Definition of clonus
Clonus is a rhythmic sustained involuntary muscular contraction (generally 5-8 Hz) evoked by sudden passive stretch of the muscle and tendon.
- Unsustained clonus (≤5 beats): may be physiological
- Sustained clonus (>5 beats): regarded as abnormal
Eliciting Clonus
Clonus is commonly elicited in gastrocnemius (ankle clonus). Other sites where clonus can be elicited are quadriceps (patellar clonus), finger flexors and jaw.
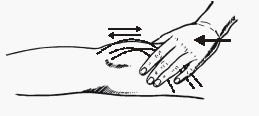
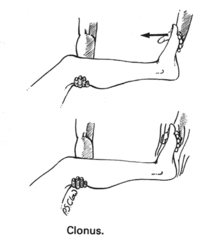 1. Ankle clonus:
1. Ankle clonus:
- Support the patient’s leg, with both the knee and ankle resting in 90° flexion.
- Briskly dorsiflex and partially evert the foot, sustaining the pressure (do not leave the hand after dorsiflexing).
- Clonus is felt as repeated beats of dorsiflexion/plantar flexion.
 2. Patellar clonus:
2. Patellar clonus:
- The legs should be extended and relaxed.
- Examiner grasps the patella between index finger and thumb and executes a sudden, sharp, downward thrust, holding downward pressure at the end of the movement.
- Clonus is felt as repeated upward and downward movement of the patella.
Pseduoclonus or False clonus
Pseduoclonus is observed in psychogenic disorders – it is poorly sustained and irregular in rate, rhythm and excursion. When eliciting, ankle clonus – true clonus can usually be stopped by sharp passive plantar flexion of the foot or great toe while the false clonus remains unaltered.
Causes of Clonus
1. Hyperreflexia in Upper Motor Neuron Lesion (UMNL)
- Cerebral infarction/hemorrhage
- Lacunar infarction – posterior limb of internal capsule
- Multiple sclerosis
- Spinal cord injury
- Space occupying lesions (AVM, abscess, tumor)
2. Serotonin syndrome
Mechanism of Clonus
1. Clonus in UMNL:
Upper motor neuron lesions cause an increase in gamma motor neuron activity and a decrease in inhibitory interneuron (renshaw cell) activity, resulting in a state of hyperexcitability of alpha motor neurons. Upper motor neuron lesions cause contralateral hyperreflexia if present above the pyramidal decussation (e.g. pons, medulla, posterior limb internal capsule, motor cortex) and ipsilateral hyperreflexia if the lesion is present below the pyramidal decussation (e.g. spinal cord).
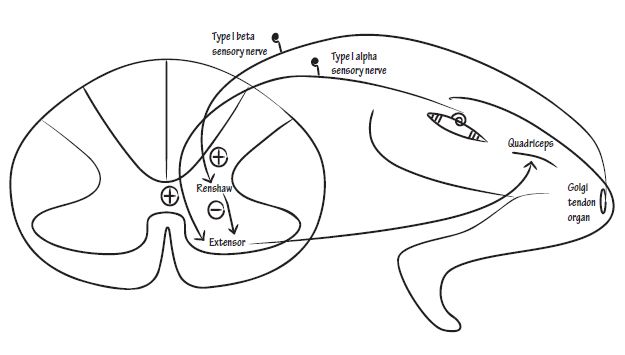
For ankle clonus – the sudden stretch of gastrosoleus muscle elicits a contraction essentially analogous to a stretch reflex that causes a contraction with resultant plantar flexion of the foot. The foot goes down. This contraction increases tension in the Golgi tendon organs in the gastrosoleus tendon, sending a volley of impulses via the Ib fibers that then inhibit the contraction of the gastrosoleus and facilitate contraction of its antagonist, the tibialis anterior muscle. The foot goes up. This in turn passively stretches the gastrosoleus, and the cycle is repeated.
2. Clonus in Serotonin syndrome:
It likely results from an excessive agonism of 5-HT receptors in the peripheral nervous system, resulting in sensitization of monosynaptic stretch reflexes.