Origin of Pathology
Periosteum
- The periosteum could create a fibrous band causing an increase in local pressure around the bone resulting in reduced vascularization as well as bone atrophy
Clinical features
Mnemonic: ABCDeF
- Age of onset:
- Early (<4 years old) – majority present with bowing in 1st year of life
- Late (>4 years old)
- Bowing: Antero-lateral (junction of middle 1/3 and distal 1/3)
- Cafe-au-lait spots and Neurofibromatosis type 1 (in 55% cases)
- Deformity
- Fractures; Fibrous dysplasia (in 15% cases)
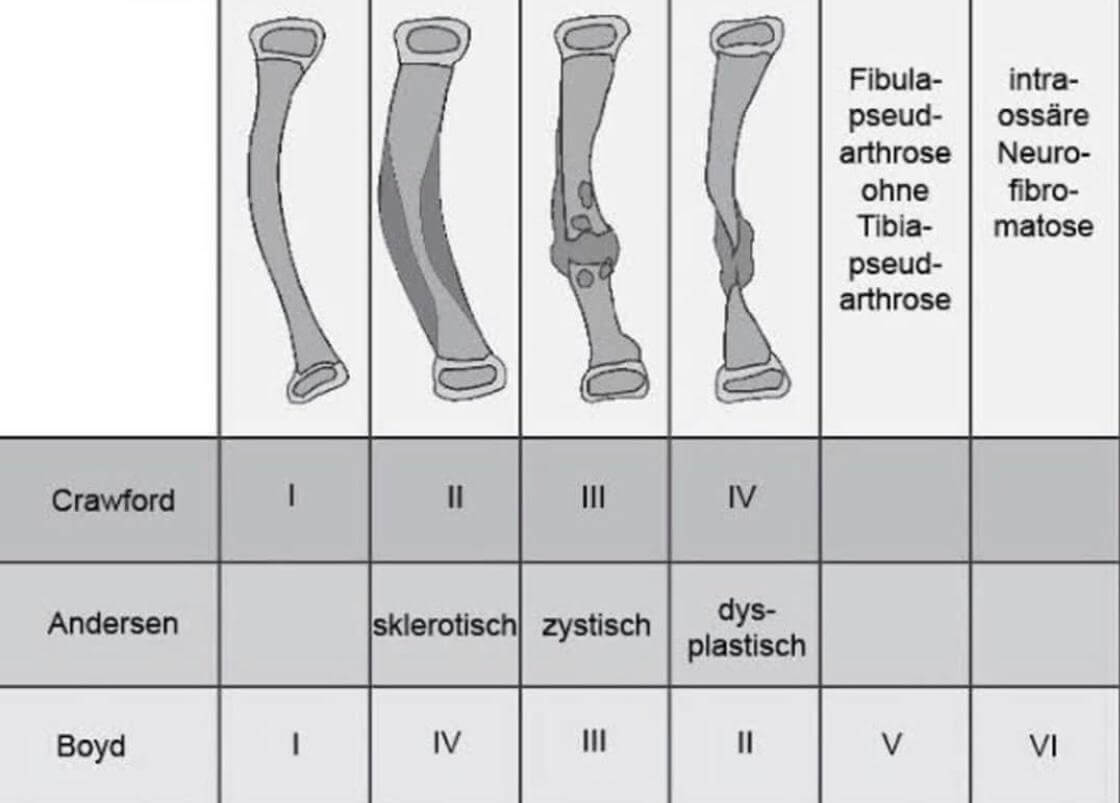
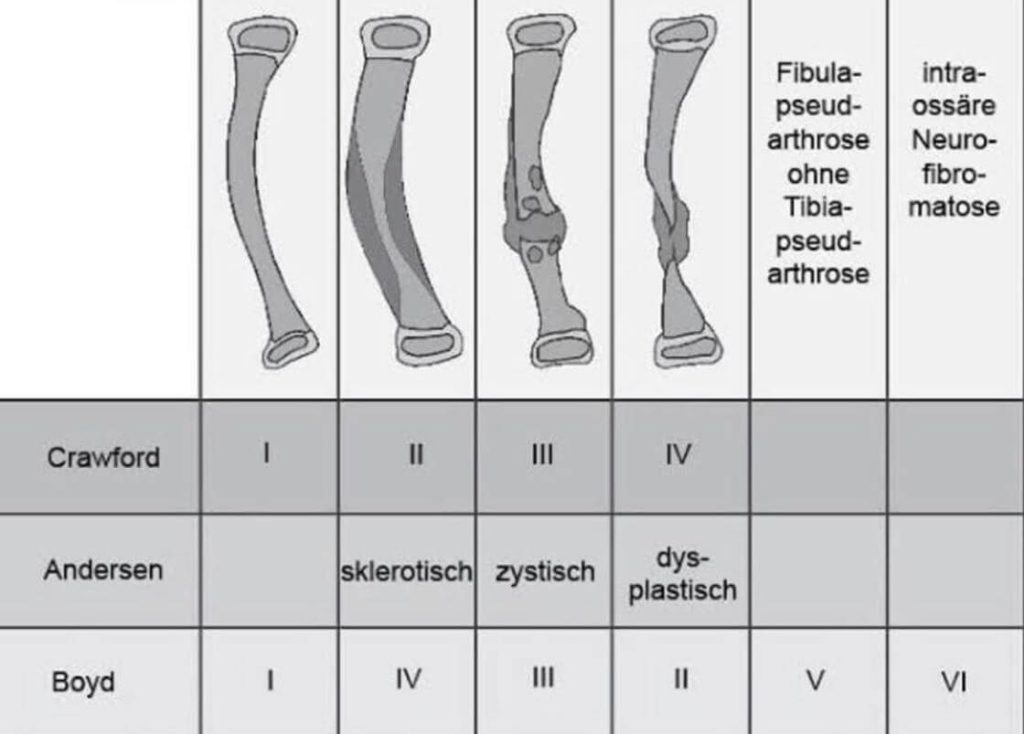
Boyd Classification
Mnemonic: B-2C-2D-E
I – Bowing
II – Constriction (hourlgass)
- Most common type
- Poorest prognosis
- More often associated with NF1
III – Cyst
IV – Dense (Sclerotic)
V – Dysplastic fibula
VI – “Endosseous” (Intraosseous) neurofibroma or schwannoma
Paley Classification
| Type | Bone ends | Pseudoarthrosis mobility | Previous surgical intervention |
| 1 | Atrophic | Mobile | Absent |
| 2 | Atrophic | Mobile | Present |
| 3 | Hypertrophic | Stiff | Absent/Present |
Treatment

Differential Diagnoses
1. Osteofibrous dysplasia of long bones
2. Congenital angulation of tubular bones
3. Monostotic fibrous dysplasia
Poor Prognostic Factors
- Markedly progressed disease
- Early fractures
- Inferior metaphyseal location of pseudoarthrosis
- Atrophy of bone
- Extensive sclerotic lesions with a smaller diameter bone
- Significant shortening
- Associated fibular involvement