Indications
- Cavus, Adductus and Varus are fully corrected but ankle dorsiflexion remains <10 degrees above neutral
- Adequate abduction:
- Best sign: Ability to palpate anterior process of the calcaneus as it abducts out from beneath the talus
- Abduction of approximately 60 degrees
- Neutral or slight valgus of os calcis
Technique
1. Anesthesia: General anesthesia or Local anesthesia
2. Skin preparation: Prepare the foot thoroughly from midcalf to midfoot with antispetic
3. Position: Assistant holds the foot in maximum dorsiflexion with knee extended
4. Site of tenotomy: about 1.5-2 cm above the calcaneus
5. Equipment for tenotomy:
- Blade: Size #11 or #15 or other smaller blades OR
- Needle: 18 G (<6 months age); 16 G (>6 months age)
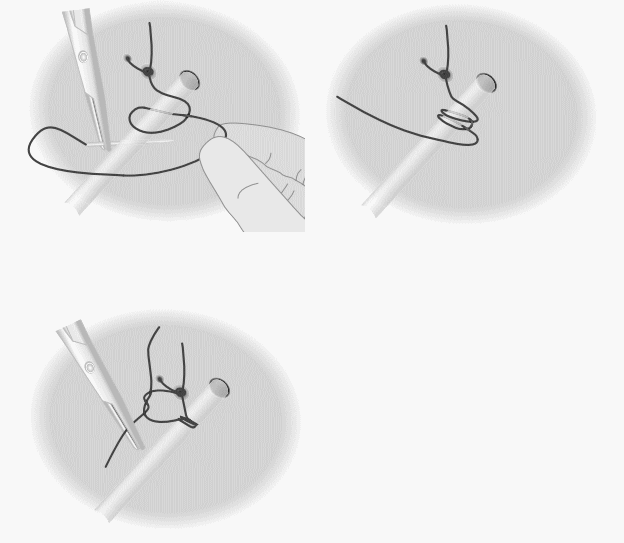
6. Tenotomy:
- Blade tenotomy:
- Insert the tip of the scalpel blade from the medial side, directed immediately anterior to the taut tendon keeping the flat part of blade parallel to the tendon
- The blade is then rotated, so that its sharp edge is directed posteriorly towards the tendon. The blade is then moved a little posteriorly.
- Needle tenotomy:
- Cut the tendon with the tip of needle from medial to lateral (grating sensation is felt as the fibers are cut)
- Signs of completed tenotomy:
- A “pop” is felt as the sharp edge releases the tendon
- Additional 15 to 20 degrees of dorsiflexion is typically gained after the tenotomy
- Negative Thompson test
7. Post-tenotomy cast:
- Type: Above knee cast
- Position: 60-70 degrees abduction of foot and 15 degrees dorsiflexion
- Duration: 3 weeks
References:
- Clubfoot: Ponseti Management (3rd Edition)
- Percutaneous Achilles Tenotomy with a Large Gauge Needle in Ponseti Management of CTEV: A Modified Technique

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.