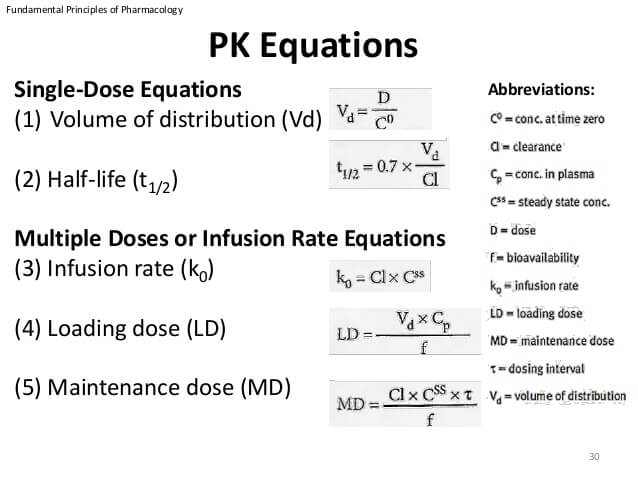
Features of Bronchopulmonary segments:
- Subdivision of the lobe of lung
- Pyramidal in shape – apex towards hilum and base towards lung surface
- Surrounded by connective tissue
- Aerated by segmental (tertiary) bronchus
- Each segment has it’s own artery (segmental branch of pulmonary artery)
- Drained by intersegmental veins (tributaries of pulmonary veins)
- Surgically resectable
Right Lung
Mnemonic: A PALM Seed Makes Another Little Palm (from top to bottom)
1. Superior lobe:
- Apical
- Posterior
- Anterior
2. Middle lobe:
- Lateral
- Medial
3. Inferior lobe:
- Superior
- Medial basal
- Anterior basal
- Lateral basal
- Posterior basal
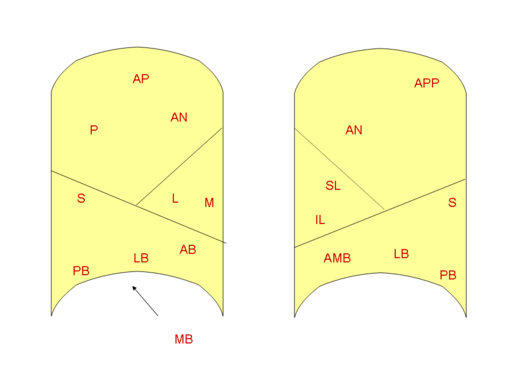
Left Lung
Instead of lateral and medial segment as described in middle lobe of right lung, the left lung lingula has:
- Superior lingular bronchopulmonary segment
- Inferior lingular bronchopulmonary segment
Some books mention 8 bronchopulmonary segments in left lung, and in these situations, it is due to merging of:
- Apical + Posterior segment in upper lobe = Apicoposterior
- Anterior + Medial basal segments in lower lobe = Anteromedial