As you have already read Systematic way of Reading Chest Xrays and few other xray lessons in epomedicine classes. Here is you first Skill test. We will give you few case scenarios and Xray and you need to answer the following. Self Assessment Test: I. A neonate on Mechanical ventilator needing…
Author: Epomedicine
Chest Xray – Approach to hilum
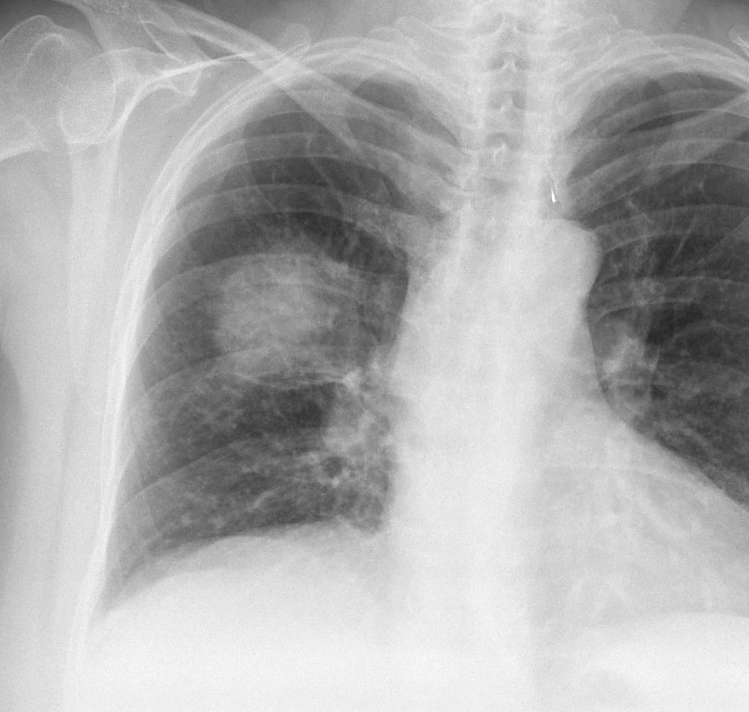
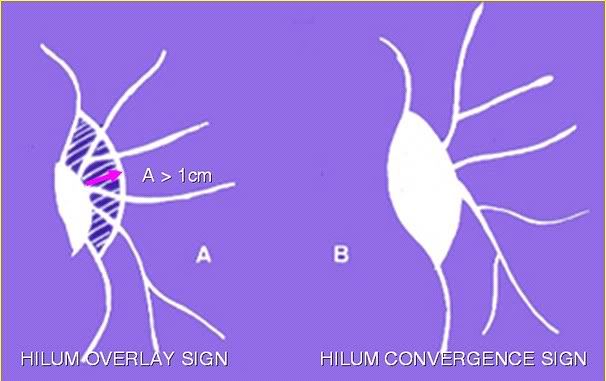
Hilum in human anatomy refers to the depression where structures such as blood vessels and nerves enter an organ. The structures contributing to hilar shadows in a Chest X-ray are: Major: Pulmonary artery and veins Minor: Fat, Lymph nodes and Bronchial walls Normal Hilum: Position: Left hilum is slightly higher…
Chest X-ray – Pleural Effusion
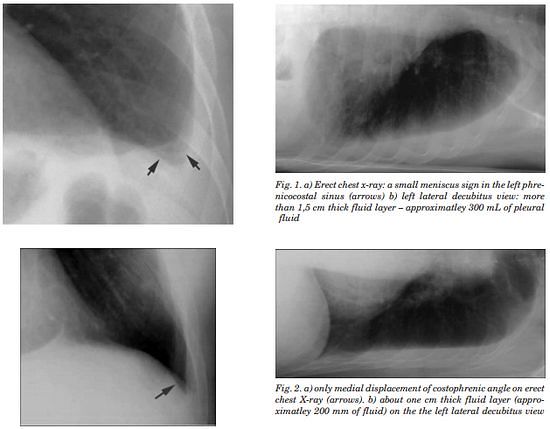
Pleura is a mesothelial lined sac that envelopes the lungs and comprises of 2 membranous walls i.e. visceral pleura and parietal pleura that encloses pleural space filled with pleural fluid. Pleural space contains about 0.3 ml/kg body weight of pleural fluid. The pleura is not visible on a normal CXR…
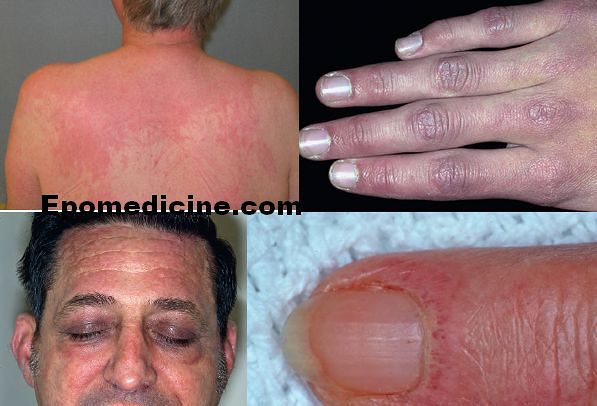
Skin signs of Dermatomyositis: Heliotrope rash, Grotton papules and Shawl sign
Dermatomyositis is a connective tissue disorder characterized by chronic inflammation of voluntary muscles and skin. It is more common in women and the age of onset is 50-70 years. A) Heliotrope Rash: It is a macular, confluent, purple or purple/red rash over both eyelids and periorbital tissue present with or…
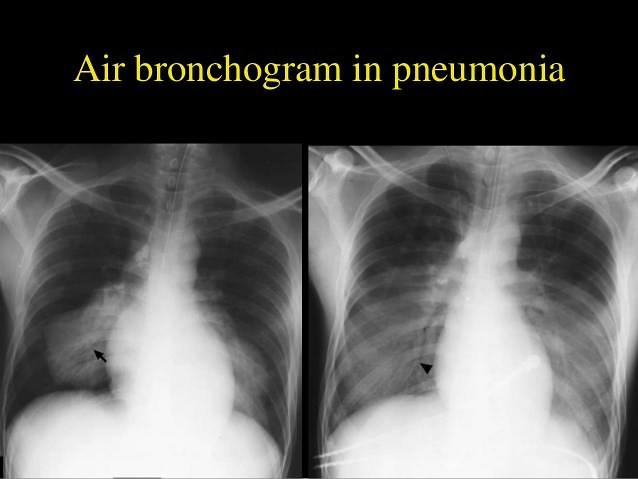
