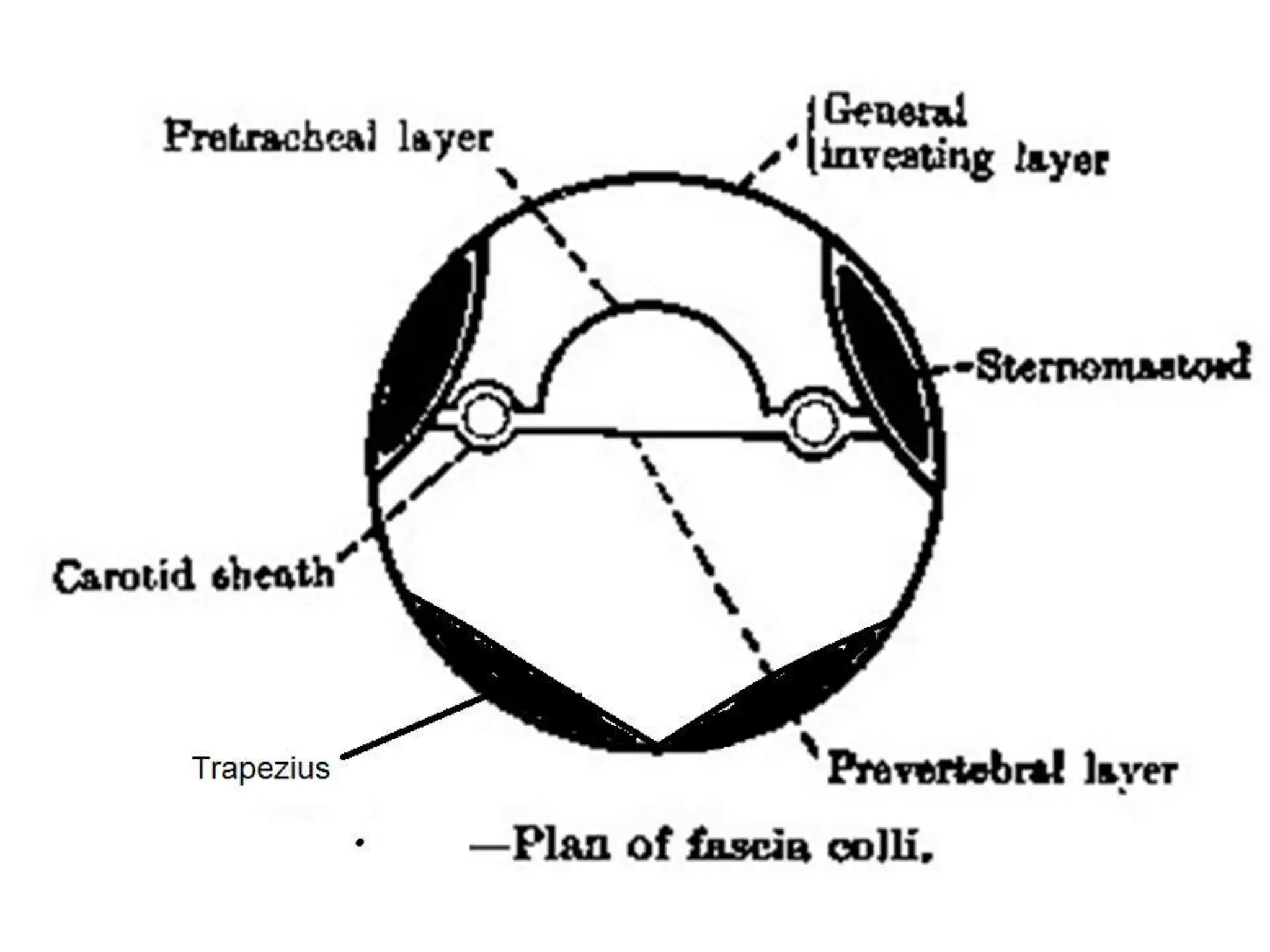
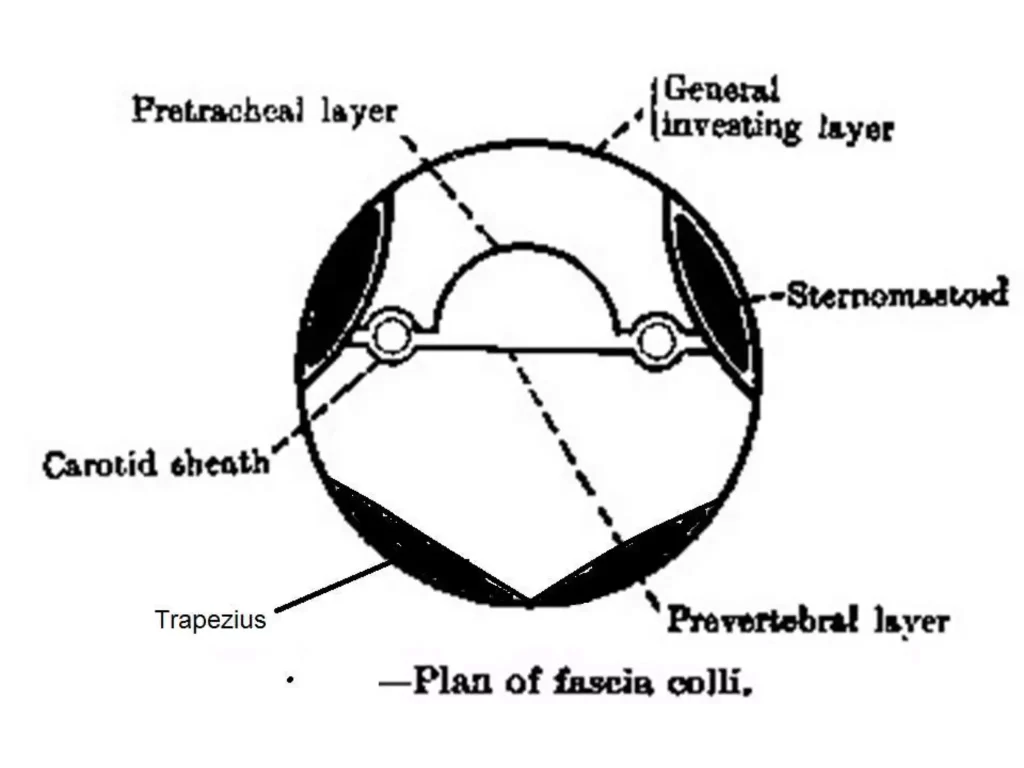
Deep cervical fascia or Fascia colli
1. Investing layer
- Mnemonic: Encloses 2 muscles, 2 salivary glands and 2 spaces
- 2 muscles: Sternocleidomastoid and Trapezius
- 2 glands: Submandibular and Parotid
- 2 spaces: Suprasternal and Supraclavicular
2. Pretracheal layer
- Muscular layer: encloses infrahyoid muscles
- Visceral layer: encloses thyroid gland (forms false capsule and posteriorly suspensory ligament of Berry), trachea and esophagus
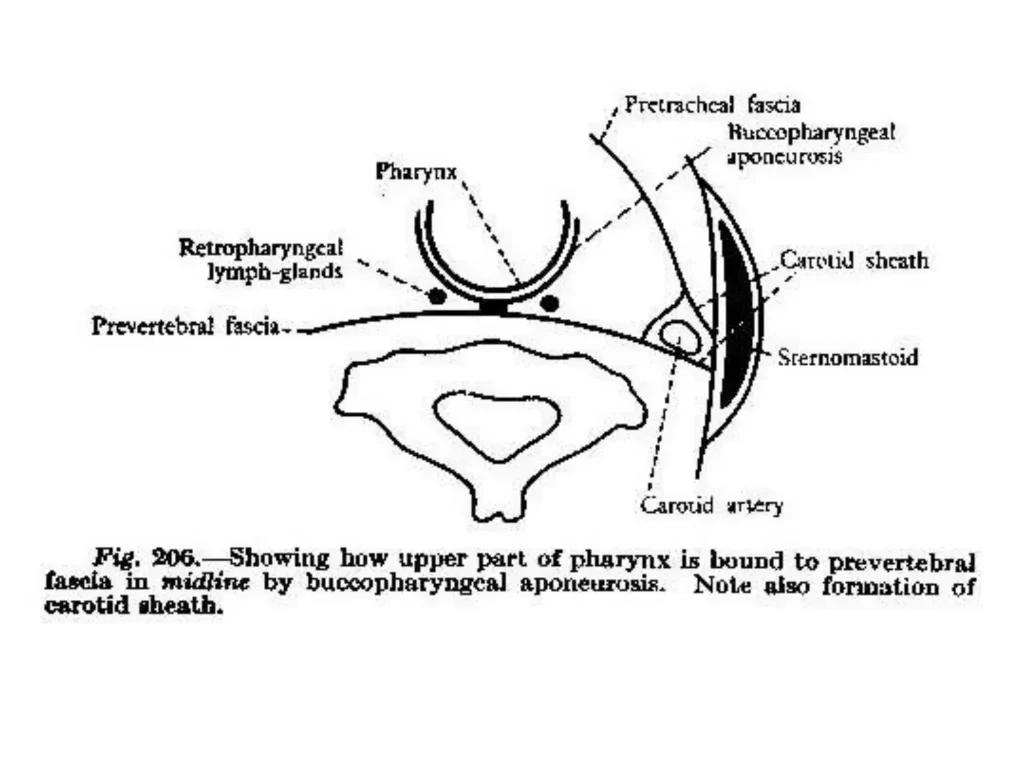
- Posterior part: form buccopharyngeal fascia (outside pharyngeal muscles)
3. Carotid sheath: Formed anteriorly by pretracheal fascia and posteriorly by prevertebral fascia
Encloses:
- CCA
- IJV
- CN X
- CN IX, XI and XII also present in upper part, but they pierce out
Relations:
- Anteriorly: Ansa cervicalis (CN XII + C1, C2, C3 spinal nerves)
- Posteriorly: Cervical sympathetic chain
4. Pharyngobasilar fascia (deep to pharynx): lines the inner surface of pharyngeal muscles
- Retropharyngeal space exists between buccopharyngeal fascia and pharyngobasilar fascia
5. Prevertebral layer
- Encloses vertebrae and prevertebral muscles
- Forms floor of posterior triangle of neck
- Extends with brachial plexus as axillary sheath (subclavian and axillary veins lie outside the sheath)
- Alar fascia: between buccopharyngeal fascia and prevertebral fascia
Spread of Infections
1. Infection between investing layer and muscular layer of pretracheal fascia: Upto superior edge of manubirum
2. Infection between investing layer and visceral layer of pretracheal fascia: Into thoracic cavity anterior to pericardium
3. Retropharyngeal space infections (suppuration of retropharyngeal lymph nodes): Through the superior mediastinum into the posterior mediastinum
4. Infection behind prevertebral fascia (vertebral TB): May spread to various directions –
- Anterior: Chronic retropharyngeal abscess
- Lateral: Through axially sheath and point in posterior triangle or lateral wall of axilla
- Inferior: Superior mediastinum