| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation |
| Anterior compartment | ||||
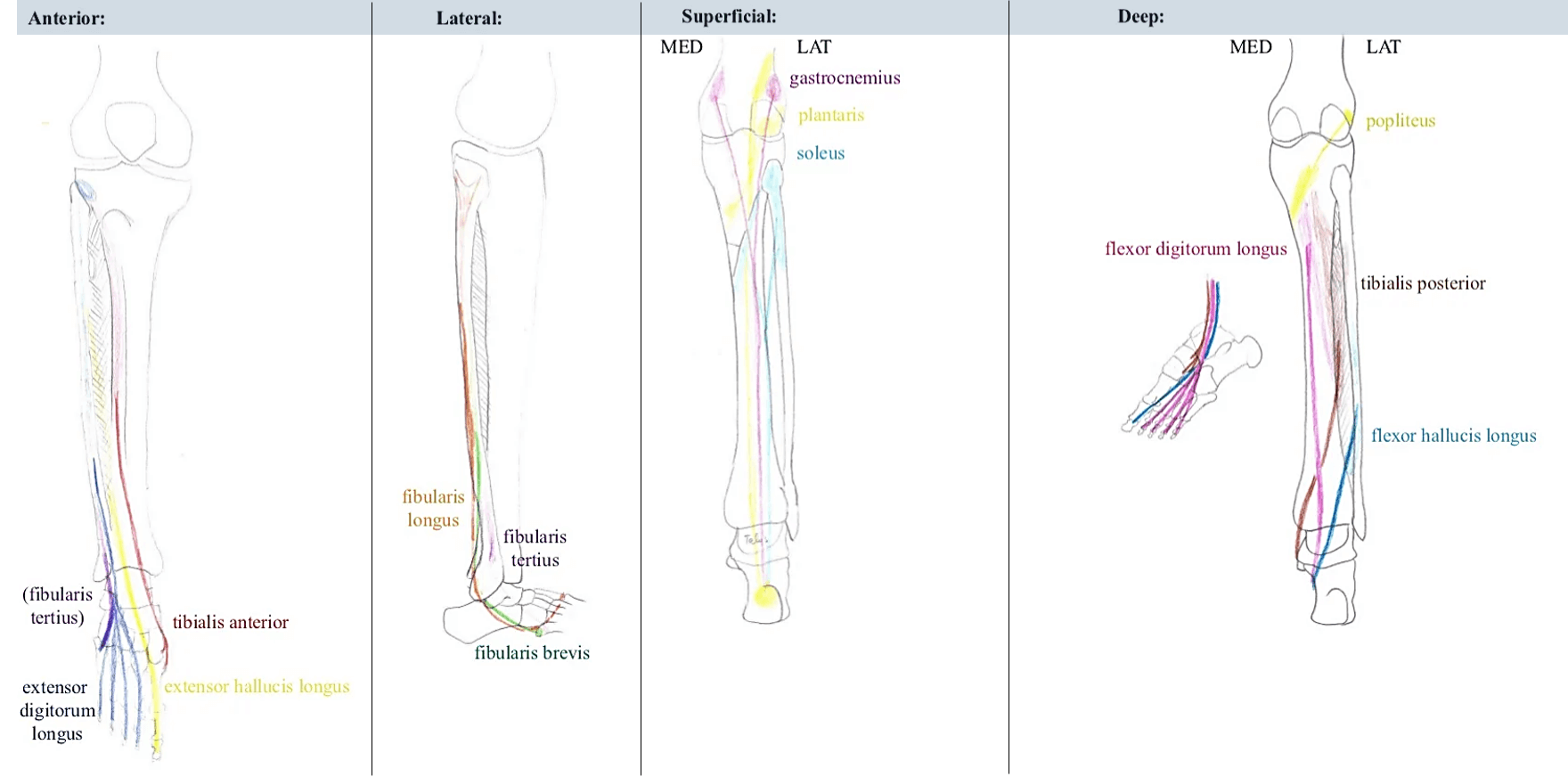
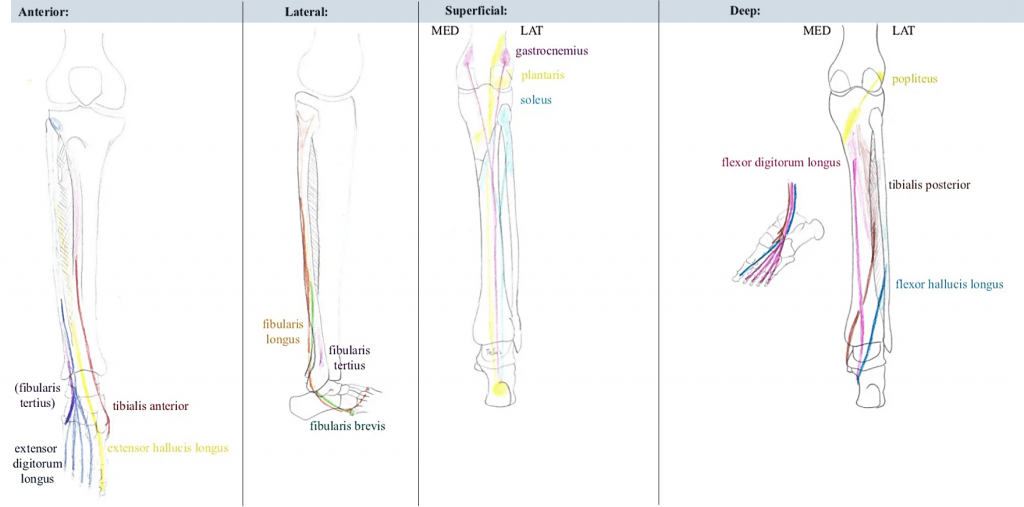
| 1. Tibialis anterior (TA) | Superior 2/3 lateral surface of tibia | Medial cuneiform, 1st metatarsal | Dorsiflexion, foot inversion | Deep peroneal nerve (L5) |
| 2. Extensor digitorum longus (EDL) | Superior 2/3 of fibula and interosseous membrane | Middle and distal phalanx, lateral 4 toes | Dorsiflexion, toe extension | As above |
| 3. Extensor hallucis longus (EHL) | Middle 1/3 of fibula and interosseous membrane | Distal phalanx, great toe | Dorsiflexion, toe extension | As above |
| 4. Peroneus tertius (PT) | Distal end of fibula and EDL tendon | 5th metatarsal base | Foot eversion, dorsiflexion, abduction | Deep peroneal nerve (S1) |
| Lateral compartment | ||||
| 1. Peroneus longus | Proximal lateral fibula | First metatarsal base, medial cuneiform (runs behind lateral malleolus) | Foot eversion, plantar flexion, abduction | Superficial peroneal nerve (S1) |
| 2. Peroneus brevis | Distal fibula | 5th metatarsal tuberosity (runs behind lateral malleolus) | Foot eversion | As above |
| Superficial posterior compartment | ||||
| Gastrocnemius | Posterior medial and lateral femoral condyles (medial and lateral head respectively; above knee) | Posterior calcaneus | Foot plantarflexion (flexes knee during it) | Tibial nerve (S1) |
| Soleus | Soleal line and medial border of tibia; Upper 1/4 fibula | Posterior calcaneus | Foot plantar flexion | As above |
| Plantaris | Lateral femoral condyle (above head of gastrocnemius) | Calcaneus or calcaneal tendon | Foot plantar flexion | As above |
