| Monofilament | Polyfilament | |
| Absorbable | Caprosyn (Polyglytone 621) Monocryl (Polyglecaprone 25) Biosyn (Polyglecaprone CV-23) Maxon (Polytrimethylate carbon) PDS (Polydiaxonone) | Catgut Vicryl rapide (Polyglactin 910 rapide) Vicryl (Polyglactin 910) Dexon (Polyglycolic acid) |
| Non-absorbable | Nylon Ethilon (Monofilament polyamide) Prolene (Polypropylene) | Silk Dacron Ethibond (Polyester) Braided nylon (Surgilon, Nurolon) Supramid |
Monofilament sutures:
- Smooth and strong
- Less chances of bacterial contamination
- Knot tied may become loose
Polyfilament/Multifilament sutures:
- Easier to handle and knot tied doesn’t slip
- Bacteria may lodge in crevices of sutures – not suitable in presence of infection
Natural sutures:
- Ingredient: Proteins
- Degradation: Proteolysis
- Strength distribution: Uneven
- Inflammatory reaction: High
- Absorption rate: Rapid
Synthetic sutures:
- Ingredients: Copolymers
- Degradation: Hydrolysis
- Strength distribution: Even
- Inflammatory reaction: Low
- Absorption rate: Slow
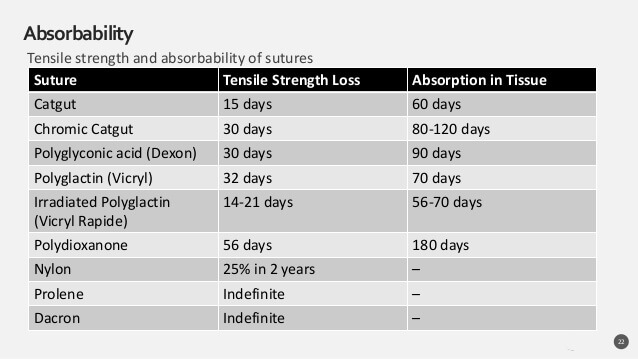
Absorbability:
There are 2 principal methods, by which the sutures are absorbed:
- Proteolytic enzyme degradation
- Hydrolysis
Suture needles:
| Shape | Point geometry |
| Straight | Taper: Round body that smoothly tapers to a point |
| Half curved | Cutting: Triangular body, sharp cutting edge on inside |
| 1/4 circle | Reverse cutting: Cutting edge on outside |
| 3/8 circle | Trocar point: Small triangular cutting point & round, tapered body |
| 1/2 circle | Blunt: Blunt tip |
| 5/8 circle | |
| Compound curve |
Suture size and Time of removal by Location:
| Location | Type of suture* | Timing of suture removal (days) |
|---|---|---|
| Arms | 4-0 | 7 to 10 |
| Face | 5-0 or 6-0 | 3 to 5 |
| Hands or feet | 4-0 or 5-0 | 10 to 14 |
| Legs | 4-0 | 10 to 14 |
| Palms or soles | 3-0 or 4-0 | 14 to 21 |
| Scalp | 4-0 | 7 to 10 |
| Trunk | 3-0 or 4-0 | 10 to 14 |


It is very helpful for Surgical Student
I really thankful to you
Thank you so much