Central nervous system (CNS) examination is the most difficult thing to complete within a time limit during final exam and the dilemma is that, most of time the CNS is what is kept as a long case. Examiners love judging you on the basis of CNS case because:
1. CNS is maths and science – it needs a lot of logic and understanding
2. CNS is the most methodological system
3. CNS is the most lengthy and only organized students can complete examination in time
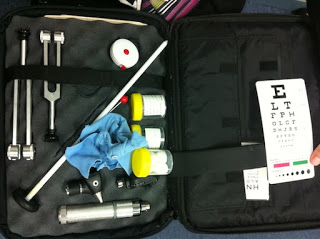
Without a proper planning and preparation for CNS case, you will seldom be able to complete it in time. An incomplete examination is one of the common cause of failure in PG, MBBS though can be excused sometimes. I will not try to be a Guru, rather I will only share our experience, how we practiced and completed the examination 1 minutes before 20 minutes in the final, thus assuring a fair results.
Which Book to Refer?
Standard Standard Standard! Always the books should be standard.
We did not prefer Hutchinson, despite of the hype it has had all the time. Macleod is much better tool and with videos available on youtube, it is the key.
Being a Pediatrician, you must also review the Books- Meherban Singh and Piyush Gupta Bedside books.
What you need?
1. 3 friends minimum, maximum 4.
2. Each must be ready to volunteer.
3. Each must be ready to be the Judge or critic
4. A neurological Kit- complete.
5. Watch the Macleod videos and read the book
6. A pattern in mind or written on a paper.
How to proceed?
1.Before exam , going to bedside and doing it was neither time friendly nor easy. It only caused us to lose time and get more anxious. So we decided to practice at hostel.
2. Discuss and create a pattern or sequence to follow, which will be the protocol you all will follow till exam.
Eg. For HMF (Higher Mental Function):
A- appearance
B- behaviour
C- conscousness
D-Delerium
E-Emotion
I- Intelligence
J- Judgement
L- Learning
M-Memory
O-Orientation
S- Speech
What questions you will ask to assess? For judgement – Fire in the house, Post a letter (Read Hutchison for these questions once – Standard questions)
3. One volunteers as patient
4. Other examines
5. The Onlooker and critic sets time – initially 20 minutes of just cranial nerves, Higher mental functions each
6. Start practising, you may make a lot of mistakes.
7. In the end, the critic tells you all you have done wrongly. This way both will remember the mistakes and will not repeat it.
8. With practice , your speed will boost on each another time. And as you do, your spine picks the pattern and you will get fluency with steps.
Try to completely learn normal examination first then you can move to Diseases and deficits.
The Sequence of examination is:
1. Higher Mental Function
2. Cranial Nerves Examination
3. Motor system examination
4. Sensory System examination
5. Cerebellar signs examination
6. Gait
7. Abnormal movements
8. Skull and spine
9. Autonomic nervous system.
Repeating all the theory is out of scope, as books are always best for learners.
Hope it would be of help in a way for medical students.
The Formula is – Practice , Practice and Practice : keep examination videos in cellphones.
Courtsey: Dr Binit Kharel, Dr Nischal Maskey, Dr Arif Mohd. This was exclusively our experience.

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.