Synonyms: Gower’s maneuver, Myopathic walking, Butt-first maneuver
Identifying Gower’s sign
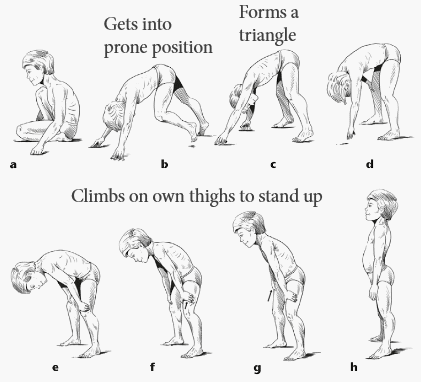
To check for Gower’s sign, place the patient in the supine position and ask him to rise. A positive Gower’s sign – an inability to lift the trunk without using the hands and arms to brace and push – indicates proximal muscle weakness. 1
From the lying position, the patient rolls to the kneeling position, pushes on the ground with extended forearms to lift the hips and straighten the legs, so forming a triangle with hips at the apex and hands and feet on the floor forming the base. The hands are then used to push on the knees and so lift up the trunk (climbing upon yourself). 2
Patho-mechanics of Gower’s sign
With most of the trunk weight resting on the extended arms, they push the body backward to shift the weight of the trunk over the extended legs. To extend the hip, the child places their hands onto the knees and walks the arms up the thighs until upright. Children with mild disease may not even need a hand on the knee as they are able to bend at the hips once the knees are extended. 3
Causes of Gower’s sign
Gower’s sign is typically seen in cases of pelvic muscle weakness or proximal muscle weakness.
- Muscular dystrophies
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
- Proximal ascending pseudomyopathic diseases
- Polymyositides
- Discitis
- Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
Importance of Gower’s sign
A child continuing Gower’s maneuver after 3 years of age is likely to have a neuromuscular condition.
For lumbar spine instability:
- Specificity: high (100%)
- Sensitivity: moderate (56%) 4
Other Eponymous Conditions not to be confused with
Gowers’ phenomenon in Epielpsy – “seizures beget seizures” (can be said as a historic model for kindling theory).
Gowers’ distal myopathy – Laing early onset distal myopathy
Gowers’ solution – in the treatment of migraine
Gowers’ anterior spinocerebellar tract
3 Gowers’ signs:
- Pain along the compressed sciatic nerve on passive dorsiflexion of the foot
- Irregular contraction of the pupil in early Tabes (cf Argyll Robertson)
- Climbing up the thigs sign in Duchenne dystrophy