| Deep posterior compartment | ||||
| Popliteus | Tendinous origin – 1. Popliteal groove on lateral surface of lateral femoral condyle 2. Lateral meniscus 3. Arcuate popliteal ligament (fibular head) | Broad insertion – Tibia above soleal line | Flexion and internal rotation of knee | Tibial nerve (L5,S1) |
| Flexor digitorum longus | Posterior tibia | Distal phalanges, 2-5 toes | Toe and foot plantarflexion | Tibial nerve (S1,S2) |
| Flexor hallucis longus | Fibula midshaft, interosseous membrane | Distal phalanx, great toe | Toe and foot plantarflexion | Tibial nerve (S1) |
| Tibialis posterior | Superior tibia and fibula, Interosseous membrane | Navicular, medial cuneiform | Foot inversion and plantarflexion | Tibial nerve (L4,L5) |
Fasciotomy
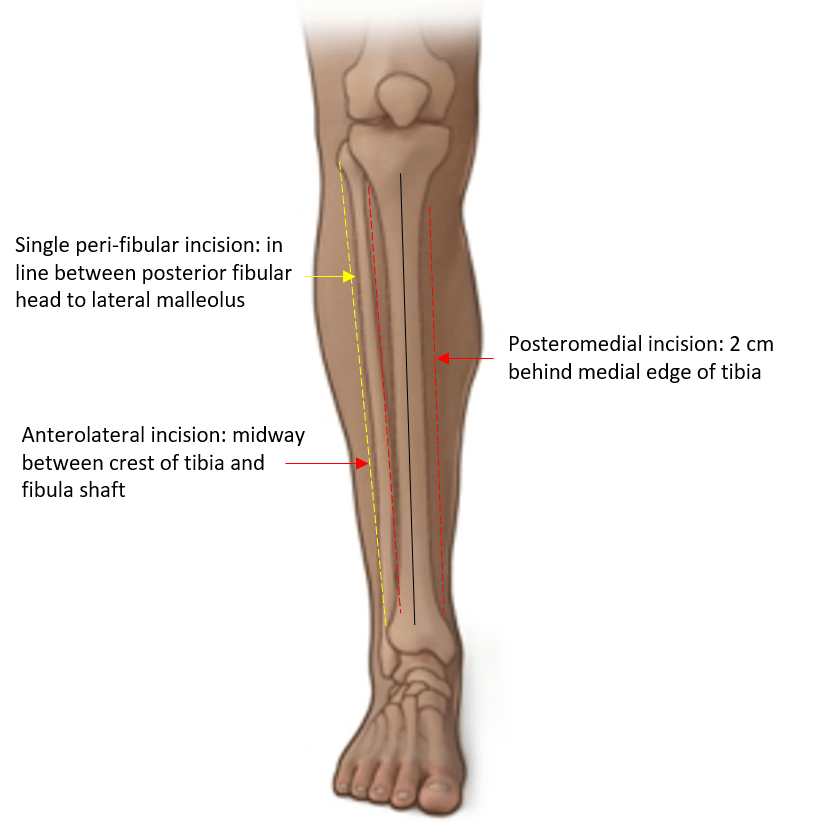
Double incision (Mubarak): Recommended by BOA and BAPRAS
- Anterolateral incision: Half-way between the tibial crest and the shaft of fibula over the anterior intermuscular septum
- Avoid superficial peroneal nerve (exits from lateral compartment about 10 cm above lateral malleolus and courses into the anterior compartment)
- Posteromedial incision: 2 cm behind the medial tibial border (ensure sufficient skin bridge between 2 incisions; atleast >5 cm)
- Avoid saphenous nerve and vein
- Soleus may be required to release to decompress deep posterior compartment adequately
Single peri-fibular incision (Matsen): In a line posterior to fibular head to just above lateral malleolus
- Protect common peroneal nerve proximally
- More difficult to decompress deep compartment