A. Synoynms: Hydrothalmos, Congenital glaucoma
B. Definiton: Buphthalmos is the enlargement of the eye due to congenital glaucoma.
C. Classification:
- True congenital glaucoma (Increased intraocular pressure (IOP) during intrauterine life)
- Infantile glaucoma (Birth to 3 years)
- Juvenile glaucoma (>3 years)
D. Pathogenesis:
- Isolated trabeculo-dysgenesis: Absence of angle recess; iris inserted directly into surface of trabeculum
- Revealed by Gonioscopy as Barkan’s membrane
- Flat or concave iris insertion
E. Clinical features:
1. Corneal haze: due to corneal epithelial/stromal edema
- With lacrimation, photophobia and blepharospasm
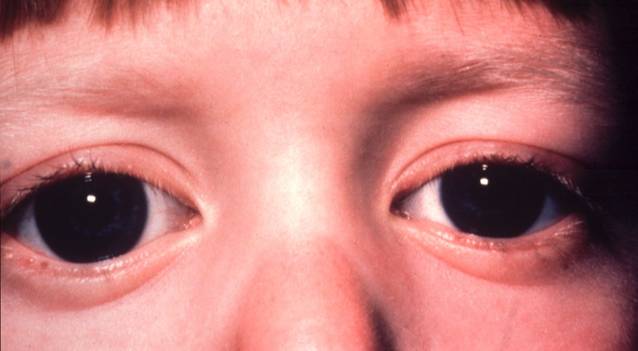
2. Buphthalmos: In birth to 3 years
- Enlarged eye due to stretching when IOP increases
- Stretched sclera – thin and translucent (appears blue)
- Deep Anterior Chamber (AC)
- Zonular fibers stretch and lens subluxate
- Axial myopia can cause amblyopia if untreated
3. Haab striae:
- Horizontal or circular curvilinear lines
- Healed breaks in Descemet’s membrane
4. Optic disc cupping may regress if treated early:
- Cup to disc ratio > 0.3
- Scleral canal enlarges
- Lamina cribrosa may bow posteriorly
Possible causes of vision loss in Buphthalmos:
- Optic damage
- Corneal scarring
- Amblyopia
- Cataract
- Lens subluxation
F. Differential diagnoses:
1. Cloudy cornea:
- Mucopolysaccharidoses
- Birth trauma
- Congenital hereditary endothelial dystrophy
- Sclerocornea
- Keratitis (Rubella)
2. Megalocornea (Myopia)
3. Lacrimation (Nasolacrimal duct obstruction)
4. Secondary infantile glaucoma:
- Retinoblastoma
- Juvenile Xanthogranuloma
- Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous (PHPV)
- Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
- Trauma
- Ectopia lentis
G. Evaluation:
- IOP with Perkin’s tonometer/tonopen
- Corneal diameter (to rule out megalocornea)
- Gonioscopy with a koeppe lens
- Retinoscopy
- Optic disc evaluation
H. Surgical treatment:
- Medical treatment before surgery:
- Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors
- Avoid alpha 2-agonists (may cause sleep apnea and respiratory failure)
- Goniotomy, Trabeculotomy
- Trabeculectomy + Trabeculotomy
- Aqueous drainage implants
- Trans-scleral cyclophotocoagulation
I. Follow up:
- Life-long
- Appropriate refractive and amblyopia therapy
- Treatment of media opacities like corneal scars and cataracts