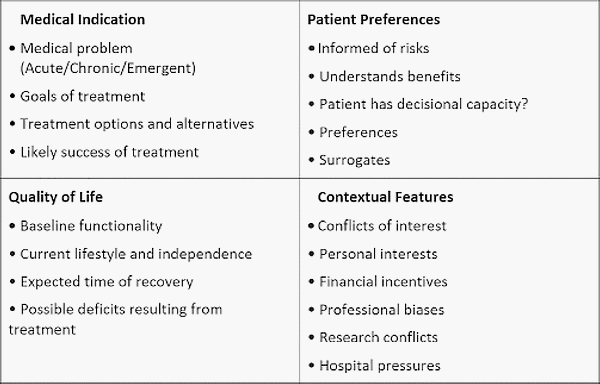
Remember the 4 Cs:
- Clinical indication (Principle of Benevolence and Non-maleficence)
- Choice of patient (Principle of respect for Autonomy)
- Contextual features (Principle of Loyalty and Fairness)
- Condition (quality) of life (Principle of Benevolence, Non-maleficence and respect for Autonomy)
- A 5th box can be added: Catholic perspective
Example:
| Clinical indications 18 yr old male with blood mixed sputum in cough and fever for 2 week and findings suggestive of right sided exudative pleural effusion Patient needs chest tube or pigtail catheter insertion and aspiration of pus | Choice of patient Only IV antibiotics No chest tube Patient refuses Mother and relatives wants indicated treatment |
| Condition (Quality) of life At Present not good May be improved with treatment as it is curable with antibiotics and aspiration of Pus | Contextual features Taking consent from mother and counselling the patient |
Marugg L, Atkinson MN, Fernandes A. The five-box method: The “four-box method” for the Catholic physician. Linacre Q. 2014 Nov;81(4):363-71. doi: 10.1179/2050854914Y.0000000032. PMID: 25473133; PMCID: PMC4240053.