Approach the patient with 9 Ps. 0-10 minutes (Possibility of Success): Anticipating difficult airway Mnemonic: LEMON approach 1. Look externally: Remember “BONES“ Beard Obesity No teeth Elderly Sleep apnea/Snoring 2. Evaluate 3-3-2 rule: Ideal dimensions for visualization of larynx 3 fingers in mouth: adequate mouth opening 3 fingers under the…
Category: Emergency Medicine
The Real Emergency Room scenarios, cases and topic reviews. Medical emergency conditions – approach to diagnosis and management.

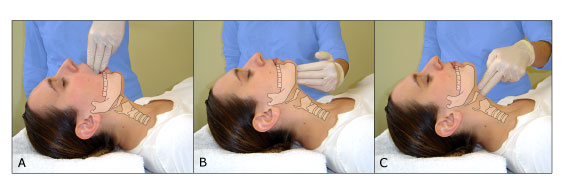
Log Rolling Maneuver : Steps
Step 1: Rescuer 1 stabilizes head and neck in neutral position without applying traction. He/she should grasp the patient’s shoulders at the neck and gently position the patient’s head betweeen the forearms. Another rescuer should apply a semirigid extrication collar. Even with the collar in place, Rescuer 1 must maintain…
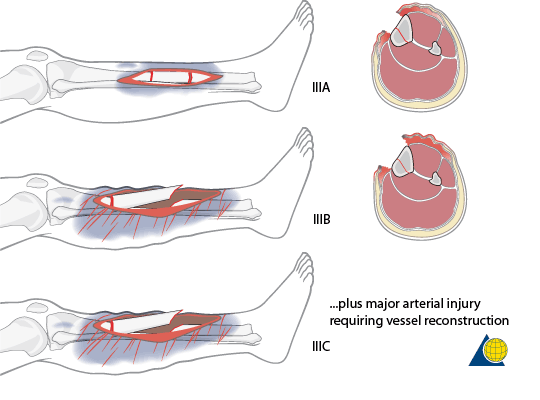
Open fractures : Mnemonics
Gustilo Anderson Classification Mnemonics:1. Parameters: ABCD’S (Area, Bone, Circulation, Dirt, Soft tissue)2. Classification: I, II, III then A, B, C Progression for grade I to III C implies a higher degree of energy involved in the injury, higher soft tissue and bone damage, and higher potential for complications. Type I:…
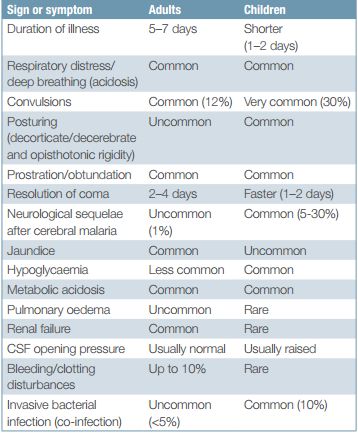
Severe Malaria : Quick revision
Criteria for Severe and Complicated Malaria Positive peripheral blood smear for P.falciparum + ≥1 of the CHAPLINS (Mnemonic) Convulsions: >2 in 24 hour Cerebral edema (Consciousness impaired) Hypoglycemia (glucose <40 mg/dl) Hemorrhage (DIC) Hemoglobinuria (Black water fever) Anemia (hemoglobin <5 gm/dl or PCV <15% in children; hemoglobin <7 gm/dl or…
