Don’t Marry Too Soon
DRILL
- Choose the correct drill bit
- Insert the drill bit correctly in the chuck
- Tighten the chuck sufficiently
- Start the drill home perpendicular to the surface
- Maintain adequate pressure
- Maintain the proper direction
- Irrigation with normal saline should be commenced simultaneously with drilling
- Keep the drill rotating while backing it out
- Countersink (create circular sit for undersurface of screw head) when screw is used outside plate in cortical bone.
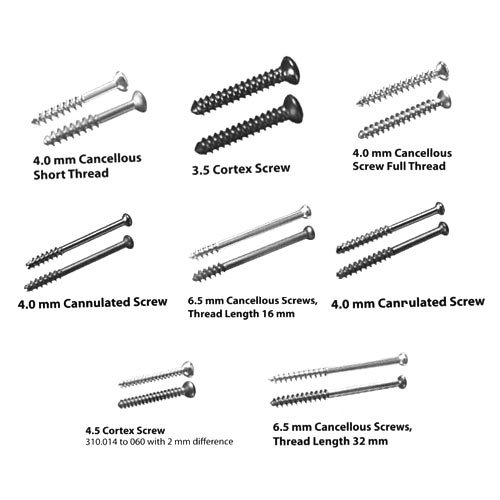
- Drill bit size:
- For thread hole: Core diameter (4.5 mm cortical and malleolar screw and 6 mm cancellous screw all have core diameter of 3 mm – hence, 3.2 mm drill bit is used for all)
- For gliding hole: Outer diameter for cortical screw and Shaft diameter for cancellous screw (Shaft diameter of 6 mm cancellous screw is 4.5 mm)
| Screw diameter (mm) | Screw type | Thread hole (mm) | Gliding hole (mm) |
| 1 | Cortical | 0.8 | 1 |
| 1.3 | Cortical | 1 | 1.3 |
| 1.5 | Cortical | 1.1 | 1.5 |
| 2 | Cortical | 1.5 | 2 |
| 2.4 | Cortical | 1.8 | 2.4 |
| 2.7 | Cortical | 2 | 2.7 |
| 3.5 | Cortical | 2.5 | 3.5 |
| 4 | Cortical | 2.9 | 4 |
| Cancellous | 2.5 | ||
| 4.5 | Cortical | 3.2 | 4.5 |
| Malleolar | 3.2 | 4.5 | |
| 6 | Cancellous | 3.2 | 4.5 |
MEASURE
Measure before tapping as depth gauge may damage the thread.
Correct way of measuring in oblique hole: The hook of depth gauge tends to slip off the obtuse angled tip of the thread hole, but engaging the obtuse angle of the hole is is the correct way of making measurement as engagement of acute angled lip of thread hole gives short reading.
Appropriate length:
- Measure the length with head for locking screws and without head for non-locking screws
- Add plate thickness to the measured length (2-4 mm)
- For cortical bone:
- >/= 1 full thread must exit far cortex
- Self-tapping: Flutes must be out of far cortex and >/= 1 full thread must engage cortex (add 2 mm more)
- For cancellous bone: Sharp tip threatens the soft tissues, hence engagement of full thread in far cortex as in cortical screw is unnecessary
TAP
Tapping refers to cutting threads in a drill hole.
Center line of tap should coincide with the center line of hole.
Tap in couples of 2 turns forward and 1/2 reverse turn until 2 threads of tap emerges out of far cortex.
Tap is removed by twisting in reverse direction.
Tap only near cortex in cancellous bone.
SCREW
Keep insertional torque (recommended 2.824 Nm) and axial force as low as possible.
Screw is centered and inserted perpendicular to the hole in a plate.
Avoid overtightening of screw.
Washer – used as an artificial cortex in cancellous bone to prevent burying of screw head into thin cortex.
- Flat side: rests on bone
- Concave (Countersink) side: underside of screw head

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.