History
- Discovered by Johann Hoffmann in 1904.
- Originally described in literature by Hans Curschmann in 1911 and labeled the reflex as “Hoffmann’s sign”. 1
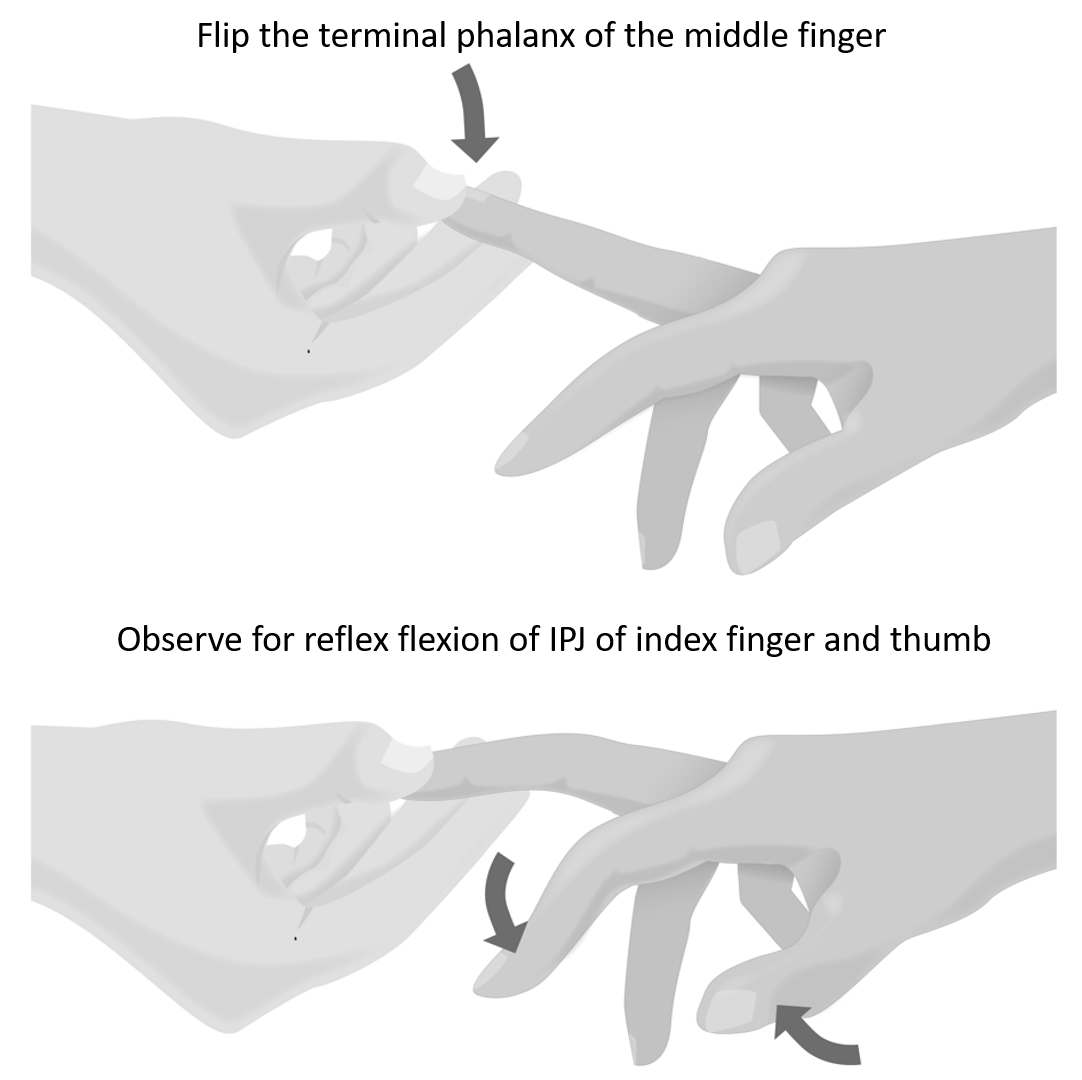
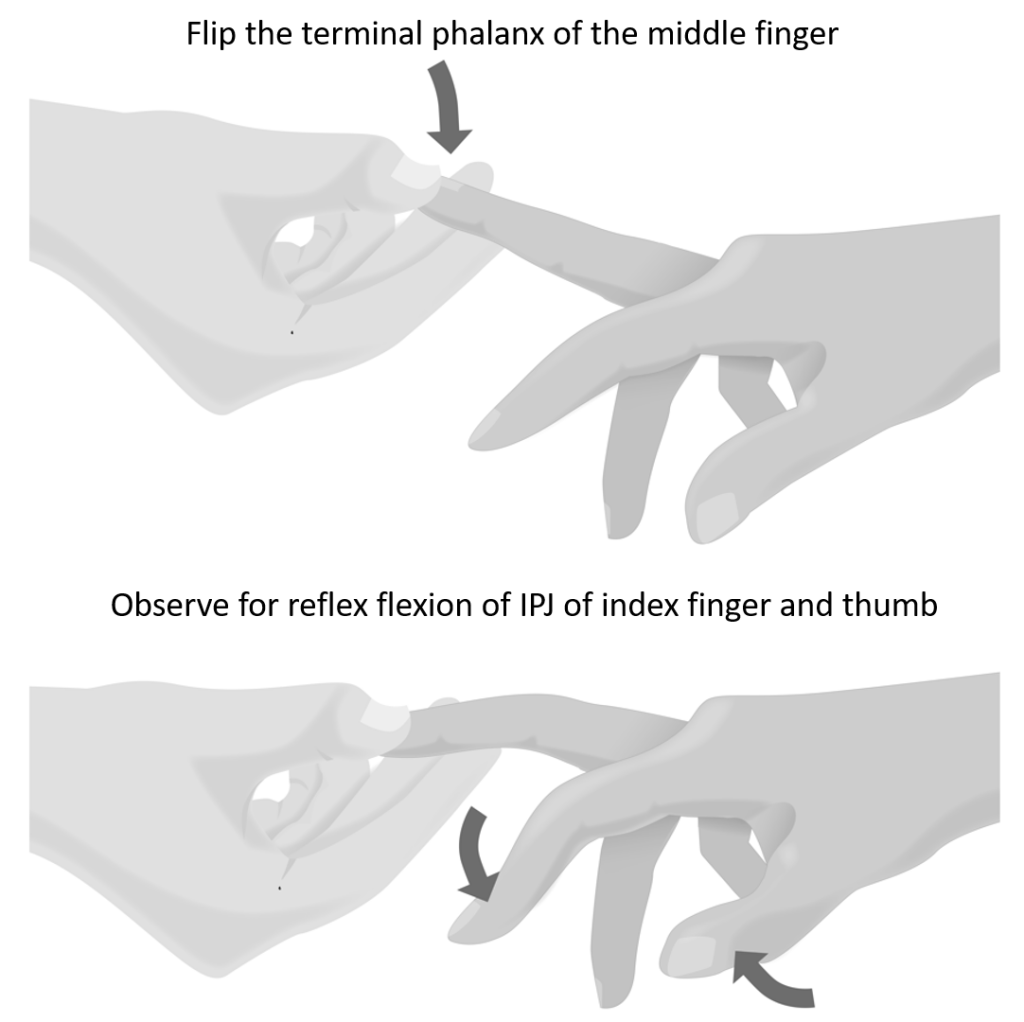
Method of Eliciting Hoffmann’s Reflex
- Technique: Flip the fingernail of the middle finger
- Positive Hoffmann’s sign: Reflex contraction (flexion) of ipsilateral interphalangeal joints of the thumb and index finger
- Extension of the neck during the test increases its sensitivity.
- Dynamic Hoffmann’s sign: Positive Hoffmann’s sign after repeated active flexion and extension of neck as tolerated in a patient with initial negative test. 2
Mechanism of Positive Hoffmann’s Reflex
Sudden stretch of the finger flexors causes involuntary finger flexor contraction due to activation of a monosynaptic stretch reflex.
Exaggeration of the reflex is caused by hyperreflexia in the setting of upper motor neuron dysfunction.
Upper motor neuron lesions cause an increase in gamma motor neuron activity and a decrease in inhibitory interneuron activity, resulting in a state of hyperexcitability of alpha motor neurons. 3
Clinical Significance
- Observed in 2/3 patients (~67%): with cervical myelopathy with positive cord signal changes in MRI.
- False positive: 3% 4
- It does not indicate the severity of the cervical myelopathy but does localize it to the C5/6 level or higher.
- Hoffmann’s sign may become negative following successful decompressive surgery. 5