Anterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (AHCA)
Origin: Axillary artery
Course:
- Along the inferior border of subscapularis
- Gives anterolateral ascending branch which courses along lateral aspect of bicipital groove entering the humeral head and becoming arcuate artery
- Continues posterolaterally to anastomose with Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (PHCA)
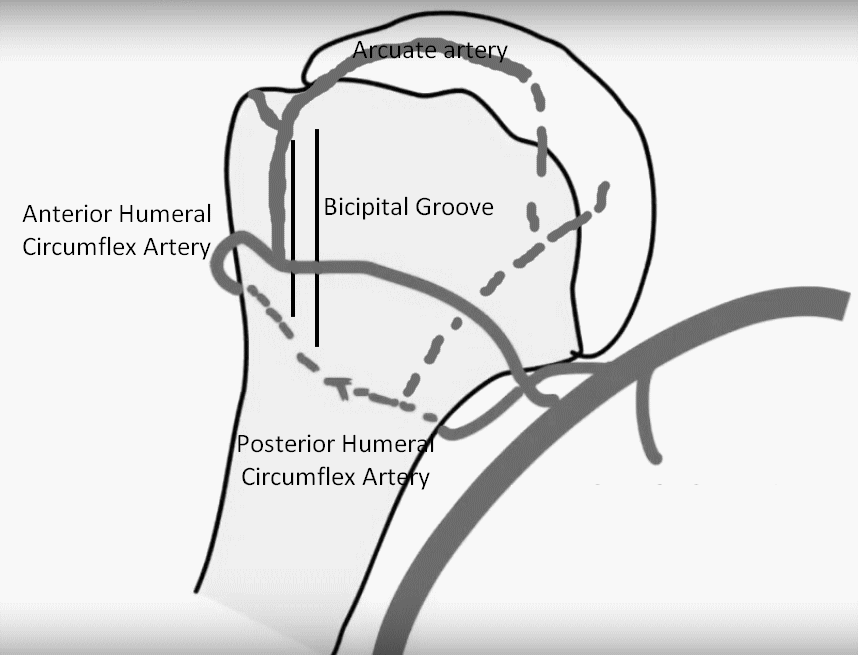
Posterior Humeral Circumflex Artery (PHCA)
Origin: Axillary artery
Course:
- Travels through quadrilateral space along with axillary nerve
- Anastomose with PHCA
- Posteromedially, gives branches that enter the humeral head
Contribution
- From the older studies, there was a general consensus that anterolateral branch of AHCA was the most important source of perfusion.
- However, recent studies have challenged this with the finding that 64% of humeral head blood supply is from the PHCA. AHCA is disrupted in 80% cases of proximal humerus fractures and PHCA remains intact in 85% cases which suggests for PHCA as the major contributor accounting for low rates of AVN.
References:
- Proximal Humerus Fractures: Evaluation and Management edited by Lynn A. Crosby, Robert J. Neviaser