Syringe Preparation:
- Size: 1 ml
- Needle: 25 G 16 mm
- Steroid: 0.5 ml 20 mg triamcinolone or methylprednisolone
- Local anesthesia: 0.5 ml 1% lidocaine
- Volume: 1 ml
Position:
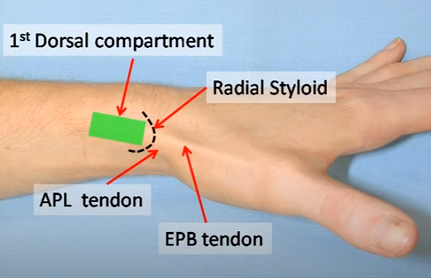
Comfortably seated with neutral forearm rotation with radial styloid facing upwards – position the wrist in slight ulnar deviation.
Technique:
- Identify tendons: Thumb extension and abduction makes tendon readily visible
- Relax the tendons for injection
- Site of injection: Between 5-10mm proximal to the tip of the radial styloid, between the two tendons, through the retinaculum, within the sheath.
- Angle: 15-20 degrees
- If the needle is withdrawn while injecting very gently, then a point should be reached where fluid between 5-10mm proximal to the tip of the radial styloid, between the two tendons, through the retinaculum, within the sheath flows freely, indicating that the needle tip has left the tendon and is within the sheath.