1st published in Pedchrome on February 5, 2015.
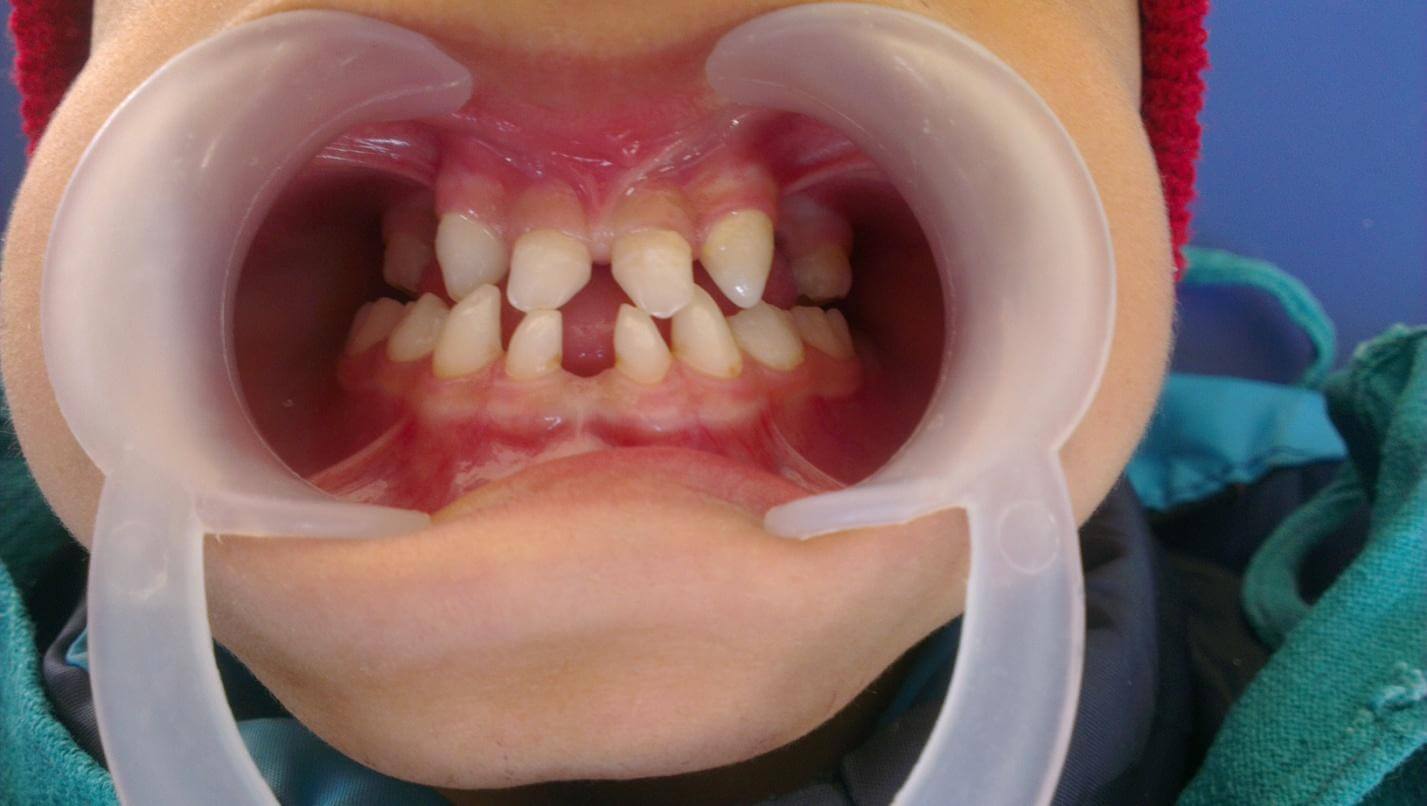
The perfect smile on a parent’s face rotates to a frown when they are informed that their child may have a smaller number of teeth than normal. The total number of teeth in the primary dentition is 20 and that in the adult dentition is 32. The parents may not be more worried about losing a tooth to dental decay than they are to know that the teeth are missing congenitally. So, when we break the news to parents about these missing teeth, they question: Where? When? How? And now what?
Dental Terminologies
Hypodontia: 1 to 6 teeth missing
Oligodontia: more than 6 teeth missing
Anodontia: complete absence of teeth
How common is it?
Congenitally missing teeth are one of the most common dental findings and is even more common than having extra tooth. It is reported to vary from 2.6 to 11.3% (excluding third molars) in permanent dentition. It is more commonly seen in permanent dentition and only about 0.5 to 0.9% baby tooth may be missing.
Causes of missing teeth
Genetic: The cause may be genetic, and the condition may run in the family. Studies have shown that in many cases, multiple genetic and environmental factors act together.
Syndromic: in certain cases, it may be found clubbed other medical conditions in the form of a syndrome. E.g., Down’s syndrome, Ectodermal dysplasia.
The most common permanent teeth to be congenitally missing are:
- Wisdom Teeth
- Second Premolars
- Upper Lateral Incisors
- Lower Central Incisors
Management
In the developmental phase of child (up to the age of 15 to 16 years) the missing tooth space is maintained by giving removable or fixed partial space maintainers are given and no permanent treatment is done.
Replacement of the missing teeth can be done by removal dentures, fixed partial dentures (bridge) or implants.
- Removable Partial Denture: is an appliance that can be put in and taken out of the mouth. It consists of an acrylic plate that holds the missing teeth.
- Bridge: it uses two or three adjacent teeth for support and replaces the missing teeth. The missing as well as supporting teeth are given crowns which are interconnected like a bridge.
- Implant: An implant replaces the missing tooth with a metal root like structure that integrates with the jawbone and a crown is put on top for a natural tooth like appearance.
Conclusion
Congenitally missing teeth is not as rare as you may have guessed. The causes are varied, but there are multiple treatment options available. So, if you or your near ones are facing such a problem, please visit a dentist as soon as possible.

Dr. Parajeeta Dikshit is a Professor, Dept of Pedodontics and Preventive Dentistry (Pediatric Dentistry) at Kantipur Dental College teaching hospital and research center, Basundhara, Kathmandu and Consultant Pediatric Dentist at Smile Square Dental Care Center, Maharajgunj, Kathmandu.