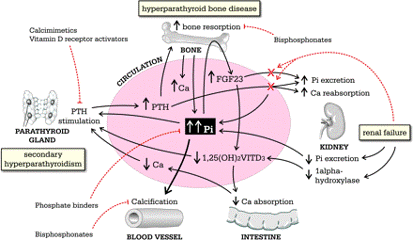
A) Cardiovascular complications 1. Exacerbation or Precipitation of CHF – Voluminous AV Fistula AV shunting → Decreased TPR → BP fall → Sympathetic stimulation & RAAS activation → Ventricular remodeling → Heart failure Several studies have investigated the cut-off fistula access flow that is associated with a higher risk of high-output cardiac failure, with results ranging…
Category: PGMEE, MRCS, USMLE, MBBS, MD/MS
Medical knowledge in bullet points with understandable language, simplified images and graspable mnemonics.
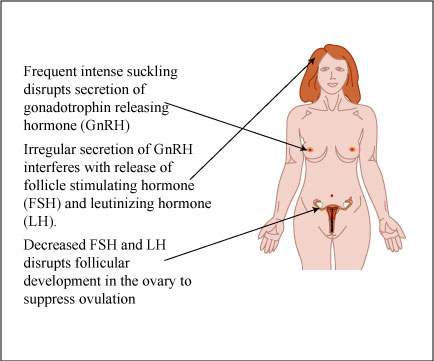
Management of Puerperium
Normal puerperium has been already discussed earlier here. A) Immediately after labor within 1 hour Blood pressure and heart rate atleast every 15 minutes Monitor amount of vaginal bleeding Palpate fundus to ensure amount adequate contractions (if relaxed – massage uterus to enhance oxytocin release) B) 1st several hours 1….
Normal Puerperium Made Simple
Definition of Puerperium: Period following childbirth during which the body tissues, specially the pelvic organs involute i.e. revert back approximately to the pre-pregnant state both anatomically and physiologically – and lasts 6 weeks or 42 days. Immediate: Within 24 hours of childbirth Early: Within 7 days of childbirth Remote: Within…
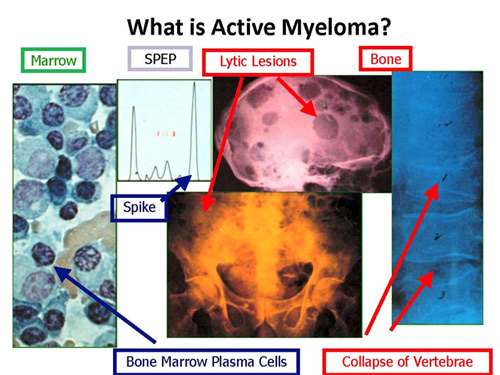
Multiple Myeloma : Quick Approach
Plasma cell dyscrasia refers to an abnormal proliferation of plasma cells that usually secrete a monoclonal immunoglobulin. A) CLINICAL FEATURES Features vary among various conditions: Mnemonic: CRAB Infection 1. Calcium increased: Hypercalcemia Nephrocalcinosis and
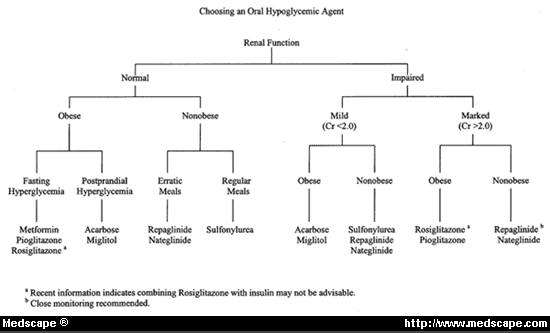
Approach to Uncomplicated Diabetes Mellitus : Simplified
A) GLUCOSE LEVEL 1. Post-prandial: 140-200 mg/dl: Impaired glucose tolerance (Pre-diabetes) Diabetes prevented with: weight loss, exercise, metformin (in high risk) ≥200 mg/dl (+ Clinical symptoms): Diabetes confirmed 2. Fasting: 100-126 mg/dl: Impaired fasting glucose (Pre-diabetes) ≥126 mg/dl (+ Clinical symptoms): Diabetes confirmed
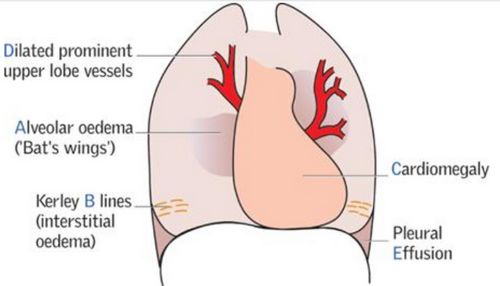
Cardiac (Heart) Failure Made Easy (Pathophysiology and Diagnosis)
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC FAILURE It is a state in which there is: a. Forward failure: inability of heart to maintain cardiac output sufficient to meet the metabolic demands of peripheral tissues AND/OR b. Backward failure: ability to do so with elevated filling pressure PATHOGENESIS OF CARDIAC FAILURE 1. Myocyte loss…
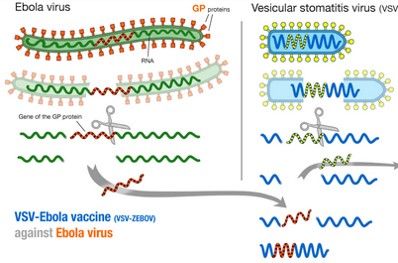
Ebola Virus Disease
Author: Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, KISTMCTH The “Red Death” had long devastated the country. No pestilence had ever been so fatal, or so hideous. Blood was its Avatar and its seal—the redness and the horror of blood. There were sharp pains, and sudden dizziness, and then profuse bleeding at the pores, with dissolution. The scarlet stains…
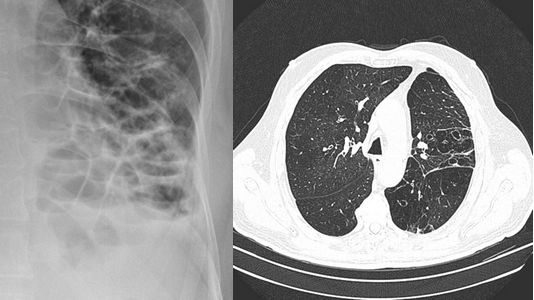
Bronchiectasis Revision Notes
DEFINITION OF BRONCHIECTASIS Bronchiectais refers to the end-stage of variety of pathologic processes characterized by abnormal, irreversibly dilated thick-walled bronchi due to destruction of elastic and muscular components of bronchial wall. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF BRONCHIECTASIS Mnemonic: CVS 1. Cylindircal (Fusiform):