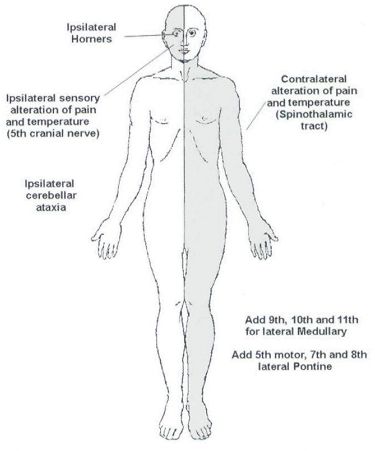
Before proceeding into the disease itself, let’s review – relevant anatomy of the medulla with a simple mnemonic. The Side (lateral) part of Medulla contains 6 “S“ 1. Spinocerebellar tract Posterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters to ipsilateral cerebellum via ipsilateral inferior cerebellar peduncle Anterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters…
Tag: Anatomy
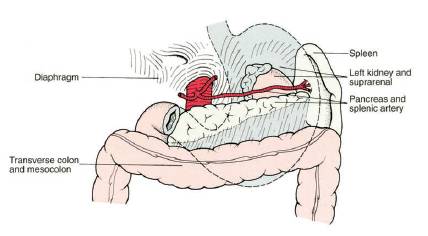
Surgical Anatomy of Stomach
GASTROESOPHAGEAL JUNCTION (CARDIA) It is the junction between esophagus and cardia of stomach Histologically: Mucosal transition from squamous to columnar epithelium Functionally: High pressure zone (Lower esophageal sphincter or LES) – Normally, LES is intraperitoneal, >2 cm long, and has a resting pressure >6 mmHg; not an anatomical sphincter but a…
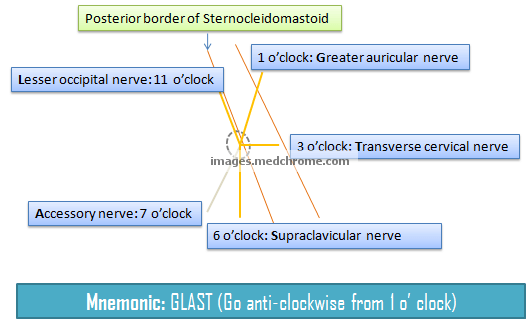
Superficial Cervical Plexus Block : Mnemonic
This is a visual mnemonic for the nerve arrangement of superficial cervical cutaneous branches of cervical plexus. This mnemonic was created only for the ease to remember and may not resemble exact anatomy. The site of injection for superior cervical plexus nerve block is the midpoint of posterior border of…
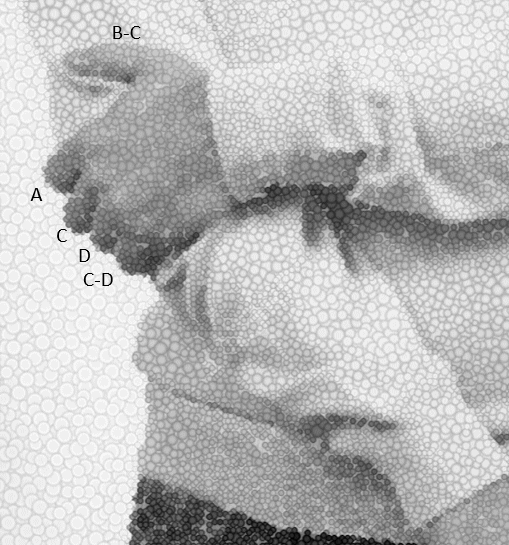
Forearm muscles : Tricks to remember
Anterior Forearm (Compartment) Muscles Total muscles: 8 (4 superficial + 1 intermediate + 3 deep) Mnemonic: Do it yourself as shown in the figure below! Place your thenar/hypothenar eminence over medial epicondyle and fan out 5 fingers with thumb resting below the 4 fingers. The 4 fingers represent superficial flexors…
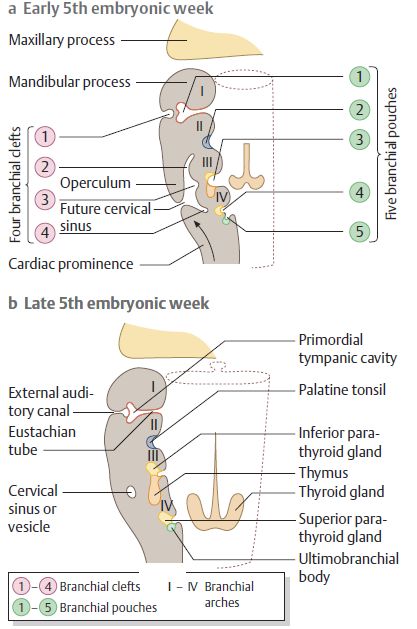
Branchial Apparatus (Pharyngeal arches and pouches) : Mnemonics
Synonym: Pharyngeal apparatus Mnemonic: CAP covers from out to in Pharyngeal arches are equivalent of gill arches in fish that develop in a cranio-caudal sequence. Derivatives of Pharyngeal or Branchial Apparatus Pharyngeal cleft Pharyngeal arch Pharyngeal pouch Ectoderm Mesoderm Neural crest Cranial Nerves Arteries Endoderm 1st External Auditory Meatus…
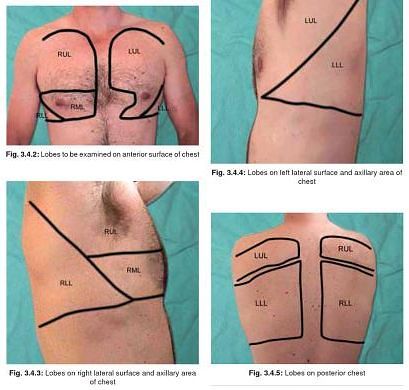
Respiratory Examination – Relevant Anatomy and Physiology
1. Division of Airway: Extrathoracic (Upper) airway: Nose to Upper trachea Intrathoracic (Lower) airway: Lower trachea to Alveoli and lungs Note: Vocal fold is also regarded as the demarcating line between upper and lower respiratory tract 2. Angle of Louis: Junction of body of sternum to manubrium (2nd costal cartilage…

Applied Anatomy of Submandibular Salivary Gland
Synonyms: Submaxillary gland (SMG), Mandibular gland Definition: Submandibular glands are one of the major salivary glands comprised of mixed serous and mucous acini and located below the lower border of the body of mandible. It is the second largest salivary gland and produces approximately 70% of the saliva. Location: Submandibular triangle…
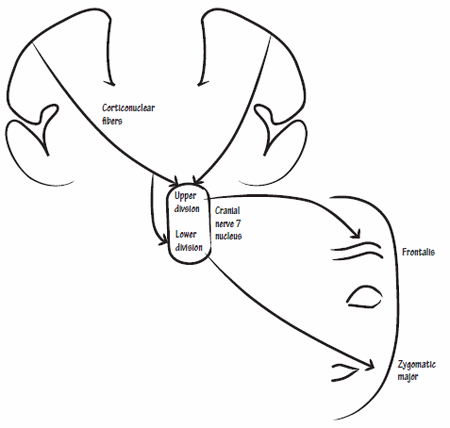
Facial Nerve Anatomy
SYNONYMS: Cranial nerve seven (VII), Nervus facialis Supranuclear pathways 1. Somatomotor cortex: controlling motor component of facial nerve lies in precentral gyrus (Broadmann area 4,6,8) 2. Volitional component: Corticonuclear tracts descend and cross to supply both ipsilateral and contralateral facial (mainly to the contralateral side) nucleus i.e. frontal branch components…