Rheumatoid factor (RF; also mistakenly called RA factor) is an auto-antibody (commonly IgM and rarely IgG or IgA) directed against the Fc portion of IgG. Increase in both IgM and IgA RFs is almost exclusively observed in patients with RA (Rheumatoid Arthritis).
Clinical Significance of Rheumatoid Factor
1. A positive rheumatoid factor can be found in rheumatic disorders, non-rheumatic disorders, and healthy subjects:
- Rheumatic disorders: Rheumatoid arthritis (26-90%), Sjogren’s syndrome (75-95%), Mixed connective tissue disease (50-60%), Mixed cryoglobulinemia (40-100%), SLE (15-35%), Polymyositis/dermatomyositis (5-10%), Juvenile RA (5%)
- Non-rheumatic disorders: Subacute bacterial endocarditis/SBE (40%), Hepatitis B (25%) or C (40-76%), Malignancy (5-25%), Primary biliary cirrhosis (25%)
- Healthy individuals: Young (upto 4%), Elderly (3-25%)
The negative predictive value for RA and for any rheumatic disease was 89 and 85 percent, respectively.
2. RF titer and value:
- Normal titer is <1:80. Higher the titer, higher is the sensitivity and specificity for rheumatic diseases.
- Normal value of RF is <15 IU/ml (defer according to lab). Low positive means >ULN; high positive means >3× ULN.
3. Prognostic value:
RF-positive (seropositive) patients with RA may experience more aggressive and erosive joint disease and extra-articular manifestations than those who are RF-negative (seronegative).
Approach to Rheumatoid Factor Positive test
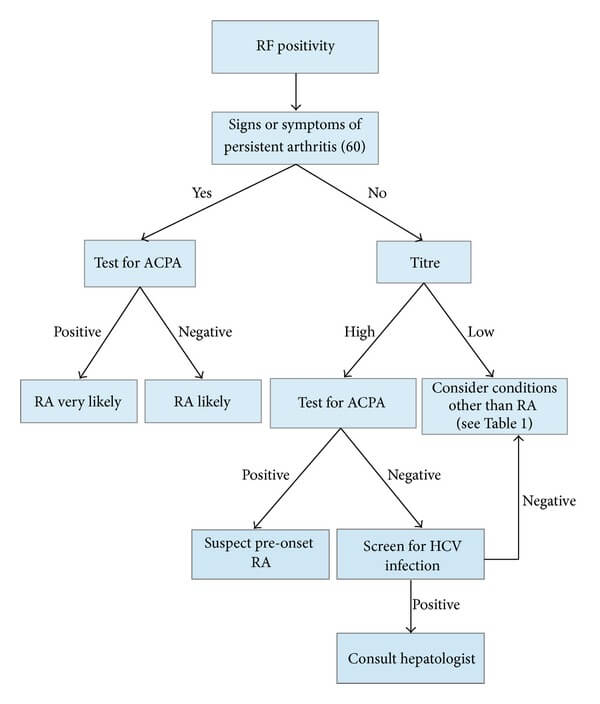
- High titer RF or Low titer RF with Clinical features of RA = Test for ACPA
- High titer RF without clinical features of RA + Negative ACPA = Screen for HCV infection
- Low titer RF without clinical features of RA = Consider other conditions where RF is positive
References:
- Ingegnoli F, Castelli R, Gualtierotti R. Rheumatoid factors: clinical applications. Dis Markers. 2013;35(6):727-34. doi: 10.1155/2013/726598. Epub 2013 Nov 13. PMID: 24324289; PMCID: PMC3845430.
- Khan F. The role of rheumatoid factor in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Tiwari V, Jandu JS, Bergman MJ. Rheumatoid Factor. [Updated 2022 Jul 25]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532898/