Classification
Non-nitrogen containing (1st generation):
- Etidronate
- Clodronate
- Tiludronate
Nitrogen containing (2nd and 3rd generation):
a. 2nd generation (alky-amino nitrogen containing):
- Pamidronate
- Alendronate
- Ibadronate
- Olpadronate
b. 3rd generation (heterocyclic nitrogen containing):
- Risedronate
- Zoledronate
Chemical structure
Stable derivatives of inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi)
Mechanism of action
- Strong attachment to hydroxyapatite mineral found in bone
- Uptake by osteoclasts resorbing bone
- Inhibition of osteoclast function or induction of osteoclast apoptosis
- Non-nitrogen containing bisphosphonates: Metabolized to non-hydrolyzable ATP analogues in osteoclast cytosol leading to inhibition of multiple ATP dependent processes (cytotoxicity)
- Nitrogen containing bisphosphonates: Bind to and inhibit the activity of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (key regulatory enzyme of mevalonate pathway for cholesterol and other sterol synthesis) leading to inhibition of isoprenylation of small proteins (GTPases):
- Rho, Rac (regulate cell survival): induction of apoptosis
- Rabs (regulate vesicular transport): loss of ruffled border
- Rho, Rac, Cdc42 (regulate actin cytoskeleton): cytoskeleton disruption
In addition to their inhibitory effect on osteoclasts, bisphosphonates appear to have antiapoptotic effects on osteocytes and osteobalsts. These can open Connexin-43 (Cx-43) hemichannels and activate anti-apoptotic signalling pathways via ERKS.
Bisphosphonates have different affinities for hydroxyapatite. Lower affinity Bisphosphonates should be able to gain access to more sites in bone than higher affinity ones which will get ‘stuck’ at sites of first contact.
Relative potency
Mnemonic: ECT PAIRZ
- Etidronate: 1
- Clodronate: 10
- Tiludronate: 10
- Pamidronate: 100
- Alendronate: 500
- Ibandronate: 1000
- Risedronate: 2000
- Zoledronate: 10000
Important Pharmacologic Features
- <1% drug is absorbed from gastrointestinal tract when taken orally
- From circulation, 50% reaches bone and 50% is excreted unchanged in urine
- Estimated average half-life: >10 years
- Maximum suppression of bone resorption occurs within approximately 3 months of initiation of oral bisphosphonate therapy given daily, weekly, or monthly and remains roughly constant with continuation of treatment. Resorption is suppressed more rapidly after intravenous (IV) bisphosphonate administration than after oral bisphosphonate therapy.
- Oral administration require patients to remain upright for 30 minutes and refrain from eating any food both 2 hours before and at least 30 minutes after pill ingestion
- Data from long-term studies with bisphosphonates (up to 10 years) suggest that some patients may be able to take a break from treatment without incurring additional fracture risk after three to five years
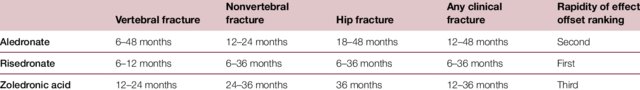
Indications
a. Osteoporosis
- Hip or vertebral (clinical or asymptomatic) fractures with T-scores ≤ −2.5 at the femoral neck, total hip, or lumbar spine by DEXA scan
- Postmenopausal women and men age >/= 50 and with low bone mass (T-score between−1.0 and−2.5, i.e. osteopenia) at the femoral neck, total hip, or lumbar spine by DEXA and a 10-year hip fracture probability ≥3 % or a 10-year major osteoporosis-related fracture probability ≥20 % based on the USA-adapted WHO absolute fracture risk model (FRAX tool)
- Glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis (GIO): Risedronate has been approved in the United States for both prevention and treatment of GIO and Alendronate for the treatment of GIO
b. Paget’s disease of bone: given cyclically
c. Hypercalcemia of malignancy
d. Avascular necrosis: early pre-collapse AVN
e. Relieve pain of lytic bone lesions
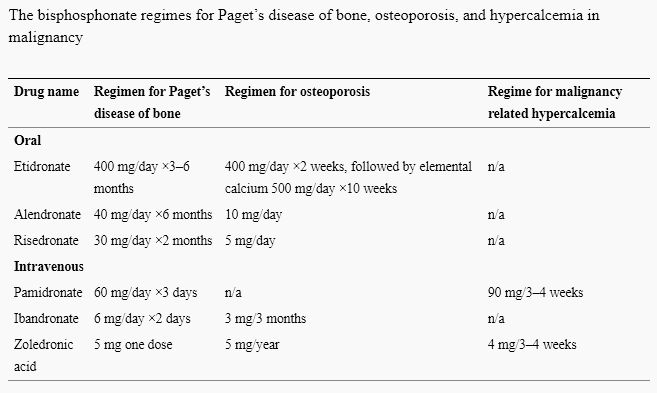
Dosage
Adverse effects
- Osteonecrosis of jaw (ONJ)
- Atypical femoral neck fractures
- Atrial fibrillation
- Hypocalcemia
- Acute inflammatory response
- Severe musculoskeletal pain
- Esophageal irritation and erosion (oral bisphosphonate)