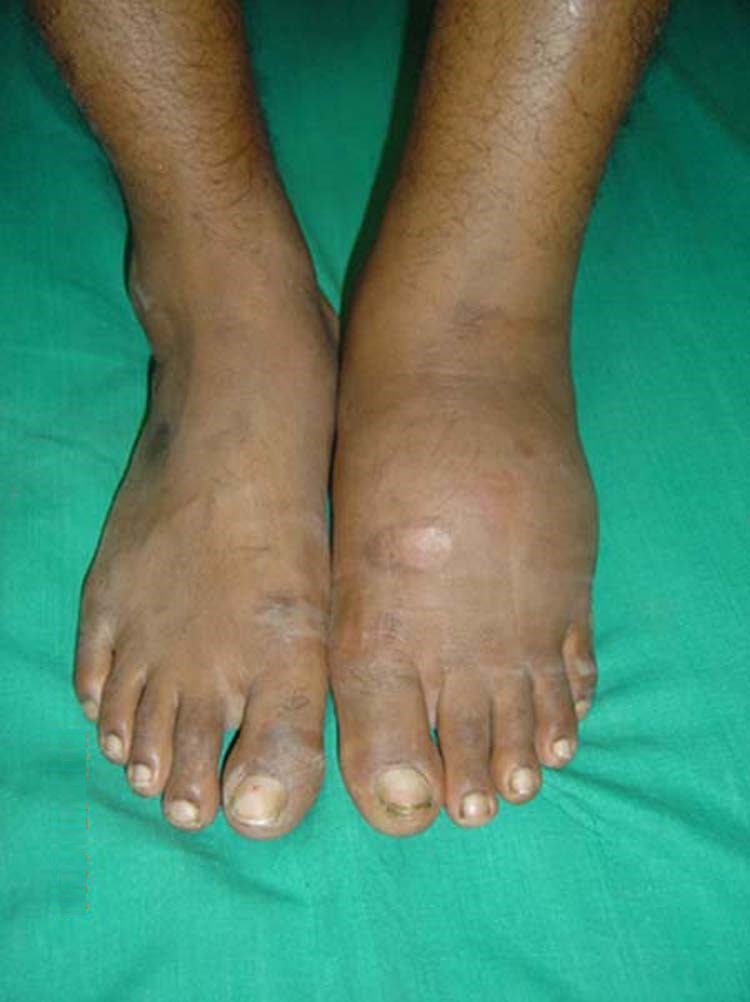
Causes of Charcot Arthropathy
Mnemonic: 10 S
- Sugar (diabetes) – most commonly foot and ankle
- Syringomyelia – 80% in shoulder and elbow
- Spinal cord injury – hip, knee, ankle and spine
- Spastic paraplegia
- Syphilis – most commonly knee
- Spirits (alcohol)
- Subacute combined degeneration
- Steroids
- Scaly disease (leprosy) – 2nd most common cause in upper extremity
- Scleroderma
3 Theories of Charcot Arthropathy
a. Neuro-traumatic: Damage to sensory feedback → Repeated microtrauma → Release of proinflammatory cytokines → Bone resorption
b. Neuro-vascular: Change in vascularity caused by dysregulation of vasomotor and trophic nerve supply
c. Neuro-inflammatory: Abnormal persistence of inflammatory response and inability to terminate inflammatory response
Classic features
Mnemonic: 6 Ds
- Destruction
- Disorganization
- Debris (loose bodies)
- Density (sclerosis)
- Distension (joint effusion)
- Dislocation (dislocation/subluxation)
Eichenholz classification
Mnemonic: CDCR or IFCC
- Clinical (Inflammatory) – Demineralization
- Dissolution (Fragmentation) – Debris and Dislocation
- Coalescence – Debris absorption and Density increase
- Resolution (Consolidation) – Deformity
Treatment
Mnemonic: ABCDEF
- Activity limitation
- Bracing or Casting (Total contact cast)
- Discontinue when skin temperature normal
- Evade total joint arthroplasty
- Fusion after inflammatory phase in feet
| Stage | Treatment |
| 0 – Clinical | Limited weight bearing (possibly TCC or PPWB), close observation |
| 1 – Fragmentation | TCC, limited weight bearing |
| 2 – Coalescence | TCC followed by CROW |
| 3 – Reparative | Possible surgical intervention for removal of bony prominences associated with ulceration |