Synonyms
Tache noire
Definition of Eschar
An eschar is a local skin lesions coated by a thick coagulated crust or slough that usually results from burn or infection.
Causes of Eschar
- Tick bite fever
- Scrub typhus
- Anthrax
- Tularaemia
- Spider bites
- Disseminated fungal infection
- Post-burn
Diagnostic Clues
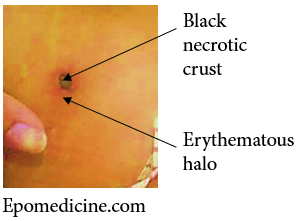
Cigarette-burn Sign
In scrub typhus, the eschar begins as a small papule, then enlarges, undergoes central necrosis, and eventually acquires a blackened crust with an erythematous halo that resembles a cigarette burn. The eschar resembling ‘cigarette burn mark’ is seen in 95% of cases and is most important diagnostic clue of scrub typhus 1.
Regional lymphadenopathy
Eschars are usually painless and non-pruritic and have great potential to go unnoticed and missed by the physicians. When an eschar is noticed, other regions of the body must be searched for the similar lesion and the draining lymph node region must be examined. A painful lymph node enlargement accompanies in several infections.