Schirmer’s test is a measurement of tear production, devised by the German ophthalmologist Otto W.A. Schirmer. Originally, Schirmer used blotting paper to collect tears elicited by one of the 3 methods of stimulating lacrimation:
- Inserting the strip of paper itself
- Irritating the nasal mucosa after the cornea had been anesthetized
- Having the patient look into the sun
Indication: Evaluation of dry eye (Measures aqueous tear production)
Mnemonic:
Test 1 measures 2 things.
Test 2 measures 1 thing.
Test 3 measures Nose thing.
Types:
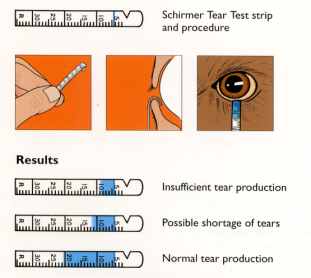
1. Schirmer I (without anesthetic): measures baseline and reflex tear secretion
- function of main lacrimal gland, whose secretory activity is stimulated by the irritating nature of filter paper
2. Schirmer II (with anesthetic): measures baseline secretion
- function of accesory lacrimal glands (the basic secretors)
3. Schirmer III (without anesthetic): with nasal irritation
- nasal mucosal stimulation represents a maximal secretory stimulation for the lacrimal glands and can thus reveal the maximal secretory capacity of the lacrimal glands.
According to some authors: Schirmer I is divided into a. without anesthetic and b. with anesthetic. While Schirmer II represents test with nasal irritation.
Materials required: 5 X 35 mm of Schirmer’s strip or Whatman filter paper no. 41
Procedure:
- The eye is gently dried of excess tears
- The schirmer strip is folded 5 mm from one end and kept in the lower fornix at the junction of lateral 1/3 and medial 2/3 (do not touch cornea or lashes)
- The patient is asked to close the eyes.
- Tears in the conjunctival sac will cause progressive wetting of the paper strip.
- After 5 minutes, the filter paper is removed and the distance between the leading edge of wetness and the initial fold is measured, using a millimeter ruler.
Normal: >15 mm
Mild-moderate Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS): 5-10 mm
Severe KCS: <5 mm
<10 mm is considered abnormal in Schirmer 1 and <5 mm in Schirmer 2
Causes of KCS:
- Idiopathic
- Congenial alacimia
- Xerophthalmia
- Lacrimal gland ablation
- Sensory denervation
- Collagen vascular disease: Sjogren syndrome, SLE, RA

The above test types have some disagreements with what is written on “2019-2020 BCSC 08 External Disease and Cornea” books