Fascia lata and Tensor fascia lata althought different structures is often mistaken as the same by the students.
Fascia Lata
It is the fascial ‘stocking’ deep to the skin and superficial fascial and encloses the muscle of thigh. Proximally, its attachment can be traced around the pelvis and distally, it is attached to the tibia and fibula and continues as the deep fascia of calf. It is thinnest on the medial side where it covers the adductor muscles.
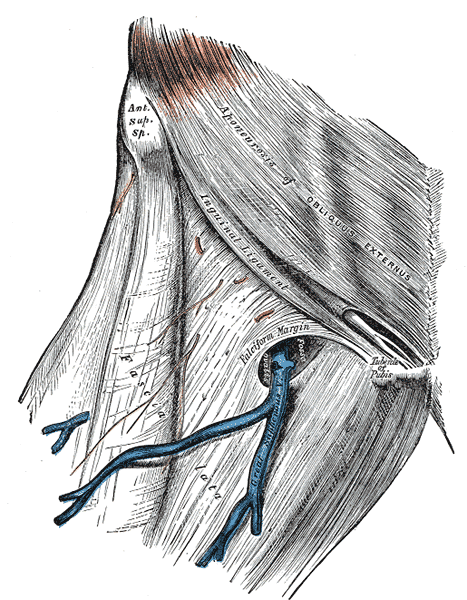
The intermuscular septa dividing the thigh into different osteofascial compartments originate from the fascia lata.
Just inferior to the inguinal ligament, there is a slit in the fascia whose medial edge is tucked deep to the lateral part forming an ovoid hiatus known as saphenous opening.
On the lateral aspect, the fascia is thickened to form the iliotibial tract (iliotibial band or Maissiat’s band). The iliotibial tract extends from the tubercle of iliac crest to the lateral tibial condyle (Gerdy’s tubercle). About 3/4th of the gluteus maximus also inserts on the Iliotibial tract.
It is regarded as the donor site of fascia for reconstruction surgeries.
Tensor Fascia Lata (TFL)
The Tensor Fascia Lata originates from a 5 cm length of the external lip of iliac crest between the anterior superior iliac spine and the tubercle of crest and inserts into the iliotibial tract.
Like gluteus medius and minimus, it is supplied by the superior gluteal nerve.
When it contracts, it pulls and tenses the fascia lata, thus bringing the anterior and posterior compartments closer towards the femur. Contraction within each compartment centralises muscle weight and limits outward expansion, which in turn reduces the overall force required for movement at the hip joint.
Analogy: Fascia lata as a stocking and Tensor fascia lata as the strap of stocking. When you pull the strap up, the stocking tightens.

It works with other hip muscles to produce hip movements:
- gluteus medius and gluteus minimus: internally rotate and abduct hip
- gluteus maximus via (iliotibial tract): abduct hip
- rectus femoris: flexion of hip
In knee, it functions:
- as an accessory flexor
- with the IT band to stabilize the knee when the knee is in full extension
- via the IT band in the lateral rotation of the tibia
It stabilizes the pelvis during walking by assisting gluteus medius and minimus in resisting adduction of the hip. It pulls the ilium inferiorly on the weight bearing side and contralteral hip rise in non-weight bearing side, thus allowing the non-weight bearing side to swing during gait cycle.
References:
1. Last’s Anatomy – Regional and Applied, 12th Edition
2. Trammell AP, Nahian A, Pilson H. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Tensor Fasciae Latae Muscle. [Updated 2020 May 7]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499870/