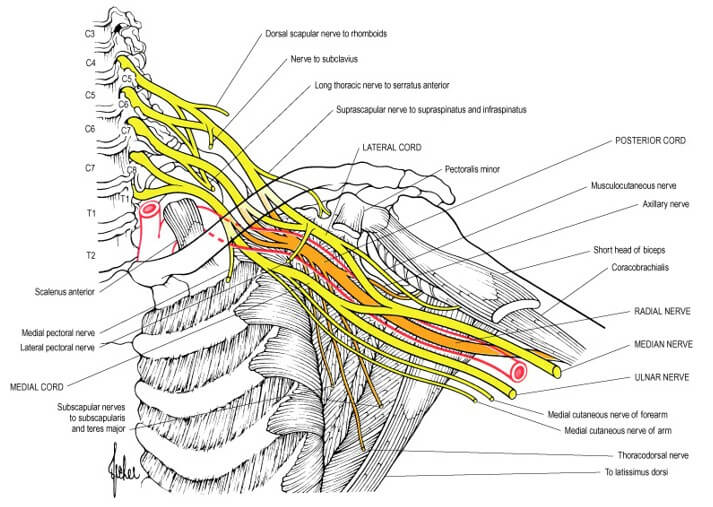
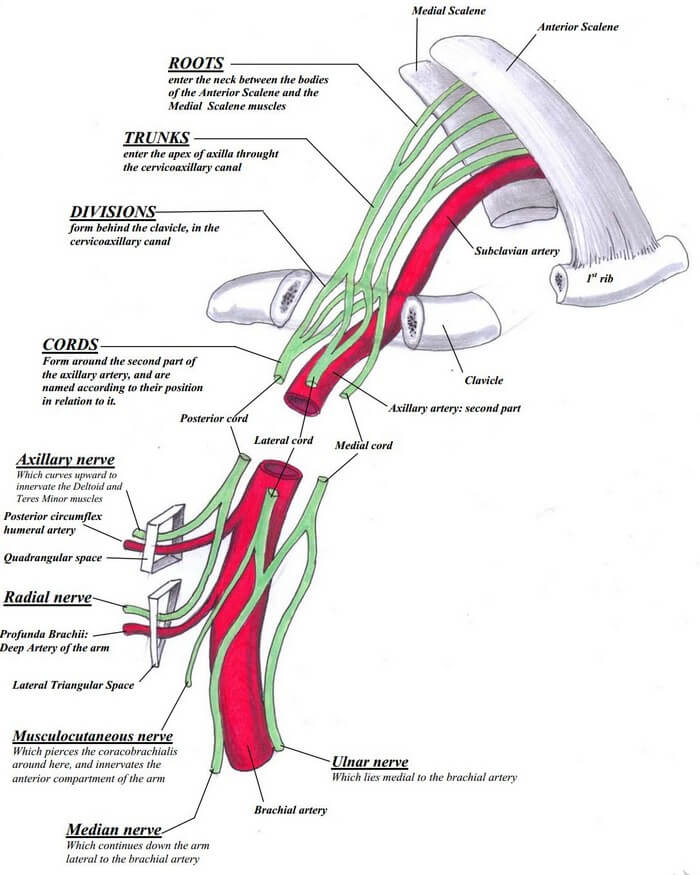
Components of Brachial Plexus
Mnemonic: Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer
From proximal to distal, brachial plexus consists of:
- Randy – Roots (C5-T1) = 5 Roots
- Travis – Trunks (Upper, Middle and Lower) = 3 Trunks
- Drinks – Divisions (Anterior and Posterior from each of 3 trunks) = 6 Divisions
- Cold – Cords (Lateral, Posterior and Medial) = 3 Cords
- Beer – Branches = 5 Terminal branches
How are the roots formed?
From the Ventral Rami of C5 to T1 spinal nerves.
Extent and course: Intervertebral foramina to Transverse process to Interscalene triangle (bounded by anterior scalene and middle scalene)
Ventral rami is not to be confused with ventral rootlets. Ventral rootlets (motor) and Dorsal rootlets (sensory) unite to form spinal nerve. Ventral rami of sensory nerve form brachial plexus and Dorsal rami paraspinal muscles and skin.
These rootlets lack connective tissue and meningeal covering, hence, more prone to avulsion injuries. However, fibrous attachment of C4-C7 spinal nerves may be found to the transverse process which makes them less likely for avulsion injuries compared to C8 and T1 nerves.
The neurons of the sympathetic system providing innervation to the upper extremity starts in T1 to T3/T4 spinal segement. The pre-ganglionic fibers synapse in the cervicothoracic (stellate) and middle cervical ganglia. The post-ganglionic fibers reach the nerves of the brachial plexus or the arteries of the upper extremity via the grey rami. The post-ganglionic fibers then reach and control the activities of the smooth muscles in the blood vessels walls, the arrectores pilorum muscles and the sweat glands of the upper extremity.
How do the ventral rami or roots mix to form trunks?
C5 + C6 = Upper trunk
- Confluence of C5 and C6 at upper trunk = Erb’s point
C7 = Middle trunk
C8 + T1 = Lower trunk
Extent: Outer border of interscalene triangle to Supraclavicular space of posterior triangle bounded by sternocleidomastoid anteriorly and trapezius posteriorly.
In the posterior triangle the plexus is covered by platysma. The neurovascular relation here, can be remembered by “VAN” mnemonic from anterior to posterior, i.e. Subclavian vein and artery anterior to the trunks.
