Synonyms: Emphysema, Chronic bronchitis, Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (COLD), Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease (COAD), Smoker’s lung
Definition: COPD is a lung disease characterized by airflow limitation (FEV1/FVC ratio of less than 70%) that is not fully reversible (FEV1 increase of 200 ml and 12% improvement above baseline FEV1 following administration of either inhaled corticosteroids or bronchodilators). COPD comprises of 2 predominant conditions – Chronic bronchitis and Emphysema.
- Chronic Bronchitis is defined as a productive cough for 3 months in each of 2 successive years in a patient whom other causes of chronic sputum has been excluded.
- Emphysema is defined as the presence of enlargement of airspaces distal to the terminal bronchioles or acinus with destruction of their walls without obvious fibrosis.
Mechanism of ECG changes in COPD:
COPD is associated with increased airway resistance, alveolar and pulmonary capillary destruction, air trapping, chronic hypoxemia and increased work of breathing. In an attempt to improve oxygenation of the blood, pulmonary vessels adjacent to underventilated alveoli tend to constrict (hypoxic reflex pulmonary vasoconstriction), increasing both pulmonary vascular resistance and the work of right heart i.e. COPD imposes chronic strain on the right side of heart resulting in cor pulmonale.
COPD and Heart:
- Elongation and vertical orientation of the heart: Hyperexpanded lungs impose external compression of heart and lowering of diaphragms
- Clockwise rotation of heart in the transverse plane: Due to its fixed attachment to the great vessels
- Reduced amplitude of the QRS complexes: Due to dampening effect resulting from increased air between the heart and recording electrodes
ECG changes in COPD:
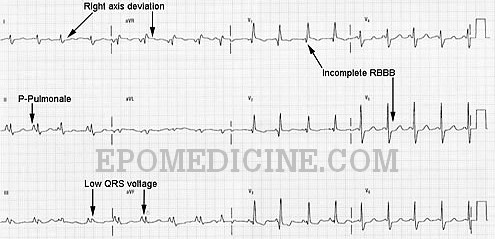
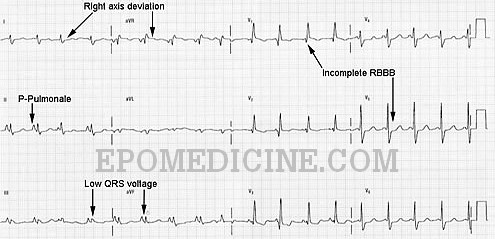
- ECG findings of right atrial and right ventricular enlargement are seen with COPD.
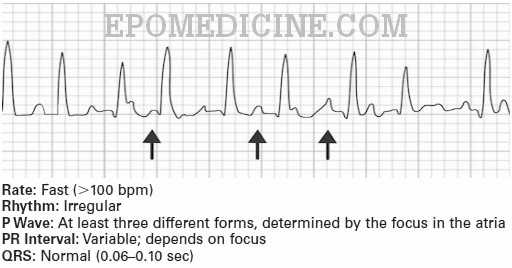
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is commonly associated with severe COPD or exacerbation of lung disease.
| ECG changes | Underlying cause |
| P pulmonale (Tall, peaked P-wave ≥ 2.5 mm height in inferior leads II, III and aVF) | Right atrial abnormality |
| Increased R wave voltage in leads V1, V2 | Right ventricular enlargement |
| Right axis deviation usually between +90° and +180° | Right ventricular dilation |
| Low voltage QRS complex (<5 mm height) in limb leads | Increased distance between the recording electrode and heart |
| Poor R wave progression | Leftward or clockwise rotation of the heart |
| Supraventricular dysrhythmias – Atrial Premature Complexes (APCs), Atrial Flutter, Atrial Fibrillation, Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia and Multifocal atrial tachycardia |
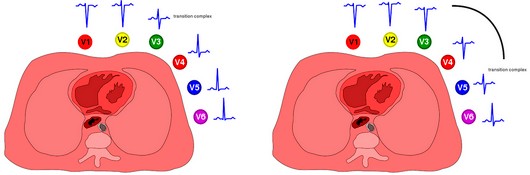
Right: Abnormal R wave progression
ECG criteria for Right Ventricular Enlargement:
1. Right axis deviation: QRS axis is between +90° and +180°
2. Increased height (voltage) of QRS complexes in leads recording right ventricular forces:
- R > S in lead V1
- R > 7 mm in lead V1 and > 5 mm in lead aVR
- S < 2 mm in lead V1
3. Negative deflection of QRS complex is increased in leads recording left ventricular forces:
- Deep S wave in leads V5 and V6
4. Delayed onset of instrinsicoid reflection (time required to depolarize the ventricle from endocardium to epicardium) beyond 0.02 second in right chest leads only: Measured from beginning of QRS complex to the peak of R wave
5. Incomplete RBBB may be present (rSR’ in lead V1)
6. QRS width may be slightly prolonged (> 0.1 s)
7. ST-T wave alterations: ST segment depression and T wave inversion in right chest leads V1 and V2
Chou’s ECG criteria for COPD
- P-pulmonale
- P wave axis ≥ +80°
- QRS amplitude less than 5 mm in all limb leads
- QRS axis > +90°
- QRS amplitude less than 5 mm in V5, V6
- S1-S2-S3 pattern with R/S <1 in lead I, II, III
- Atrial arrhythmias (especially Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia or MAT)
MAT is defined electrocardio-graphically as an atrial tachycardia with an overall rate greater than 100 beats per minute and distinct P waves of at least three different morphologies. Both PR and R-R intervals are variable.
COPD is likely to be present if one P and one QRS criterion present
Schamroth’s Sign Criteria for COPD:
- Isoelectric P wave in lead I
- Very small QRS complex of less than 1.5 mm total deflection
- T wave of less than 0.5 mm in lead I