Morrey and Peterson’s Definition of Osteomyelitis
- Definite osteomyelitis: Positive bone or adjacent soft tissue culture or histologic evidence
- Probable osteomyelitis: Positive blood culture + Clinical & radiological evidence of osteomyelitis
- Likely osteomyelitis: Typical clinical and radiographic features of osteomyelitis responding to antibiotic therapy (in absence of positive culture)
Peltola and Vahvanen’s Criteria for Acute Osteomyelitis
- Pus on aspiration (from bone)
- Positive bacterial culture from bone or blood
- Presence of classic signs and symptoms of acute osteomyelitis
- Radiographic changes typical of osteomyelitis
Two of the listed findings must be present for establishment of the diagnosis.
Waldvogel Classification of Osteomyelitis
It is a simple and practical system based on 3 factors (duration, mechanism and vascular status):
a. Duration:
- Acute: <2 weeks
- Subacute: 2-6 weeks
- Chronic:
- >6 weeks
- Persistent or relapsed infection
- Infection associated with prosthetic devices
- Histologic evidence of dead or necrotic cortical bone
b. Mechanism:
- Hematogenous
- Contiguous source
- No generalized vascular disease
- Generalized vascular disease
Gledhill and Robert Classification of Subacute Osteomyelitis
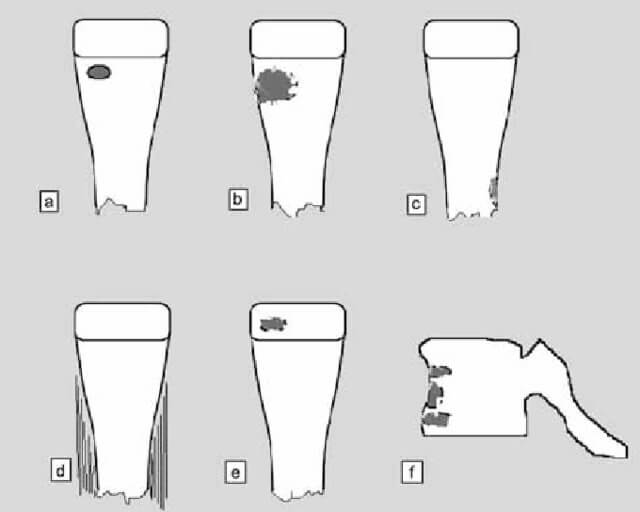
| Type | Site | Description | Differential diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Metaphysis | No cortical erosion Ia – Punched out radiolucency Ib – Ia with sclerotic margin | Ia – Eosiniophilic granuloma Ib – Brodie’s abscess |
| II | Metaphysis | Cortical erosion | Osteosarcoma |
| III | Diaphysis | Cortical hyperostosis | Osteoid osteoma |
| IV | Diaphysis | Periosteal reaction (onion skin) | Ewing’s sarcoma |
| V | Epiphysis | Radiolucency with sclerotic margin | Chondroblastoma |
| VI | Vertebra | Destructive process | Eosinophilic granuloma Tuberculous spondylitis |
Cierny and Mader Staging for Chronic Osteomyelitis
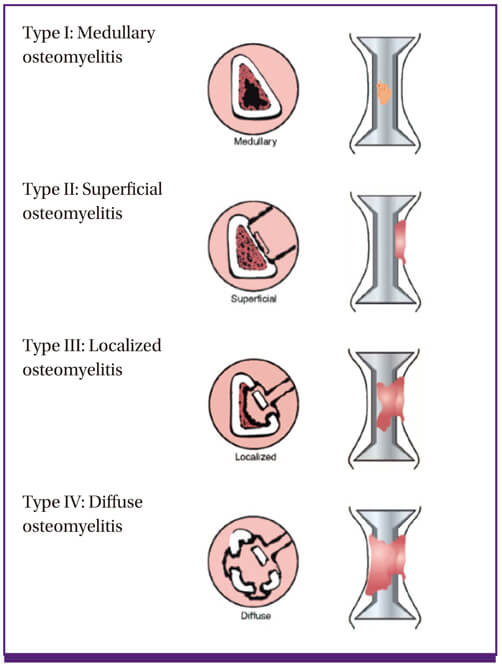
| Classification | Description | Examples |
| Stage 1 | Medullary osteomyeltitis: infection confined to the intramedullary bone surfaces | Infected intramedullary rod Hematogenous osteomyelitis |
| Stage 2 | Superficial osteomyelitis: restricted to outer cortex | Diabetic foot ulcer with infection extending to bone |
| Stage 3 | Localized osteomyelitis: full-thickness, cortical sequestration without instability | Progression from stage I or II |
| Stage 4 | Diffuse osteomyelitis: through-and-through process with instability requiring intercalary reconstruction of bone | Progression from stage I, II or III |
| A Host | Normal physiological, metabolic, and immunologic states | |
| B Host | Local compromise, systemic compromise, or both | Systemic – Diabetes, malnutrition, renal failure, hepatic failure, maliganancy, extremes of age, immune disease Local – Smoking, chronic lymphedema, major or small vessel compromise, venous stasis, arthritis, large scars, neuropathy |
| C Host | Morbidity of treatment is worse than disease | Patient who is not a surgical candidate or who cannot tolerate long-term antibiotics |
Nade’s Principles of Treatment of Acute Hematogenous Osteomyelitis
- Appropriate antibiotic will be effective before pus formation
- Antibiotics will not sterilize acascular tissues or abscesses and such area require surgical removal
- If such removal is effective, antibiotics should prevent their reformation therefore, primary closure should be safe
- Surgery should not damage already ischemic bone and soft tissue
- Antibiotics should be continued after surgery
Nade’s Indications for Surgery in Acute Osteomyelitis
- Abscess formation
- Severely ill and moribun child with features of acute osteomyelitis
- Failure to respond to antibiotics for >48 hours
References:
Peltola H, Vahvanen V. A comparative study of osteomyelitis and purulent arthritis with special reference to aetiology and recovery. Infection 1984;12(2):75–9.
Waldvogel FA, Medoff G, Swartz MN. Osteomyelitis: a review of clinical features, therapeutic considerations and unusual aspects (first of three parts). N Engl J Med 1970;282:198–206.
Cierny G, Mader JT, Pennick JJ. A clinical staging system for adult osteomyelitis. Contemp Orthop 1985; 10:17–37.
Osteomyelitis of the Foot and Ankle: Medical and Surgical Management edited by Troy J. Boffeli