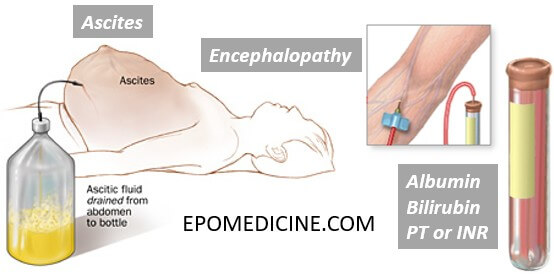
The Child-Pugh-Turcot (CTP) score consists of 5 clinical features and is used to assess the prognosis of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis.
Mnemonic: A BEAP
- Albumin (gm/dl)
- Bilirubin (mg/dl)
- Encephalopathy (Based on West Haven Criteria)
- Ascites
- Prothrombin Time (PT) Prolonged or INR
Child-Pugh-Turcot Score
| Factor | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bilirubin (mg/dl) | < 2 | 2 – 3 | < 3 |
| Albumin (g/dl) | > 3.5 | 2.8 – 3.5 | < 2.8 |
| INR or (Prothrombin time [seconds prolonged]) | < 1.7 (< 4) | 1.7 – 2.3 (4 – 6) | > 2.3 (> 6) |
| Ascites | None | Mild (Diuretic responsive) | Moderate or Severe (Diuretic refractory) |
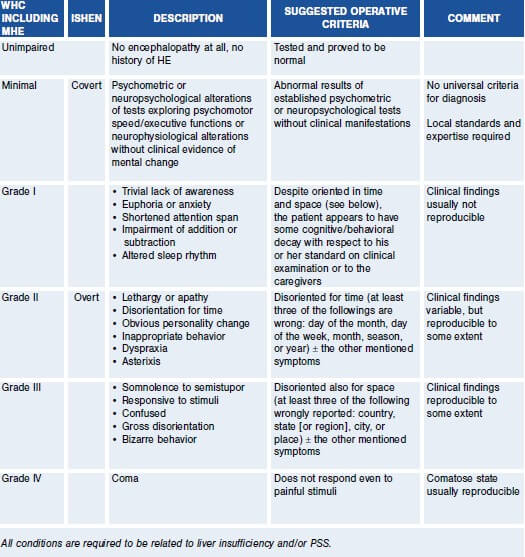
| Hepatic encephalopathy | None | Grade I – II | Grade III – IV |
West Haven Criteria for Hepatic Encephalopathy
Interpretation of Child Pugh Turcot Score
| Points | Class | One year survival | Two year survival | Operative mortality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 – 6 | A | 100% | 85% | Low (<5%) |
| 7 – 9 | B | 81% | 57% | Moderate (~25%) |
| 10 – 15 | C | 45% | 35% | High (>50%) |
MELD (Model For End Stage Liver Disease) Score
Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) is a numerical scale, ranging from 6 (less ill) to 40 (gravely ill), used for liver transplant candidates age 12 and older. It gives each person a ‘score’ (number) based on how urgently he or she needs a liver transplant within the next three months. The number is calculated by a formula using three routine lab test results:
- Bilirubin
- INR (prothrombin time)
- Creatinine
For Pediatric population (<12 years), there is PELD (Pediatric End Stage Liver Disease) Score which uses Albumin, Growth failure and Age <1 year instead of Creatinine.
Calculate MELD score.