2 Column Concept or Principle of Acetabulum (Letournel and Judet)
According to this concept, “C” shaped acetabular structure is contained between the limbs of lamda [λ] or inverted “y”. The longer limb represents anterior column and the shorter limb represents the posterior column. The anterior and posterior walls are extensions of the respective column and forms the cup of the acetabulum.
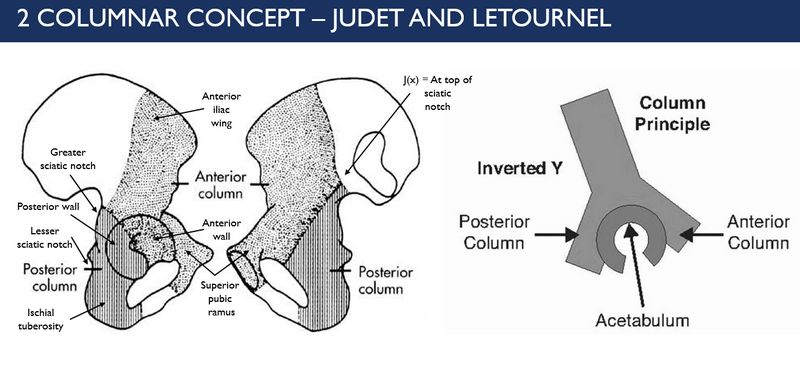
Anterior (Iliopubic) column
Marker: Iliopectineal line
Demarcation: Extending from the iliac crest down the iliac wing and through the superior obturator (pubic) ramus towards the pubic symphysis
Parts: Large portion of ilium and entire pubis
- Anterior half of iliac crest and iliac wing
- Iliac spines
- Anterior wall of acetabulum
- Pubis
Posterior (Ilioischial) column
Marker: Ilio-ischial line (Kohler’s line)
Demarcation: Posterior iliac body just below the angle of the greater sciatic notch down the ischial body into the inferior obturator (ischiopubic) ramus
Parts: Small portion of ilium and mainly of ischium
- Ischial tuberosity
- Ischial spine
- Posterior wall of acetabulum
- Dense bone forming greater sciatic notch
Above the sciatic notch, the anterior and the posterior columns meet at the sciatic buttress – which is a continuation of the iliac bone that communicates with the sacro-iliac joint. Although not a part of acetabulum, it is often employed as an anchor point in acetabular reconstruction.
The roof (dome) of the acetabulum which includes part of both the anterior and posterior column is the weight bearing area that supports the femoral head.
Approach to classifying acetabular fractures according to Letournel and Judet classification:
1. Obturator ring intact:
a. Posterior wall disruption: Posterior wall fracture
b. Iliopectineal line disruption: Anterior wall fracture
c. Both iliopectineal line and ilio-ischial line disrupted: Transverse fracture (with ot without posteior wall fracture)
2. Obturator ring disrupted:
a. Iliopectineal line disruption: Anterior column fracture
b. Ilioischial line disruption: Posterior column fracture
c. Both iliopectineal and ilioischial line disruption: Anterior column with posterior hemitransverse fracture or T-shaped fracture
d. Extension to iliac wing: Both column fracture (Spur sign)
3 Column Concept or Principle of Acetabulum – Zhang et.al.
This new concept of column is simple and proposed to have higher intertester reliability while classifying acetabular fractures.
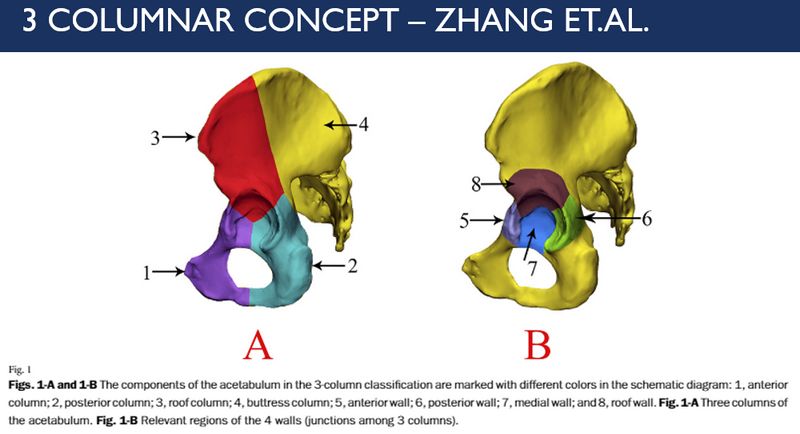
Branch of ilium: Roof column
Branch of pubis: Anterior column
Branch of ischium: Posterior column
Medial part: Buttress column
Junction between roof & anterior column: Anterior wall
Junction between roof & posterior column: Posterior wall
Junction between anterior & posterior column: Medial wall
References:
1. Fractures of the Acetabulum – Emile Letournel and Robert Judet (2nd Edition)
2. Zhang R, Yin Y, Li A, et al. Three-Column Classification for Acetabular Fractures: Introduction and Reproducibility Assessment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019;101(22):2015‐2025. doi:10.2106/JBJS.19.00284