Chest X-ray: Alveolar vs Interstitial Disease
Interstitium is the scaffolding that supports the alveolar walls and surrounds both the alveoli and the terminal bronchioles. Neither alveoli nor interstitium is visible on a chest X-ray when normal. It is necessary to analyze whether the pattern of diffuse opacification in the lung field is alveolar or interstitial. Terms:…
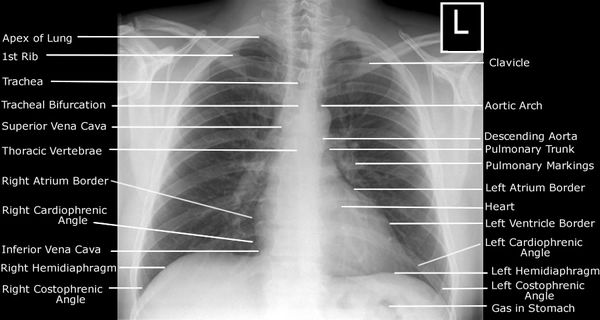
Systematic Approach to Frontal Chest X-ray
To make an appropriate diagnosis through a chest radiograph, it must be analyzed in a systematic manner. One of the common mistakes that students do is to miss the regions that needs to be looked for – commonest being the rib fractures. A mnemonic has been devised for this purpose:…
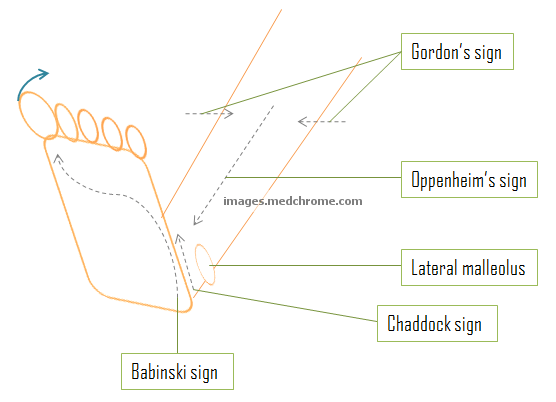
Pathological reflexes – Variations of Babinski
Normally, the pathological reflexes are not evident because they are suppressed by cerebrum at brainstem or spinal cord level by 6 months of age. Importance: Up-going (dorsiflexion) toe can be elicited at various sites and all indicated Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) lesion. Use a blunt-pointed object like fingernail or tip…
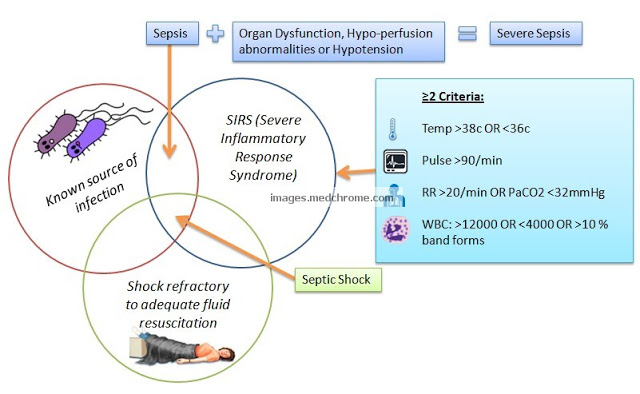
The Continuum: SIRS, Severe Sepsis and Septic Shock
SIRS criteria are mostly used as a screening tool to identify patients that may need further workup for sepsis and severe sepsis. In the emergency department it is a triage tool that helps determine patient acuity and identify patients that are potentially septic and in need of further screening. Septic…