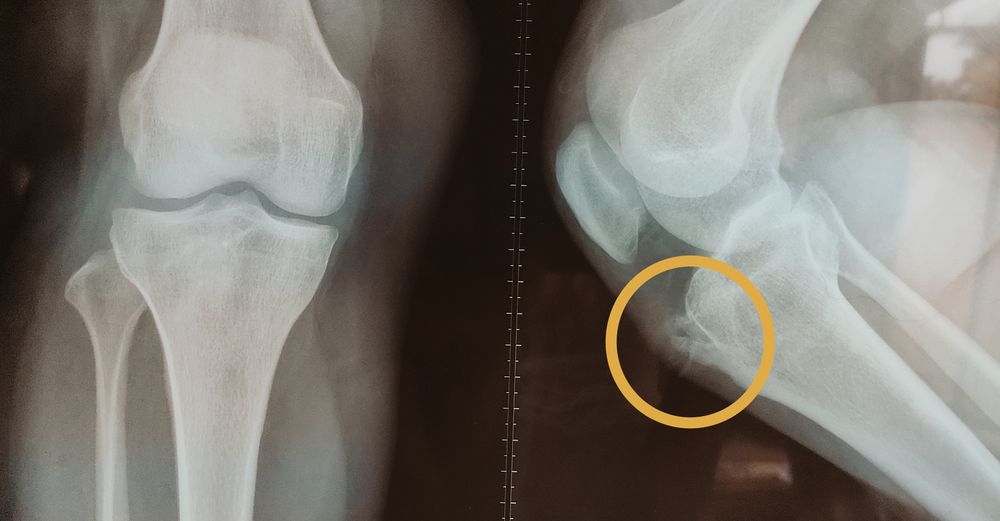
Synonym: Adult onset tibial tubercle exostoses History: Pain over anterior surface of upper tibia Pain during running, jumping, squatting, kneeling and descending stairs Usually no history of trauma, anterior knee pain or Osgood-Schlatter disease Physical examination: Tenderness over hypertrophic tibial tubercle Quadriceps tightness (Ely’s test) X-rays: AP, lateral and tangential…
Author: Dr. Sulabh Kumar Shrestha, MS Orthopedics
Modified Ashworth Scale for Spasticity : Mnemonic
Ashworth scale tests resistance to passive motion about a joint with varying degrees of velocity. Modified Ashworth Scale (Bohannon and Smith, 1987) has 1+ grading between grades 1 and 2. Modified Ashworth Scale (Ansari et.al., 2006) has been described here. Mnemonic: Ashworth is a juggling clown 0 : 0 is…

DIY Vac Dressing for Wounds
Pre-requisites for Vac Dressing Components of Vac Dressing 1. Pump for Negative Pressure: In a study, 3 closed suction drainage systems were studied – Davol Reliavac 400 Evacuator, Jackson-Pratt Closed Wound Suction Drainage System, and Snyder Hemovac 400. In all three systems, maximal negative pressures (-71 to -175 mm Hg)…

Demonic Possession From The Eyes of Science
Several cultures and religions round the globe carry a belief that the humans are capable of being possessed or inhabited by spirits and even the goddess. The ministry of different religions have formulated a set of procedures called exorcism for casting or expelling out the spirit. It comprises of but…
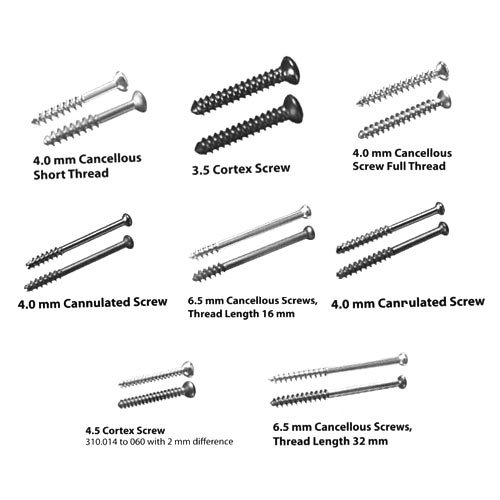

