An inverted tendon reflex refers to the elicitation of the movement opposite to that normally seen when the reflex is elicited.
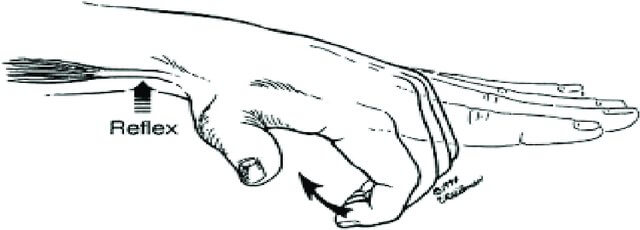
Mechanism of Inverted Reflexes
A lesion which simultaneously affects:
- A root or roots: interrupting the local reflex arc, and
- The spina cord: damaging the corticospinal tract which supply segments below the arc.
This leads to 2 components:
- Absence of the contraction of muscle tapped
- Hyperactive response of the muscle subserved by a lower spinal segment
Mechanisms of hyperactive response:
- Central mechanism:
- Babinski/Dejerine theory: reflex irradiation to a lower level by a central mechanism
- Walshe theory: emergence of an alternative motor response or, as it were, a replacement of one reflex by another
- Dietrichson/Landau/Clare theory: increase in alpha motoneuron excitability exists in upper motor neuron lesion
- Peripheral mechanism:
- Teasdall/Magladery and Lance/de Gail theory: irradiation of myotatic reflexes is not secondary to intraspinal spread but is due instead to a ‘peripheral’ mechanism attributed to the stimulation of spindles of the muscles involved due to heightened sensitivity of the spindles (Lance, 1965; Lance and de Gail, 1965).
Types of Inverted Reflexes
1. Inverted supinator reflex:
- Level of pathology: C5/6
- Positive response: Flexion of fingers and extension of elbow rather than elbow flexion when eliciting the supinator (brachioradialis) jerk.
2. Paradoxical triceps reflex:
- Level of pathology: C7
- Positive response: Flexion of elbow rather than extension when eliciting the triceps jerk.
3. Inverted knee jerk:
- Level of pathology: L2/3/4
- Positive response: Flexion of knee (hamstring contraction) rather than knee extension when eliciting the knee or quadriceps jerk.
References:
- A Dictionary of Neurological Signs By A.J. Larner
- Estanol BV, Marin OS. Mechanism of the inverted supinator reflex. A clinical and neurophysiological study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Sep;39(9):905-8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.9.905. PMID: 1086890; PMCID: PMC492480.