The order of the nephron defects in Bartter, Gitelmann and Liddle syndrome follows alphabetical order.
Bartter: Thick ascending LOH
Gitelmann: Distal tubule
Liddle: Collecting duct
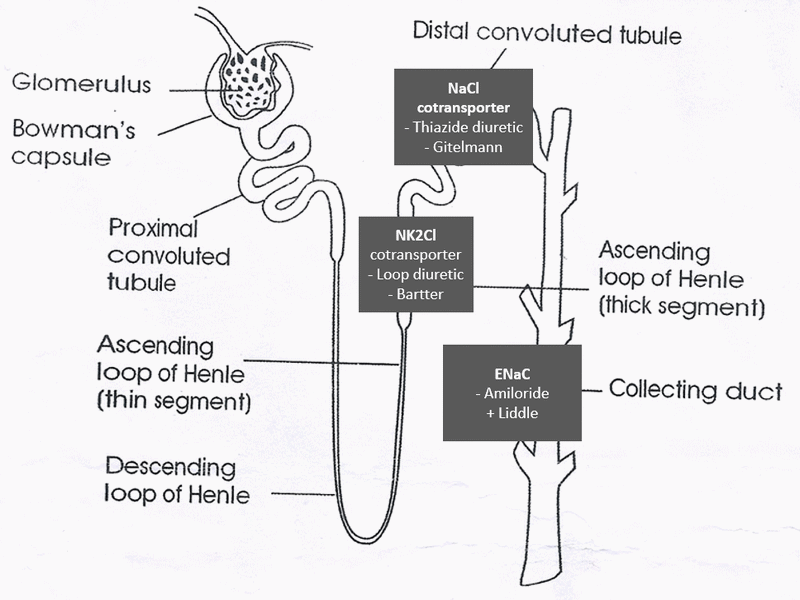
a. Bartter syndrome: Thick ascending Loop of Henle (LOH)
- Defect in Na-2K-Cl transporter (like loop diuretics)
- NaCl wasting, Hypercalciuria and mild hypomagnesemia
Mnemonic: Loop diuretics lose calcium
b. Gitelmann syndrome: Distal tubule
- Defect in Na-Cl co-transporter (like thiazide diuretics)
- NaCl wasting, Hypocalciuria and Hypomagnesemia
Mnemonic: Thiazides preserve calcium
c. Liddle syndrome: Collecting duct
- Continuous activation of ENaC in collecting duct leading to increased Na absorption
- Early and severe hypertension with low renin and aldosterone
- Hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis
- Amiloride or triamterene block ENaC (basis of treatment)
Important points to remember:
- All of these cause hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
- Bartter and Gitelmann causes normotension or hypotension while Liddle causes hypertension.
- Bartter’s syndrome causes hypercalciuria while Gitelmann’s syndrome causes hypocalciuria.
- Gitelmann’s syndrome causes hpomagnesemia.
- NSAIDs reduce polyuria and salt wasting in Bartter’s syndrome (increased renal PGE2 production in Bartter’s).
- Bartter’s and Gitelmann’s are autosomal recessive (AR) while Liddle’s is autosomal dominant (AD).
- In Bartter’s and Gitelmann’s there is secondary hyperaldosteronism and in Liddle’s, there is hypoaldosteronism.
1.All causes Na,K and Ca business.
2. Bartter and Gittleman :Na wasting.So hypotension. Secondary Hyperaldosteronism.
3.Liddle cause Na retention.So HTN,Hyporenininsm and Hypoaldosteronism
4.We give Thiazide for HTN.S/e:Hypo Natremia,Hypokalemia,Hypercalcemia.From Hypercalcemia Hypercalciuria ensues.
5.We give Loop diuretics=Lasix for Hypercalcemia.Which cause Hypocalcemia and Hypocalciuria.
6.Liddle is ENaC;S o Na retention ensued and that can be countered with Amiloride /Trimethoprime,Anti-Aldosterone medicine.
7.Bartter=Baratender=Fat=Prostate=PGE2.So Brufen =NSAIDs as Inhibitor and treatment.
8.First Alphabet B =Bartter(Ascending loop),Then Alphabet G=Gittleman(DCT),Next Alphabet L.So Liddle(CT).
9.Barter and Gittleman=involve enzymes.So AR.Liddle =defect in Structural protein gene mutation;so AD.
Assalamualaikum
Really useful.
Thanks@epomedicine