Synonyms: Acute pericarditis, Viral pericarditis, Infectious pericarditis
Definition: Diffuse inflammation of the pericardial lining surrounding the heart and characterized by sharp pleuritic, retrosternal chest pain worsened with recumbency and relieved by leaning forwards.
Causes of Pericarditis:
a. Infectious:
- Viral: Coxsackievirus, Echovirus, Ebstein-Barr virus, Influenza, HIV, Mumps virus
- Bacterial: Staphylococcus, Hemophilus, Pneumococcus, Salmonella, Tuberculosis, Meningococcus, Syphilis
- Miscellaneous: Histoplasmosis, Blastomycosis, Coccidiodomycosis, Aspergillosis, Amebiasis, Rickettsia
b. Rheumatogenic: SLE, Rheumatoid arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, Sarcoidosis, Scleroderma, Vasculitis
c. Neoplastic: Secondaries, Sarcomas, Mesothelioma
d. Drugs: Hydralazine, Procainamide
e. Immunologic: Celiac sprue, Inflammatory Bowel Disease
f. Other: Chest trauma, Uremia, Myxedema, Aortic dissection, Radiation therapy, Myocardial infarction, Dressler’s syndrome
g. Idiopathic
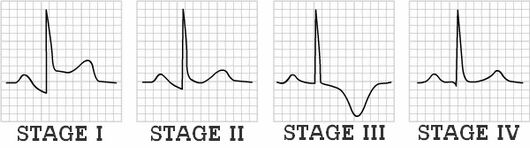
Stages of ECG changes in Pericarditis:
The duration for evolution through each of the 4 ECG stages is highly variable ranging from hours to weeks. Practically, Stage I is the only diagnostic phase because Stage II looks normal and Stage III mimics ischemia.
| Stage | ECG changes | Electrical basis or Mechanism |
| I (Everything is up) | Diffuse, concave ST elevation | Generalized pericardial inflammatory process and associated myocarditis |
| II (Transition or pseudonormalization) | ST segment returns to baseline | Resolution of superficial myocarditis |
| T-wave flattening | ||
| PR depression (ST segment appears to be elevated) | Generalized epicardial atrial injury | |
| III (Everything is down) | T wave inversion | Delay in repolarization of whole subepicardial healing epicardium |
| IV (Normalization) | ECG abnormalities normalizesT wave inversions may become permanent | Resolution of pericarditis |
Since, the secondary myocarditis is usually superficial:
- Q waves do not form
- R waves are unaffected
- QRS is not prolonged
- QT is not prolonged
Differential diagnoses:
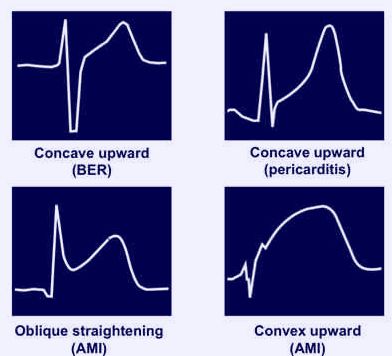
a. Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI):
| ECG features | Acute Pericarditis | Acute Myocardial Infarction |
| PR segment depression | Common | Rare |
| Q-waves | Absent | Present |
| St-segment elevation | DiffuseConcave-up | LocalizedConvex-up |
| Reciprocal T-wave changes | Absent | Often |
| T-wave inversion | After ST normalization | Concomittantly |
Summary to approach:
A. Evaluate for STEMI
- ST depression in leads other than V1 and aVR or
- ST Elevation convex upwards or horizontal or
- ST Elevation in Lead III more than Lead II
B. Evaluate for Pericarditis (if all 3 ECG criteria above are negative)
- PR Segment depression in multiple leads
- Clinically search for pericardial rub
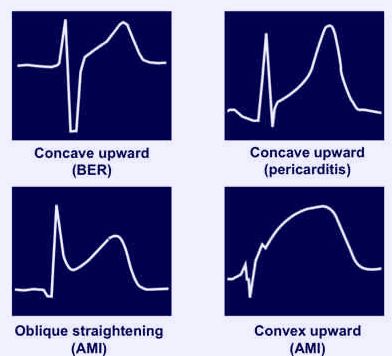
b. Benign Early Repolarization (BER):
| ECG features | Acute Pericarditis | Benign Early Repolarization |
| ST elevation | Generalized | Limited to precordial leads |
| PR depression | Present | Absent |
| T waves | Normal amplitude | Prominent |
| ST segment/T wave ratio | >0.25 | <0.25 |
| J-point elevation with “Fish-hook” appearance in lead V4 | Absent | Present |
| Evolution | Progressive | Stable or non-progressive |
c. Others:
- Myocarditis
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pneumothorax
- Hyperkalemia
- Pneumopericardium
- Subepicardial hemorrhage