General concepts of ETC and Oxidative Phosphorylation:
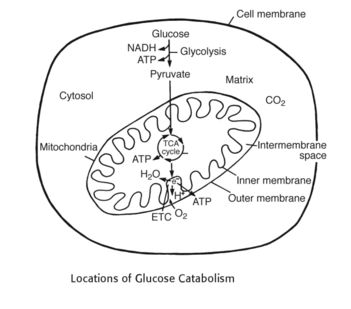
1. Occurs in cell cytosol: Glycolysis
2. Occurs in mytochondrial matrix: Kreb’s (TCA) cycle
3. Occurs in mitochondrial inner membrane: ETC – Stepwise movement of electrons from high energy to low energy that activates proton pump which transports proton from the mitochondrial matrix to mitochondrial inter-membrane and generate Proton gradient.
4. Occurs in mitochondrial intermembrane space: Creation of proton gradient
5. Occurs in mitochondrial inner membrane: Oxidative phosphorylation – This proton gradient generated from ETC is used by Oxidative Phosphorylation to generate ATP by phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
6. Oxygen is the final electron acceptor: We breathe in oxygen with our lungs, transport it with red blood cells in our arteries to cells, and oxygen is ultimately used inside the mitochondria of every cell to accept electrons at the end of the electron transport chain to form water.
ATP produced from a molecule of glucose:
Each NADH yields 2.5 ATP and each FADH2 yields 1.5 ATP.
1. Glycolysis:
- 2 ATP
- 2 NADH → 2 FADH2 (to ETC) = 3 ATP
2. Conversion of Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA:
- 1 glucose forms 2 pyruvate
- 2 NADH (to ETC) = 5 ATP
3. Kreb’s cycle: 2 Pyruvate from 1 glucose ~ 2 of each of following
- ATP from GTP (1 site: Succinyl-CoA synthetase): 2 ATP
- NADH (3 sites: Isocitrate dehydrogenase, Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, Malate dehydrogenase): 6 NADH = 15 ATP
- FADH2 (1 site: Succinate dehydrogenase): 2 FADH2 = 3 ATP
Total: (2+3) + (5) + (2+15+3) = 30 ATP
In contrast, total yield from 1 molecule of glycogen is 31 ATP:
- Glycogen is converted into glucose-1-phosphate (G1P)
- G1P is converted into glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) – this skips the 1st step of glycolysis catalized by Glucokinase/Hexokinase which uses 1 ATP
MNEMONIC: NADH Sends Bad (negative) charge And Formulate ATP
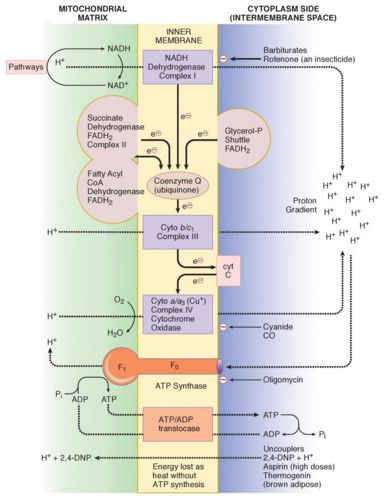
Complex I (NADH): NADH : CoQ oxidoreductase
- NADH dehdrogenase
- Ubiquinone (CoQ)
Complex II (Sends): Succinate : CoQ oxidoreductase
Complex III (Bad charge):
- Cytochrome b/c1
- Cytochrome c
Complex IV (And): Cytochrome a/a3 (Cytochrome oxidase)
Complex V (Formulate): F0F1 ATP synthase complex
ATP
Complex I: NADH : CoQ oxidoreductase
- NADH dehdrogenase: transfers 2 electrons from NADH to Ubiquinone (CoQ)
- Ubiquinone (CoQ): Ubiquinone (QH2) is reduced to ubiquinol (free to diffuse within membranes)
- 4 H+ ions move to intermembranous space
Complex II: Succinate : CoQ oxidoreductase
- Succinate dehydrogenase (In TCA cycle): converts succinate to fumarate and produces FADH2 from FAD
- Like in Complex I, FADH2 transfers 2 electrons to CoQ
- Other electron donors from FADH2 are: Fatty Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase, Glycerol 3 Phosphate shuttle
- It is not a proton pump
Complex III (Fe/heme protein):
- Cytochrome b/c1: removes 2 electron from QH2 and transfers to 2 molecules of cytochrome C
- Cytochrome c: water-soluble and located in outer mitochondrial membrane
- Pumps 4 protons across membrane
Complex IV (Copper/heme protein): Cytochrome a/a3 (Cytochrome c oxidase)
- Removes 4 electrons from 4 molecules of Cytochrome c and trasfers to O2 [In hypoxia, rate of ETC and ATP production decreases, which leads to increase in glycolysis (anaerobic in the abscence of oxygen) leading to lactic acidosis]
- Produces 2 molecules of H2O (water)
- Pumps 4 protons across membrane
4 “C”s of Complex 4
- Cytochrome oxidase
