Energy Requirement
1. For a child with normal body weight:
- 100 Kcal/kg for 1st 10 kg
- Add 50 Kcal/kg for next 10 kg
- Add 20 Kcal/kg for body weight additional to 20 kgs
2. By age:
- For ≤ 1 year: 100 Kcal/kg/day
- Every additional years till puberty: Add 100 Kcal/year
Adequacy of feeding:
1. Breastfeeding:
- Child gaining weight
- Sleeps adequately between feeds with minimum interval of 2-3 hours between feeds
- Passes urine 6-8 times per day
2. Complementary feeds:
- 6-12 months: 3 times per day if breast-fed and 5 times per day if not breastfed
- 12 months-2 years: 5 times per day
- >2 years: Family food as 3 meals/day and 2 times.day nutritious snacks between meals
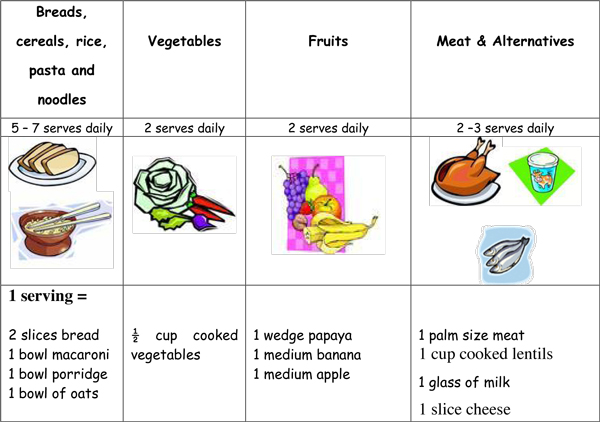
Calories provided by common foods:
Following servings of each food provides approximately 100 Kcal:
| Amount | Cooked measure | |
| Cereals | 30 gm | 1 katori or 2 chapatis |
| Pulses | 30 gm | 1 katori |
| Vegetables | ||
| Leafy | 200 gm | 1.5 katori |
| Roots | 100 gm | ¾ katori |
| Others | 300 gm | 2 katori |
| Nuts | 15 gm | |
| Fruits (Pulpy fruits) | 125 gm | 1 medium size (raw) |
| Cow’s milk | 150 ml | ¾-1 cup |
| Egg | 1 ¼ | 1 ¼ |
| Meat | 80 gm | 2 big pieces |
| Sugar | 25 gm | 5 tsp |
| Butter | 15 gm | 3 tsp |
| Oil | 10 gm | 2 tsp |
| Sago seeds (Sabudana) | 30 gm | 1 medium katori (cooked) |
Assessment of Nutrition:
The 24-hour recall is the most commonly used method of obtaining information about a child’s intake and is useful as a screening tool. Parents/caregivers are asked to describe the types and amounts of food eaten by the child in the previous 24 hour period. This may not represent a typical day’s intake, and thus, the recall may not accurately describe a child’s nutrient intake.