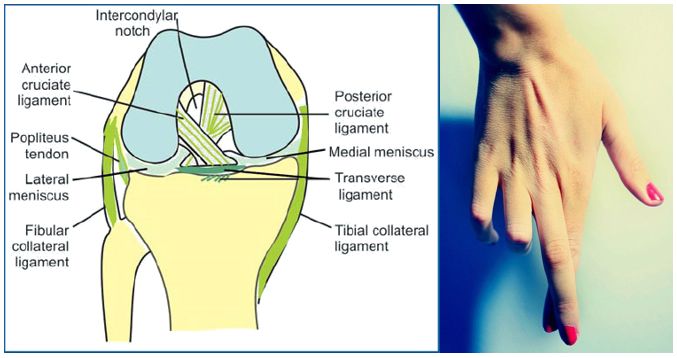
Mnemonic: Cross your long fingers over the index finger and superimpose this hand over your ipsilateral knee. This will help us to remember the orientation of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) of knee.
Also remember the mnemonic “LAMP” which means Lateral ACL and Medial PCL. These represent the femoral attachment of the cruciate ligaments.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
It originates superiorly from lateral femoral condyle along the posterior surface of intercondylar notch. It courses obliquely downward and medially like the middle finger to attach to the medial aspect of intercondylar area of tibia just in front of the intercondylar eminence.
- Size: 33 mm X 11 mm
- Tibial attachment is around 30 mm and femoral attachment 23 mm, making femoral attachment more vulnerable to injury.
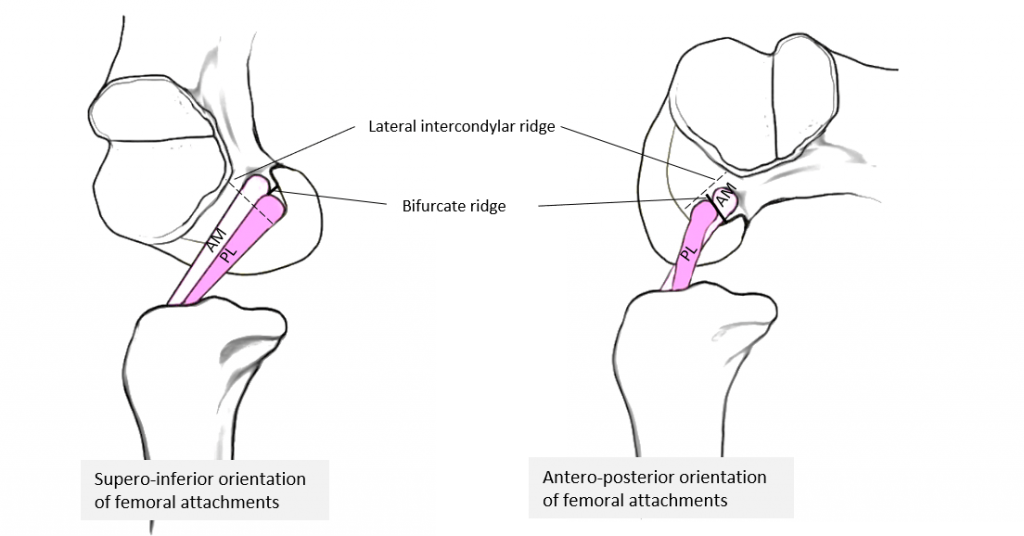
ACL has anteromedial (AM; tight in flexion) and posterolateral (PL; tight in extension) bundles. In knee extension, AM and PL bundle are parallel to each other. With increasing flexion, the parallel fiber orientation is lost, and the femoral insertion site of ACL becomes more horizontal, causing the AM to wrap around the PL bundle. Posterolateral bundle provides rotational stability and is tested with pivot shift test.
This can be remembered using mnemonic: “AMPLe” which means AnteroMedial and PosteroLateral bundle and PL is tight in extension.
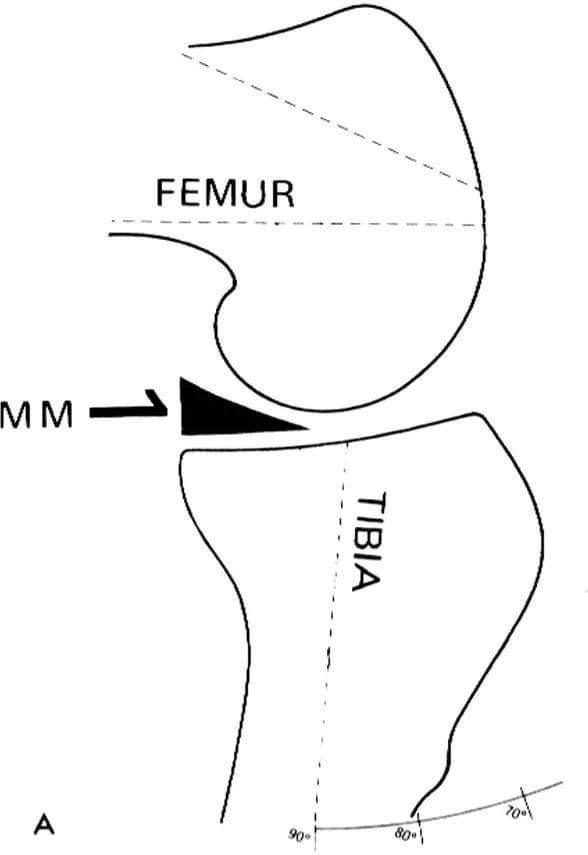
With knee flexed to 90° for classic anterior drawer sign, medial meniscus, being attached to tibia, abuts against acutely convex surface of medial femoral condyle and has “door-stopper” effect, hindering anterior translation of tibia. With knee extended however, the relatively flat weight-bearing surface of femur does not obstruct forward motion of meniscus and tibia when anterior stress is applied.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
It attaches superiorly to the medial femoral condyle along the midpart of the intercondylar notch. It courses obliquely downward, laterally and posterior to the ACL like the index finger to attach to the posterior margin of the intercondylar fossa of tibia (posterior tibial sulcus) on the lateral side.
- Size: 38 mm X 13 mm
PCL has anterolateral (tight in flexion) and posteromedial (tight in extension) bundles. This can be remembered using the mnemonic “PAL” which means PCL has AnteroLateral bundle.
2 meniscofemoral ligaments originate from the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus and insert into the substance of PCL. These include: Humphrey’s ligament (anterior to PCL) and Wrisberg ligament (posterior to PCL). This arrangement can also be remembered by the mnemonic that “H” comes forward of “W”.
PCL is 50% thicker and has twice the tensile strength of the ACL.
The main biomechanical functions of the PCL are to provide restraint against posterior tibial translation (PTT) at all flexion angles, and limit internal and external rotation beyond 90° of flexion.
The ligaments are thus named for their anteroposterior relation in tibia.
Reference: https://www.ajronline.org/doi/pdfplus/10.2214/ajr.135.5.1103
Further reading:

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.
This is the most helpful mnemonic I’ve ever come across for any topic!
I really appreciate this.. Thank you 🙂