Orthopedic Screw Insertion Mnemonic
Don’t Marry Too Soon DRILL Choose the correct drill bit Insert the drill bit correctly in the chuck Tighten the chuck sufficiently Start the drill home perpendicular to the surface Maintain adequate pressure Maintain the proper direction Irrigation with normal saline should be commenced simultaneously with drilling Keep the drill…
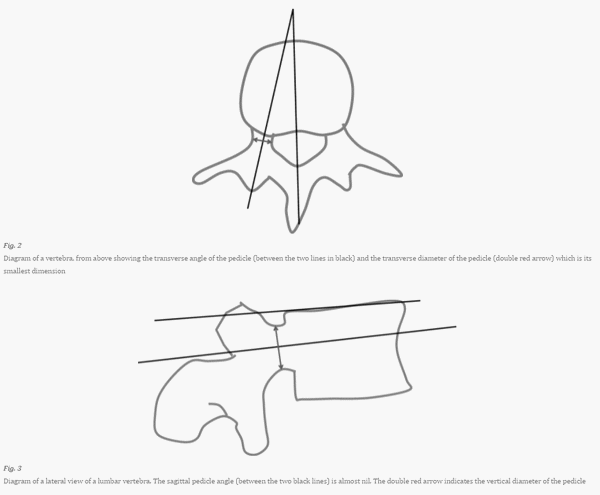
Pedicle Screw Insertion Simplified
Anatomy of Vertebral Pedicle Width (narrowest transverse diameter): Narrowest at T4-T5 (4-5 mm) Above and below this level, the width gradually increases to almost double at T1 and T11 (8 mm) Narrowest for lumbar at L2 (two for tiny; 2 X 3 = 6 mm) Increases gradually to L5 (5…
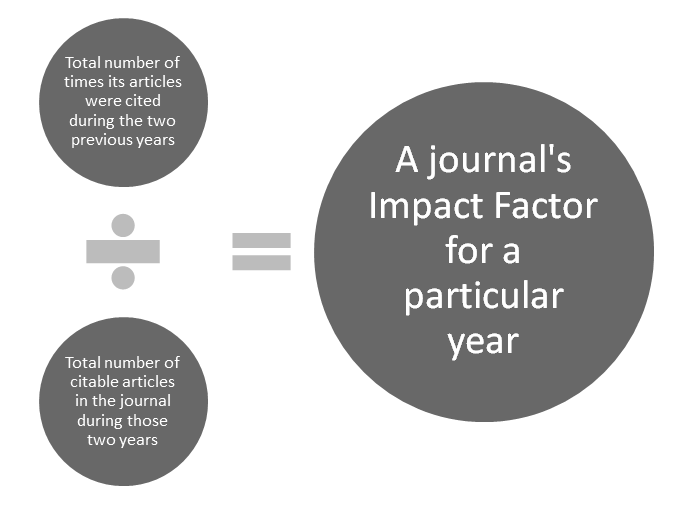
Modified Impact Factor of Journals
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a sciento-metric index calculated that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal. It is calculated as: IFᵧ = Citationsᵧ/[Publicationsᵧ₋₁ + Publicationsᵧ₋₂] For example, in 2017, there were 74090 citations of 2015 and 2016 Nature…
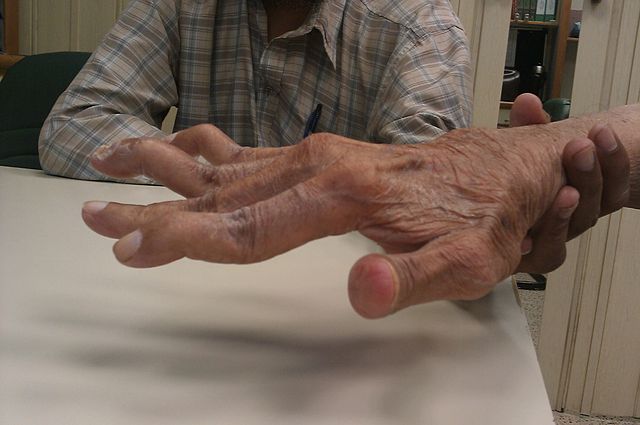
Boutonniere and Swan neck Deformity – Pathophysiology
Understanding of the Boutonniere and Swan neck deformity requires clear concept of the finger extensor apparatus, which has been discussed here. The extrinsic extensor tendons trifurcate giving a central slip which attaches to the middle phalanx base and two lateral slips which join with lateral band (formed by intrinsic muscles…