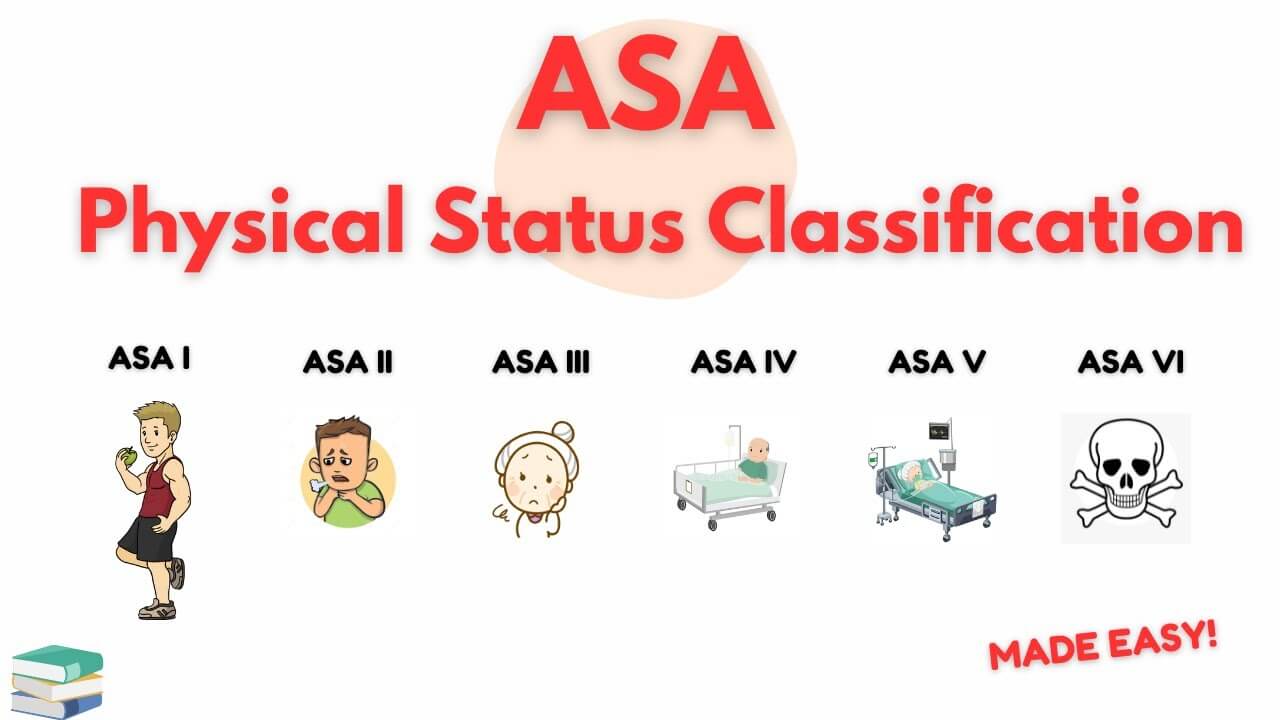
The purpose of the system is to assess and communicate a patient’s pre-anesthesia medical co-morbidities. The classification system alone does not predict the perioperative risks, but used with other factors (e.g., type of surgery, frailty, level of deconditioning), it can be helpful in predicting perioperative risks.
| ASA grade | Definition | Mortality |
|---|---|---|
| I | Normal healthy | 0.05% |
| II | Controlled mild systemic disease; no functional limitation | 0.5% |
| III | Uncontrolled severe systemic disease; functional limitation | upto 5% |
| IV | Constant threat to life | upto 25% |
| V | Moribund patients (not expected to survive 24 hours) | upto 50% |
| VI | Brain dead | 100% |
Some important examples
Smoker: ASA 2
Alcohol:
- Social drinker: ASA 2
- Alcohol dependence or abuse: ASA 3
Pregnancy: ASA 2
Obesity:
- BMI 30-40: ASA 2
- BMI >40: ASA 3
MI, CVA, TIA, CAD/stents:
- >3 months: ASA 3
- <3 months: ASA 4
Diabetes, Hypertension:
- Controlled: ASA 2
- Uncontrolled: ASA 3
Lung disease:
- Mild: ASA 2
- COPD: ASA 3
Further reading: http://www.kpcolorado.net/sites/default/files/files/KASC_2-04A_ASA_Classification_made_easy.pdf