Epiploic foramen is a vertical opening through which lesser sac (omental bursa) communicates with the greater sac (peritoneal cavity proper). It is at the level of T12 vertebra.
Boundaries
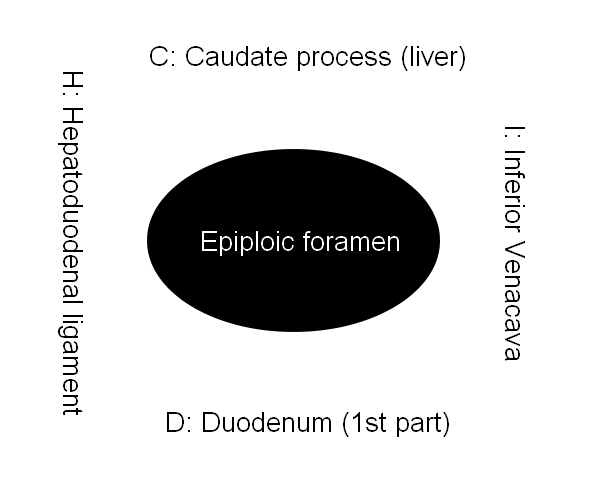
Mnemonic: Epiploic foramen is located between CD and HI.
Superior: Caudate process of liver
Inferior: Duodenum (1st part)
Anterior: Hepatoduodenal ligament (lesser omentum) free margin containing bile duct, hepatic artery and portal vein (DAV-E)
Posterior: Inferior venacava (IVC)
Clinical significance
1. Internal hernia: Uncommonly, a loop of small bowel may herniate into lesser sac through this foramen producing internal hernia (presents with intermittent bowel obstruction).
2. Pringle’s maneuver: Bleeding from hepatic artery or portal vein can be controlled by pinching the vessels with hemostat or fingers through the foramen of Winslow. If the bleeding continues with such maneuver, the bleeding is likely from hepatic vein or inferior venacava.
Helpful thanks.