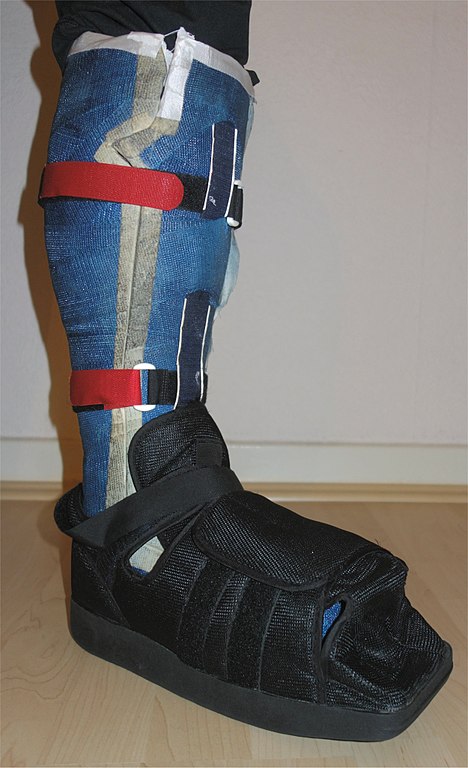
Total contact cast (TCC) is a modification of traditional below knee plaster with minimal padding, covering to protect toes, and molding to the contour of the foot and leg so that there’s no movement withing the cast.
Indications of Total Contact Cast
- Plantar non-infected neuropathic ulcers of forefoot and midfoot (Meggitt-Wagner grade I and II)
- Early stages of Charcot arthropathy
Contraindications of Total Contact Cast
1. Absolute:
- Infection
- Severe arterial insufficiency (pedal pulse must be palpable or detected by hand-held doppler)
- Active dermatoses or contact allergy to any cast components
- Involvement or exposure of deeper structures (tendon, joint capsule or exposed bone)
2. Relative:
- Pathology in hindfoot
- Blindness
- Ataxia
- Obesity
- Claustrophobia
- Bed ridden patients (significant loading of posterior aspect of heal leading to posterior heel ulcers)
- Extreme exudative wound (causes local tissue maceration)
Principles of Total Contact Cast
- It increases the weight bearing surface area and reduce pressure by distributing it over a larger area.
- Offloading: Studies have shown following –
- Reduction in peak plantar pressure in forefoot and midfoot by almost 40-80%
- Transferring foot pressure of upto 30% directly to leg
- Some degree of pressure transfer to heel (increase in 37% loading)
- Reduction in shear and sliding forces
- Immobilization can reduce edema and improve circulation
- Improvement in compliance to off-loading compared to removable devices
- Stabilization of fractures in Charcot arthropathy (primary goal rather than offloading) leading to reduced local tissue irritation and reduction in swelling.
Technique of Total Contact Cast
The precise technique of cast application is not as important as long as it is meticulously done and the critical prominences are padded.
Position: Preferably prone
1. Ulcer debridement to remove all prominent calluses if present
2. Adjuvant low-profile wound dressings (simple, thin single-layer dry gauze) if present
3. Gauze or lamb’s wool application between toes to prevent maceration
4. Apply foam or cotton batting toe cap covering both the dorsal and plantar aspect of the toes back to the level of the metatarsal heads
5. Single layer of stockinette without any wrinkles can be applied before or after step 4 if available
6. Pad bony prominences (malleoli and tibial crest) then apply a single roll of cotton or synthetic cast roll over the limb with ankle in neutral position
7. Casting:
- A well molded posterior plaster splint (made of single 4″ plaster of Paris roll) with plaster arch fillers can be applied (optional)
- A walking heel/sole can be placed – made of 1/4-inch plywood or prefabricated rubber
- A single layer of 6″ plaster of Paris cast is applied covering the limb and carefully molded to leg, ankle and foot.
- Fiberglass casting rolls are applied from the tibial tubercle to enclose the foot distally. The completed cast encloses the entire foot and leg.
Aftercare of Total Contact Cast
1. Weight bearing limitations: Avoid weight bearing for 30 minutes after cast application and limit weight bearing until next morning. However, limited weight bearing in TCC is advised throughout stage I of Charcot arthropathy (typically 10-12 weeks).
2. Change of casts: Casts are changed every 1-2 weeks (preferably 1 week) and early Charcot arthropathy may initially require cast changes in 3-5 days due to dramatic swelling issues.
3. Duration of TCC:
- Charcot arthropathy: Until swelling is resolved and Stage III consolidation of Charcot arthropathy is achieved.
- Neuropathic ulcer: Until ulcer is healed.
Complications of Total Contact Cast
- New cast-induced ulcers (higher risk in Charcot arthropathy due to dramatic reduction in edema and increase in friction)
- Malleolar ulcers progressing to osteomyelitis
References:
- Guyton, Gregory P MD. The Total Contact Cast: Indications and Technique. Techniques in Foot & Ankle Surgery 3(3):p 186-191, September 2004. | DOI: 10.1097/01.btf.0000137730.53769.7b
- The Surgical Management of the Diabetic Foot and Ankle edited by Dolfi Herscovici, Jr.
- Khan MJ, Stoupine A, Farha K, Kim JH, Klinoubol P. The Custom Total Contact Cast to Offload Foot Ulcers in the Presence of Biomechanical Deformities: A Case Report. Wound Manag Prev. 2021 Mar;67(3):12-20. PMID: 33788771.
- A Helpful Primer On Total Contact Casts (hmpgloballearningnetwork.com)