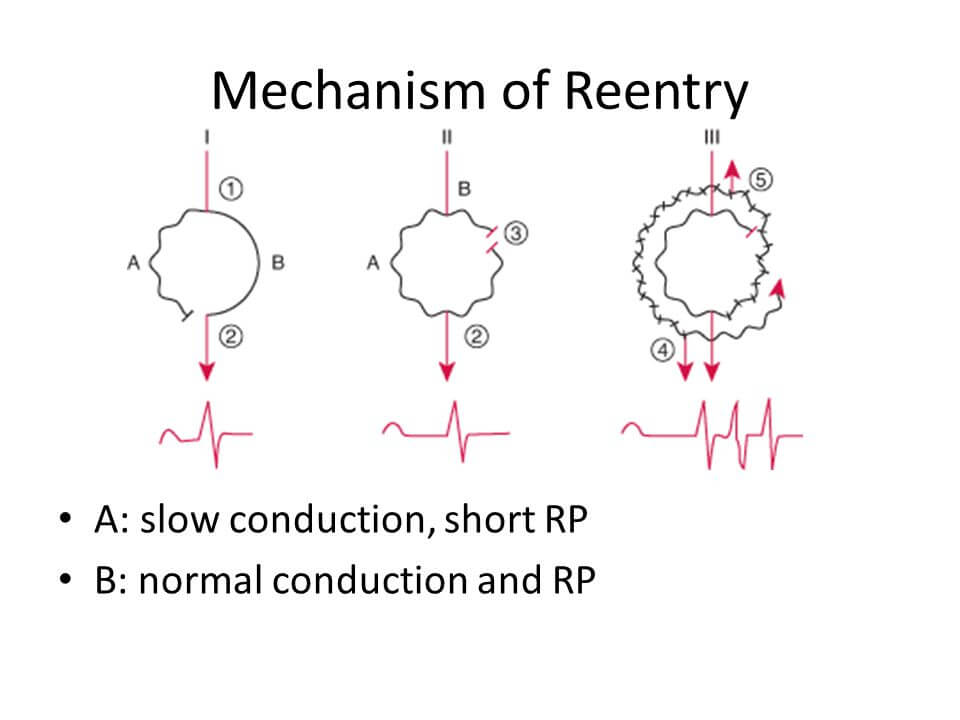
Short Approach to SVT and AVNRT management
This is an ECG from a patient who came with a complaint of palpitation: Analyze the ECG: Rhythm: Regular Heart rate: Around 170/min QRS: Around 0.08 s i.e. ≤0.1 s (narrow QRS complex) ECG diagnosis: Regular Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) Now, look for P waves – There are no P waves In…
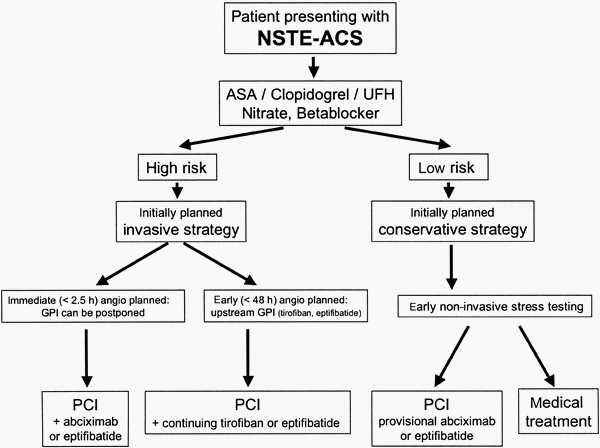
NSTEMI : Early Medical Management Pearls
Antiplatelet therapy Aspirin 2-4 non-enteric coated chewable baby aspirins (81 mg each) – buccal absorption is the fastest for platelet inhibition. Initial dose: 150 mg – 325 mg Daily dose: <150 mg For patients unable to take oral medications: Rectal suppository 325 mg Avoid in acute MI: Enteric coated preparations…
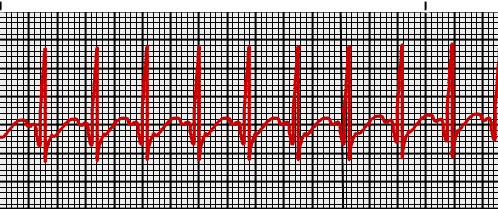
Supraventricular Tachycardia vs Sinus Tachycardia
Yesterday, I had encountered a tachycardic patient with heart rate 160/min. Somewhere in medical school, I was taught that the sinus tachycardia with heart rate >160/min must be considered as a Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). With such misinformation, it was easier for me to overlook the fact that the patient was…
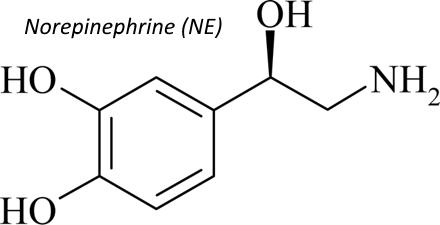
Early vs Delayed Norepinephrine Use in Septic Shock
Norepinephrine has numerous effects in sepsis including veno-constriction (increasing preload), arterial constriction (increasing systemic vascular resistance), positive inotropy, improved cardiac output, and improved renal perfusion. This addresses all the major derangements observed in cases of septic shock. It is important to realize that MAP doesn’t necessarily equate perfusion. Increasing the…