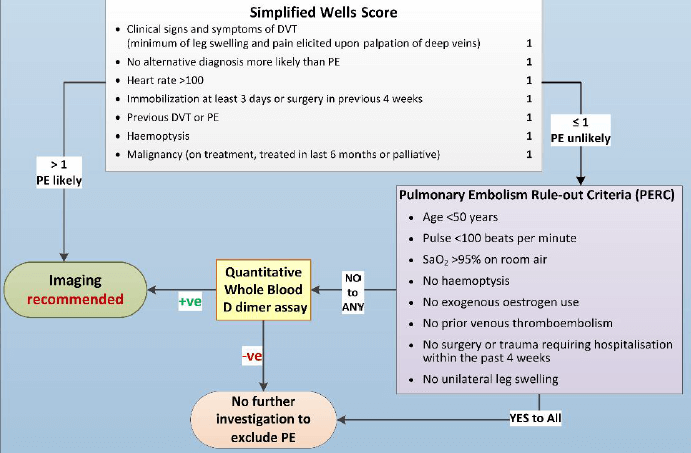
Well’s Criteria (Modified and Simplified)
Mnemonic: CHADS (Remember, this is not the CHADS2 score for Atrial Fibrillation)
- Clinical features of DVT
- Cancer
- Heart rate > 100/min
- Hemoptysis
- Alternative diagnosis less likely
- DVT/PE in past
- Surgery in past 4 weeks or Immobilization for 3 days
| Well’s criteria | Original score | Simplified score |
| Clinical features of DVT (minimum of leg swelling and pain with palpation of the deep veins) | 3 | 1 |
| Alternative diagnosis is less likely than PE | 3 | 1 |
| Heart rate > 100 beats per minute | 1.5 | 1 |
| Surgery in past 4 weeks or Immobilisation for more than 3 days | 1.5 | 1 |
| DVT/PE in past | 1.5 | 1 |
| Haemoptysis | 1 | 1 |
| Cancer (on treatment, treated in the last 6 months, or palliative) | 1 | 1 |
| Clinical probability | ||
| PE likely | More than 4 points | More than 1 points |
| PE unlikely | 4 points or less | 1 point or less |
Another mnemonic: EAT CHIPS
- Edema/pain in leg or any other symptoms of DVT: 3
- Alternative diagnosis less likely: 3
- Tachycardia: 1.5
- Cancer: 1
- Hemoptysis: 1
- Immobilization for >3 days: 1.5
- Previous history of DVT or PE: 1.5
- Surgery in past 1 month: 1.5
PERC (Pulmonary Embolism Rule-out Criteria)
Mnemonic: HAD CLOTS
1. Hormones (Estrogen use)
2. Age > 50 years
3. DVT/PE history
4. Coughing blood
5. Leg swelling
6. O2 <95%
7. Tachycardia >100/min
8. Surgery/truama within 4 weeks
If PE is unlikely or probability is low, PERC rule is used to decide if the assessment of D-dimer would be beneficial or not. If any 1 of the 8 criteria in PERC is met, D-dimer assay is beneficial.