- Copper/heme protein
- Carbon monoxide inhibits it
- Cyanide inhibits it
Complex V: F0F1 ATP synthase complex
- F0 component: Proton flows back to mitochondrial matrix from intermembrane space producing energy
- F1 component: Energy produced is used to phosphorylate ADP using Pi
ATP:
- 1 NADH = 2.5 ATP
- 1 FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
INHIBITORS OF ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN
Inhibitors of any step result in:
- Decreased oxygen consumption
- Increased intracellular NADH/NAD and FADH2/FAD ratio
- Decreased ATP
Mnemonic: CRAP Tightens Muscle And Produces Muscle ACHe
Complex I inhibitors: CRAP
- Chlorpromazine
- Rotenone (Fish poison, pesticide – Remember “one” in the last)
- Amobarbital/Amytal (Barbiturate)
- Piercidin A
Doxorubicin inhibits CoQ
Complex II inhibitors: Tightens Muscle
- Thenoyltrifluoroacetone (TTA)
- Malonate
Complex III inhibitors: AND Produces Muscle
- Antimycin A (Antifungal)
- Napthoquinone
- Dimercaprol (ABC)
- Phenformin
- Myxothiazole
Complex IV inhibitors: ACH
Remember, All complex IV inhibitors end with “-ide”
- Azide
- Carbon monoxide, Cyanide
- Hydrogen sulphide
Cyanide poisoning: Thiosulfate forms thiocyanate which is less toxic and excreted by kidneys; Nitrites convert hemoglobin to methemoglobin (which binds cyanide in blood before reaching to tissues) – must be given shortly after exposure
Carbon monoxide poisoning: Headache, nausea, tachycardia, tachypnea, cherry-red lips and cheeks, respiratory depression and coma (treated with oxygen)
Complex V inhibitor:
- Oligomycin (antibiotic)
ATP/ADP translocase inhibitor:
- Atractyloside (plant toxin)
UNCOUPLERS
Uncouplers uncouples ETC and oxidative phosphorylation by decreasing the proton gradient causing:
- Decreased ATP synthesis
- Increased oxygen consumption
- Increased oxidation of NADH
Because the rate of ETC increases, with no ATP synthsis, energy is released as heat. Important uncouplers are:
- 2,4 – Dinitrophenol (2,4-DNP)
- Aspirin (and other salicylates)
- Brown adipose tissue (thermogenin/natural uncoupling protein – kidneys, neck, breastplate, scapula in newborns)
Mnemonic: Uncouplers are BAD
- Brown fat
- Aspirin
- Dinitrophenol
MUTATIONS IN ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (ETC)
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA affect highly aerobic tissues (nerve, muscle) and is characterized by:
- Maternal inheritance
- Metabolic (Lactic) acidosis
- Massive proliferation of mitochondria in muslce (ragged red fibers)
Mnemonic: 3 “M“s of Mitochondrial DNA Mutation
1. MELAS (Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis, Stroke): Mutation in Complex I
2. LHON (Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy – Loss of Central vision): Mutation in Cytochrome reductase
3. Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (short stature, external ophthalmoplegia, pigmentary retinopathy, ataxia, cardiac conduction defects): Mutation in Complex II
4. Leigh disease (lactic acidemia, developmental delay, seizure, extraocular palsies, hypotonia; fatal by age 2): Mutation in Complex IV
Findings:
| NEUROIMAGING FINDINGS Abnormal signal in the basal ganglia, basal ganglia calcification, cerebral and cerebellar atrophy, bilateral striatal necrosis, cerebellar hypoplasia, infarcts, leukoencephalopathy |
| LABORATORORY FINDINGS Lactic acidosis, elevated lactate/pyruvate ratio in blood and CSF, elevated alanine in blood and CSF, elevated CK, myoglobinuria |

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music.
Glycolysis does NOT occur in the mitochondria matrix.