How do the trunks divide to form divisions?
Each trunk splits into Anterior and Posterior divisions just behind and above the clavicle.
- Anterior divisions are destined to innervate ventral half of upper limb.
- Posterior divisions are destined to innervate dorsal half of upper limb.
Location: Around and within Cervico-axillary canal or Apex of axilla (between clavicle anteriorly, superior border of scapula posteriorly and 1st rib medially). Here, the brachial plexus lies lateral and posterior to the Axillary artery.
How do the divisions form the cords?
Posterior divisions of All 3 trunks = Posterior cord (C5-T1)
Anterior divisions of Upper and Middle trunks = Lateral cord (C5-C7)
Anterior division of Lower trunks = Medial cord (C8-T1)
Cords are named according to their relation to the 2nd part of Axillary artery. Axillary vein is located anterior to axillary artery.
Location: Formed in the axilla above the upper border of pectoralis minor and travels behind the pectoralis minor close to its insertion at coracoid process. The brachial plexus and axillary vessels are surrounded by a fascial sheath that originates from the fascias of the anterior and middle scalene muscles and extends up to the proximal third of the arm.
How do the branches arise from the brachial plexus?
From Cords
Each cord splits into 2 terminal branches at the level of inferior border of pectoralis minor –
a. Posterior cord: C5-T1
- Axillary nerve (C5-C6)
- Radial nerve (C5-T1)
b. Lateral and medial cord (C5-C7 and C8-T1 respectively): together form “M” like structure.
- Center leg of “M” (combination of branches from lateral and medial cords) = Median nerve (C5-T1)
- Lateral leg of “M” (branch from lateral cord) = Musculocutanoeus nerve (C5-C7)
- Medial leg of “M” (branch from medial cord) = Ulnar nerve (C8-T1)
Other branches from the cords:
- Lateral cord: Lateral pectoral nerve (C5-C7)
- Medial cord:
- Medial pectoral nerve (C8-T1)
- Medial cutaneous nerve of arm (C8-T1)
- Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm (C8-T1)
- Posterior cord:
- Upper and Lower subscapular nerve (C5-C6)
- Thoracodorsal nerve (C6-C8)
From Divisions
Divisions are branchless.
Supraclavicular branches
a. From upper trunk:
- Suprascapular nerve (clinically significant) – C5, C6
- Nerve to subclavius (clinically not significant)
b. From roots:
- C3-C5: Phrenic nerve
- C5-C7: Long thoracic nerve
- C5: Dorsal scapular nerve
| Nerve | Muscle | Action |
| Dorsal scapular (C5) | Rhomboid | Stabilization of scapula |
| Long thoracic (C5) | Serratus anterior | Abduction of scapula |
| Suprascapular (C5) | Supraspinatus Infraspinatus | Abduction of shoulder External rotation of shoulder |
| Medial (C8) and lateral pectoral (C7) | Pectoralis major | Adducts the shoulder |
| Pectoralis minor | Stabilizes the scapula | |
| Subscapular (C5) | Subscapularis and teres major | Internal rotation of shoulder |
| Thoracodorsal (C7) | Latissimus dorsi | Adduction of shoulder |
| Musculocutaneous (C5) | Biceps brachii and brachialis | Flexion of elbow |
| Ulnar (C8, T1) | Flexor carpi ulnaris Intrinsic muscles of hand | Flexion of wrist and fingers Abduction of fingers |
| Median (C6, C7, C8, T1) | Pronators of forearm Flexors of wrist and fingers | Pronation of forearm Flexion of wrist and fingers |
| Radial (C6, C7, C8) | Supinator Triceps brachii Extensors of wrist and fingers | Supination of forearm Extension of elbow, wrist, and fingers |
| Axillary (C5) | Deltoid and teres minor | Abduction of shoulder |
Anatomical Variations of Brachial Plexus
Normal (77%): C5-T1
Prefixed (22%): C4-C8 + reduced contribution from T1
Postfixed (1%): C6-T2 + reduced contribution from C5
Some Ridiculous Mnemonics to help you cram Brachial Plexus
Terminal branches: MARMU (or Most Alcoholics Must Really Urinate)
- Musculocutanoeus nerve
- Axillary nerve
- Radial nerve
- Median nerve
- Ulnar nerve
Lateral cord branches: LML (or Lucy Loves Me)
- Lateral pectoral nerve
- Musculocutaneou nerve
- Lateral root of median nerve
Medial cord branches: MMMUM (Most Medical Men Use Morphine)
- Medial pectoral nerve
- Medial cutaneous nerve of arm
- Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm
- Ulnar nerve
- Medial root of median nerve
Posterior cord branches: ULTRA
- Upper subscapular nerve
- Lower subscapular nerve
- Thoracodorsal nerve
- Radial nerve
- Axillary nerve
5,6,7 raise your arms to heaven: Serratus anterior is supplied by Long Thoracic Nerve which arises from C5-C7 root.
Root values of terminal branches: 3 musketeers assassinated 5 rates, 5 mice and 2 unicorns.
- 3 musketeers: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5, C6, C7)
- Assasinated: Axillary nerve (C5-C6)
- 5 rats: Radial nere (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1)
- 5 mice: Median nerve (C5, C6, C7, C8, T1)
- 2 unicorns: Ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
See the images here for better understanding: http://www.stritch.luc.edu/lumen/meded/grossanatomy/2013_2014/revisedbp14/revisedbp14_print.html

PA stuff