Classification and Mechanism of Action
Acronyms:
- TCA = Tricyclic Antidepressant
- RIMA = Reversible Inhibitor of MAO-A
- MASSA = Meltonergic Agonist and Selective Serotonergic Antagonist
- NDRI = Noradrenaline and Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
- NASSA = Noradrenergic and Selective Serotonergic Antagonist
- NARI = Noradrenergic Reuptake Inhibitor
- SSRI = Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor
- SNRI = Serotonin & Noradrenaline Reuptake Inhibitor
- SARI = Serotonin Antagonist and Reuptake Inhibitor
- NA = Noradrenaline
- 5-HT = Serotonine
- D = Dopamine
- M = Muscarinic
- α1 = Alpha-1 adrenergic
- H = Histamine
- ADR = Adverse Drug Reaction
Mnemonic: TRIM 3N 3S
| Class | Mechanism | Drugs | Side effects |
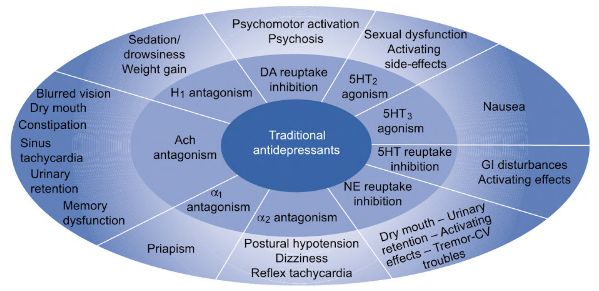
| TCA | Blocks reuptake of 5-HT, NA & other receptors (H1, ACh, α1, Voltage sensitive Na+ channel) | Mnemonic: ANTI-DeP-C 1. Amitryptiline, Amoxapine 2. Nortryptiline 3. Trimipramine 4. Imipramine 5. Doxepin, Desipramine, Dothiepin 6. Protryptiline 7. Clomipramine | M1 blockade: Muscarinic anticholinergic side-effects α1 blockade: Orthostatic hypotension H1 blockade: Weight gain, Sedation Na+ channel blockade: Arrhythmias, Seizures |
| RIMA | Selectively & Reversibly inhibits MAO-A & prevent breakdown of 5-HT, NA | Moclobemide | Serotonin syndrome Hypertensive crisis |
| Irreversible MAO Inhibitors | Irreversible inhibitor (2 weeks required for enzyme to regenerate) of MAO-A (targets 5-HT & NA) &/or MAO-B (targets D) & prevent breakdown of 5-HT, NA, D | Non-selective: Tranylcypromine, Phenelzine Selective MAO-B: Selegiline | Higher risk of: Agitation, Orthostatic hypotension, Weight gain, Sexual dysfunction, Serotonin syndrome, Hypertensive crisis |
| Modulator & stimulator of 5-HT | Inhibits 5-HT reuptake 5-HT1B partial agonist 5-HT3, 5-HT7 & 5-HT1D antagonist | Vortioxetine | Increased nasopharyngitis |
| MASSA | Melatonergic Agonist (regulates ciracadian rhythm) + Selective serotonin (5-HT2B and 5-HT2C) antagonist (increase release of NA & D) | Agomelatine | Increased liver enzymes |
| NDRI | Inhibits reuptake of NA & D (D>NA) | Bupropion (Useful for smoking cessation) | Fewer ADR than TCAs or SSRIs |
| NaSSA | NA (α2 antagonism = increased NA release) + Specific Serotonin Antagonist (5-HT2 & 5-HT3 = enhanced 5-HT1 pathway) | Mirtazapine Mianserin | 5-HT2C & H1 blockade: Weight gain 5-HT2A & H1 blockade: Sedation |
| NARI | Selective NA reuptake inhibition | Reboxetine Atomoxetine | Adrenergic excess (Awake, Anxious, Agitated) |
| SSRI | Selective 5-HT reuptake inhibition | Fluoxetine (longest acting SSRI) Fluvoxamine Paroxetine Sertraline Citalopram Escitalopram | No adverse effects of TCAs. GI symptoms, Headache, Insomnia, Sexual dysfunction |
| SNRI | 5-HT, NA (& D) reuptake inhibition | Venlafaxine Duloxetine | Mnemonic: SHAT 1. SSRI ADRs 2. Hypertension 3. Adrenergic effects (awake, anxious, agitated) 4. Tachycardia |
| SARI | 5-HT2A antagonist (reduces anxiety, insomnia, myoclonus) + 5-HT reuptake inhibitor | Trazodone | α1 blockade: Orthostatic hypotension, Priapism H1 blockade: Sedation |
Further reading: